
The refractive indices of violet and red light are 1.54 and 1.52 respectively. If the angle of the prism is 100, then the angular dispersion is :
A. 0.02
B. 2
C. 3.06
D. 30.6
Answer
579.3k+ views
Hint: The angular dispersion for a prism is given by the difference between minimum angle of deviation for given colors. Angular dispersion gives the information about the spread of various colors as they emerge out of a prism.
Formula used:
Angular dispersion between red and violet rays is given as:
$\theta = (\mu_V - \mu_R)A$
Where A is the angle of prism, $\mu_R$ and $\mu_V$ are refractive indices for red and violet rays respectively.
Complete step by step answer:
Prism is known to separate white light into its various compounds and wavelengths. This happens because different wavelengths travel with different speeds in a medium. They have different refractive indices as:
$\mu = \dfrac{c}{v}$
v is the speed of light in the media.
For a prism, minimum angle of deviation is given by:
$\delta_m = ( \mu - 1)A$
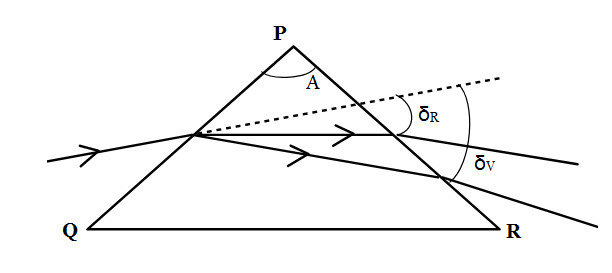
If we extend the incident ray out of the second face of prism and note the angle that the incident ray direction makes with the emergent ray, that angle will be the angle of deviation for a particular direction of incidence. At a point where angle of incidence and angle of emergence are equal we find an angle of minimum deviation.
So, the difference between the angle of deviation for violet and red rays can be written as:
$\theta = \delta_V -\delta_R = (\mu_V - \mu_R)A$
which is the angular dispersion expression.
Substituting the given values as A = 100$^{\circ}$ and $\mu_V $ = 1.54 and $\mu_R $ = 1.52, we get:
$\theta = (1.54 - 1.52) \times 100^{\circ} = 2^{\circ}$.
Therefore, the correct answer is option (B).
Note:
In a prism, it is important to note that incidence angle is the angle that the incident ray makes with the surface of the prism (at face PQ) and emergence angle is the angle that the normal (to face PR) makes with the emergent ray.
Formula used:
Angular dispersion between red and violet rays is given as:
$\theta = (\mu_V - \mu_R)A$
Where A is the angle of prism, $\mu_R$ and $\mu_V$ are refractive indices for red and violet rays respectively.
Complete step by step answer:
Prism is known to separate white light into its various compounds and wavelengths. This happens because different wavelengths travel with different speeds in a medium. They have different refractive indices as:
$\mu = \dfrac{c}{v}$
v is the speed of light in the media.
For a prism, minimum angle of deviation is given by:
$\delta_m = ( \mu - 1)A$

If we extend the incident ray out of the second face of prism and note the angle that the incident ray direction makes with the emergent ray, that angle will be the angle of deviation for a particular direction of incidence. At a point where angle of incidence and angle of emergence are equal we find an angle of minimum deviation.
So, the difference between the angle of deviation for violet and red rays can be written as:
$\theta = \delta_V -\delta_R = (\mu_V - \mu_R)A$
which is the angular dispersion expression.
Substituting the given values as A = 100$^{\circ}$ and $\mu_V $ = 1.54 and $\mu_R $ = 1.52, we get:
$\theta = (1.54 - 1.52) \times 100^{\circ} = 2^{\circ}$.
Therefore, the correct answer is option (B).
Note:
In a prism, it is important to note that incidence angle is the angle that the incident ray makes with the surface of the prism (at face PQ) and emergence angle is the angle that the normal (to face PR) makes with the emergent ray.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




