
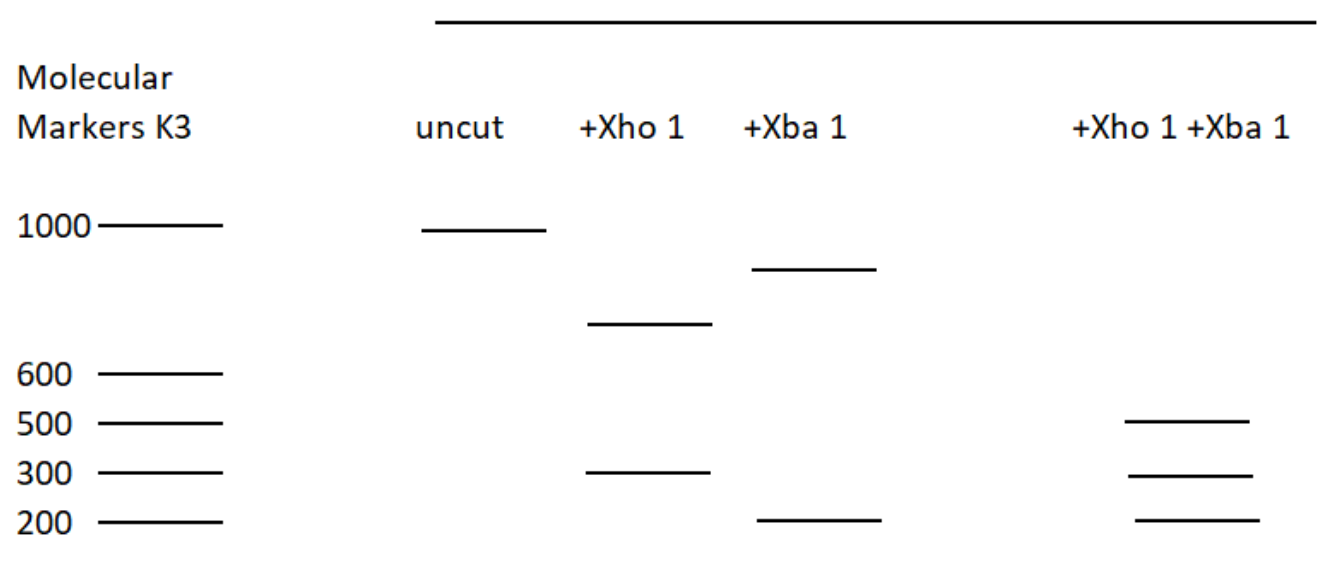
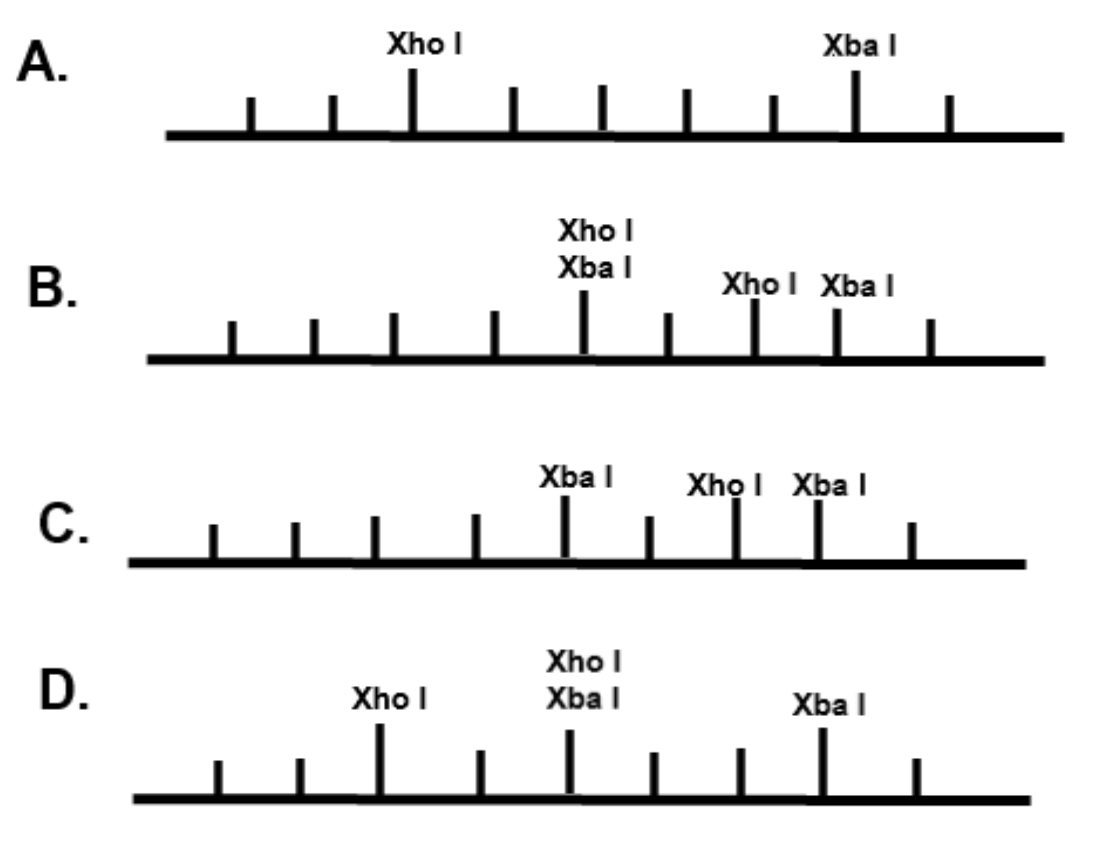
The restriction enzyme XhoI and XbaI were used to digest a linear fragment of DNA at a specific sequence such as that shown for EcoR1 (figure above). Use the information gained from the resolution of the fragments by gel electrophoresis to determine which of the following restriction maps best fits the data.


Answer
587.4k+ views
Hint: Restriction endonuclease is the enzyme that cut the DNA at specific sequence into fragments at or near the restriction sites. They are used for mapping of DNA.
Complete Answer:
- Restriction enzymes are found in bacteria. These are the classes of endonucleases which cut the DNA at specific sequences. They are also known as molecular scissors. Each restriction enzyme recognises specific sequences which are specific to certain DNA strands.
- Once the restriction enzyme is administered, the DNA strand is cut at a specific site which leads to several smaller DNA fragments. Then it is run on the gel electrophoresis. All the fragments separate as per the molecular weight. The heavier fragments travel a shorter distance than the smaller fragment.
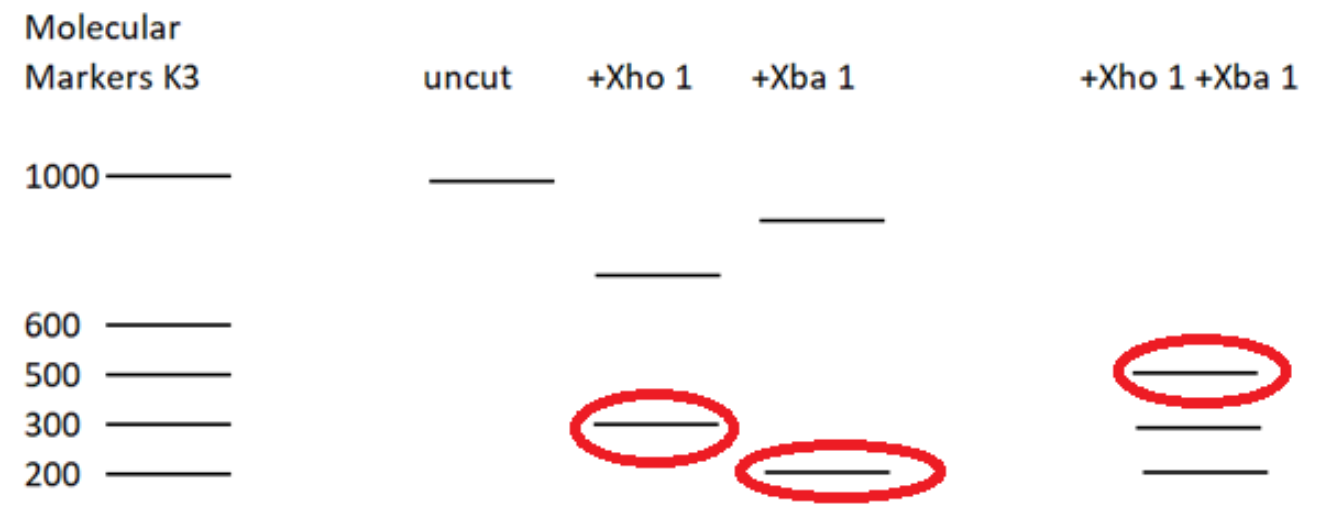
- When restriction enzymes XhoI and Xba I are administered, it will cut the DNA at sites specific to these two enzymes. Thus 3 fragments will be formed. The molecular weights of the fragments are 200 (Xba1), 300 (XhoI) and 500 (XbaI + Xho1) (according to the given figure).
In option B, C, D two restriction enzymes cannot cut the same sequence of DNA, yielding similar molecular weight fragments.
Thus the correct answer is A. Three fragments are obtained.
Note: Restriction endonucleases are specific to a particular DNA segment. They cleave the DNA at a particular site. On gel electrophoresis, DNA fragments are separated on the basis of size. The lower molecular weight fragment will be found at the end of the gel as it will move faster and farther in a gel. The reverse applies for the heavier fragment.
Complete Answer:
- Restriction enzymes are found in bacteria. These are the classes of endonucleases which cut the DNA at specific sequences. They are also known as molecular scissors. Each restriction enzyme recognises specific sequences which are specific to certain DNA strands.
- Once the restriction enzyme is administered, the DNA strand is cut at a specific site which leads to several smaller DNA fragments. Then it is run on the gel electrophoresis. All the fragments separate as per the molecular weight. The heavier fragments travel a shorter distance than the smaller fragment.
- When restriction enzymes XhoI and Xba I are administered, it will cut the DNA at sites specific to these two enzymes. Thus 3 fragments will be formed. The molecular weights of the fragments are 200 (Xba1), 300 (XhoI) and 500 (XbaI + Xho1) (according to the given figure).

In option B, C, D two restriction enzymes cannot cut the same sequence of DNA, yielding similar molecular weight fragments.
Thus the correct answer is A. Three fragments are obtained.
Note: Restriction endonucleases are specific to a particular DNA segment. They cleave the DNA at a particular site. On gel electrophoresis, DNA fragments are separated on the basis of size. The lower molecular weight fragment will be found at the end of the gel as it will move faster and farther in a gel. The reverse applies for the heavier fragment.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




