
The restoring couple in moving coil galvanometer is due to
A. current in the coil
B. magnetic field of the magnet
C. material of the coil
D. twist produced in the suspension wire
Answer
593.7k+ views
Hint: Moving coil galvanometer is an electromagnetic device that can measure small values of current. Moving coil galvanometer consists of a coil, pair of permanent horse-shoe magnet, soft iron core, a pivoted spring, non-metallic frame, scale and a pointer. It works on the principle that when a current carrying loop is placed in an external magnetic field, it experiences torque, and the value of the torque can be changed by changing the value of current in the loop.
Complete step-by-step answer:
A galvanometer is an electronic device that is used in detecting the small electric current or measuring its magnitude. The electric current and its intensity are usually indicated by the movement of a magnetic needle or that of a coil placed in a magnetic field which is an important part of a galvanometer.
A moving coil galvanometer is an electrical instrument which is used to measure electric current in a circuit. It is a sensitive electromagnetic device which has the ability to measure low currents even of the order of a few microamperes.
Principle of a moving coil galvanometer:
A current-carrying coil when placed in an external magnetic field experiences some force and resulting magnetic torque. The angle by which the coil is deflected due to the effect of the magnetic torque is proportional to the magnitude of electric current flowing in the coil.
Construction and working of a moving coil galvanometer:
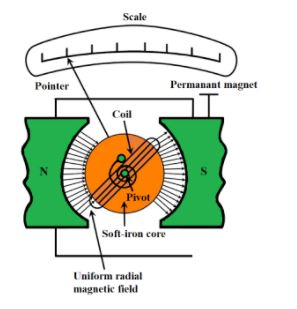
The moving coil galvanometer is a rectangular coil consisting of many turns and is usually made of a thin insulated or fine copper wire which is wounded on a metallic frame. The coil is set free to rotate about a fixed axis. A phosphor-bronze strip, being connected to a movable torsion head, is used to suspend the coil in the uniform radial magnetic field.
Essential properties of the material required for the suspension of the coil are conductivity and low value of the torsional constant. A soft and cylindrical iron core is symmetrically positioned inside the coil in order to improve the strength of the magnetic field and to make the field radial. The lower part of the coil is attached to a phosphor-bronze spring having comparatively small number of turns. The other end of the spring is connected to binding screws.
The spring is used to generate a counter torque which balances the magnetic torque and thus, helps in producing a steady angular deflection. A plane mirror is attached to the suspension wire, along with a lamp and scale arrangement, to measure the deflection of the coil. Zero-point of the scale is located at the centre of the scale.
The restoring couple in the moving coil galvanometer is due to the twist produced in the suspension wire.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: Students should remember that, when equal and opposite forces called a couple, act on the coil, it produces a torque. This torque causes the coil to deflect and in turn, the spring attached to the coil produces a counter torque or restoring torque which results in a steady angular deflection.
Complete step-by-step answer:
A galvanometer is an electronic device that is used in detecting the small electric current or measuring its magnitude. The electric current and its intensity are usually indicated by the movement of a magnetic needle or that of a coil placed in a magnetic field which is an important part of a galvanometer.
A moving coil galvanometer is an electrical instrument which is used to measure electric current in a circuit. It is a sensitive electromagnetic device which has the ability to measure low currents even of the order of a few microamperes.
Principle of a moving coil galvanometer:
A current-carrying coil when placed in an external magnetic field experiences some force and resulting magnetic torque. The angle by which the coil is deflected due to the effect of the magnetic torque is proportional to the magnitude of electric current flowing in the coil.
Construction and working of a moving coil galvanometer:

The moving coil galvanometer is a rectangular coil consisting of many turns and is usually made of a thin insulated or fine copper wire which is wounded on a metallic frame. The coil is set free to rotate about a fixed axis. A phosphor-bronze strip, being connected to a movable torsion head, is used to suspend the coil in the uniform radial magnetic field.
Essential properties of the material required for the suspension of the coil are conductivity and low value of the torsional constant. A soft and cylindrical iron core is symmetrically positioned inside the coil in order to improve the strength of the magnetic field and to make the field radial. The lower part of the coil is attached to a phosphor-bronze spring having comparatively small number of turns. The other end of the spring is connected to binding screws.
The spring is used to generate a counter torque which balances the magnetic torque and thus, helps in producing a steady angular deflection. A plane mirror is attached to the suspension wire, along with a lamp and scale arrangement, to measure the deflection of the coil. Zero-point of the scale is located at the centre of the scale.
The restoring couple in the moving coil galvanometer is due to the twist produced in the suspension wire.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: Students should remember that, when equal and opposite forces called a couple, act on the coil, it produces a torque. This torque causes the coil to deflect and in turn, the spring attached to the coil produces a counter torque or restoring torque which results in a steady angular deflection.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




