
The relation between voltage sensitivity (${{\sigma }_{V}}$) and current sensitivity (${{\sigma }_{1}}$) of a moving coil galvanometer is (resistance of galvanometer if G)
$\begin{align}
& a)\dfrac{{{\sigma }_{1}}}{G}={{\sigma }_{V}} \\
& b)\dfrac{{{\sigma }_{V}}}{G}={{\sigma }_{1}} \\
& c)\dfrac{G}{{{\sigma }_{1}}}={{\sigma }_{V}} \\
& d)\dfrac{G}{{{\sigma }_{V}}}={{\sigma }_{1}} \\
\end{align}$
Answer
595.5k+ views
Hint: Current sensitivity is given as the deflection per unit current. Similarly voltage sensitivity is defined as deflection per unit volt. From the obtained equation current sensitivity and voltage sensitivity of a moving coil galvanometer, compare the equation and obtain a relation between the two quantities.
Complete solution:
First let us understand how a moving coil galvanometer works.
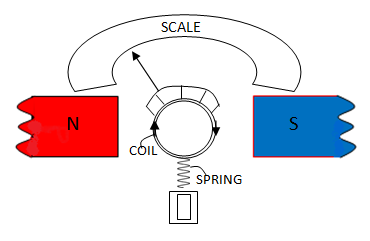
In the above diagram as shown a galvanometer consists of a coil placed in a radial magnetic field. When a current passes into the coil, it gets rotated due to the force by the magnetic field. Hence the coil experiences a torque equal to,
$\tau =NIAB\operatorname{Sin}\theta $ …… (1)
In the above equation N is the number of turns in the coil, A is the area of cross section I is the current through the galvanometer and $\theta $ is the angle between magnetic field and coil which is equal to 90 since the magnetic field is radial. Hence equation 1 can be written as $\tau =NIAB$
A scale is calibrated in such a manner that the rotation produces a deflection which shows the degree of current in the circuit.
A spring is attached to the coil which produces a restoring torque To bring the needle back to equilibrium. This restoring torque is given by,
${{\tau }_{S}}=k\phi $ …..(2), where k is the springs constant and $\phi $ is the angle of deflection.
At equilibrium,
$\tau ={{\tau }_{s}}$
Hence using equation 1 and two we get,
$k\phi =NIAB$
$\phi =\dfrac{NIAB}{k}$
As per the definition of current sensitivity and voltage sensitivity ,
Current sensitivity= ${{\sigma }_{1}}=\dfrac{\phi }{I}=\dfrac{NIAB}{kI}=\dfrac{NAB}{k}rad{{A}^{-1}}.........(3)$
Voltage sensitivity=${{\sigma }_{V}}=\dfrac{\phi }{V}=\dfrac{NIAB}{kIG}=\dfrac{NAB}{kG}rad{{V}^{-1}}..........(4)$ ,here G is the resistance of the galvanometer.
Using equation 3 and 4 let us compare ${{\sigma }_{V}}and{{\sigma }_{1}}$,
${{\sigma }_{1}}=\dfrac{NAB}{k}rad{{A}^{-1}}$ and ${{\sigma }_{V}}=\dfrac{NAB}{kG}rad{{V}^{-1}}$
If we observe the above equation the ${{\sigma }_{1}}$ can be substituted in equation of ${{\sigma }_{V}}$,
After substituting we get, $\dfrac{{{\sigma }_{1}}}{G}={{\sigma }_{V}}$
Hence, the correct answer is option A.
Note: Increasing current sensitivity does not necessarily mean voltage sensitivity also increases. Let us say we increase the current sensitivity by increasing the number of turns in the coil. But at the same time the voltage sensitivity gets decreased because the value of G increases as resistance is directly proportional to length.
Complete solution:
First let us understand how a moving coil galvanometer works.

In the above diagram as shown a galvanometer consists of a coil placed in a radial magnetic field. When a current passes into the coil, it gets rotated due to the force by the magnetic field. Hence the coil experiences a torque equal to,
$\tau =NIAB\operatorname{Sin}\theta $ …… (1)
In the above equation N is the number of turns in the coil, A is the area of cross section I is the current through the galvanometer and $\theta $ is the angle between magnetic field and coil which is equal to 90 since the magnetic field is radial. Hence equation 1 can be written as $\tau =NIAB$
A scale is calibrated in such a manner that the rotation produces a deflection which shows the degree of current in the circuit.
A spring is attached to the coil which produces a restoring torque To bring the needle back to equilibrium. This restoring torque is given by,
${{\tau }_{S}}=k\phi $ …..(2), where k is the springs constant and $\phi $ is the angle of deflection.
At equilibrium,
$\tau ={{\tau }_{s}}$
Hence using equation 1 and two we get,
$k\phi =NIAB$
$\phi =\dfrac{NIAB}{k}$
As per the definition of current sensitivity and voltage sensitivity ,
Current sensitivity= ${{\sigma }_{1}}=\dfrac{\phi }{I}=\dfrac{NIAB}{kI}=\dfrac{NAB}{k}rad{{A}^{-1}}.........(3)$
Voltage sensitivity=${{\sigma }_{V}}=\dfrac{\phi }{V}=\dfrac{NIAB}{kIG}=\dfrac{NAB}{kG}rad{{V}^{-1}}..........(4)$ ,here G is the resistance of the galvanometer.
Using equation 3 and 4 let us compare ${{\sigma }_{V}}and{{\sigma }_{1}}$,
${{\sigma }_{1}}=\dfrac{NAB}{k}rad{{A}^{-1}}$ and ${{\sigma }_{V}}=\dfrac{NAB}{kG}rad{{V}^{-1}}$
If we observe the above equation the ${{\sigma }_{1}}$ can be substituted in equation of ${{\sigma }_{V}}$,
After substituting we get, $\dfrac{{{\sigma }_{1}}}{G}={{\sigma }_{V}}$
Hence, the correct answer is option A.
Note: Increasing current sensitivity does not necessarily mean voltage sensitivity also increases. Let us say we increase the current sensitivity by increasing the number of turns in the coil. But at the same time the voltage sensitivity gets decreased because the value of G increases as resistance is directly proportional to length.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




