
The rise of a liquid in a capillary tube depends on:
A. The material
B. The length
C. The outer radius
D. The inner radius of the tube
Answer
597k+ views
Hint: The force of surface tension is balanced by weight of liquid. We can make use of this relation to calculate the formula for rise of a liquid in a capillary tube. The contact angle of liquid is the angle it makes with the walls of the container. It depends both on liquid as well as container.
Complete step by step solution:
When a capillary is dipped in a liquid, the force of surface tension lifts the liquid upward. As there is no other force to balance it, the liquid starts rising. As it happens the weight of the raised liquid starts countering force due to surface tension. After a specific length the force due to surface tension is balanced by weight of liquid. So, the liquid stops rising. Hence, we can say that the weight of liquid must be equal to force due to surface tension.
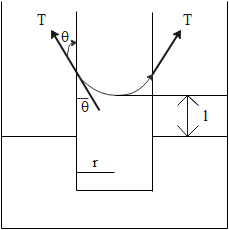
Let us consider a capillary, the liquid has raised its final length l, T is surface tension of liquid, r is radius of capillary, $\rho $is density of liquid and $\theta $is the contact angle (angle made by liquid with the walls of capillary).
The liquid forms a cylinder of radius r and height l. Weight of the liquid can be written as product of density and volume
$W = \rho \times \pi {r^2}l$
Force due to surface tension can be written as a product of surface tension and the length where it’s acting. The length where its acting is equal to $2\pi r$ as it is acting on complete circumference or tube. So the magnitude of this force will be
\[T \times 2\pi r\]
But this force is acting along the contact angle and only a component of it will balance the weight. And that component will be
\[T \times 2\pi r\cos \theta \]
So we can say that
\[T \times 2\pi r\cos \theta = \rho \times \pi {r^2}l\]
On solving for l, we get
$l = \dfrac{{2T\cos \theta }}{{\rho gr}}$
So the rise of a liquid in a capillary tube depends on surface tension of liquid, contact angle, density of liquid and inner radius of capillary.
Contact angle depends on material of capillary tube.
So the correct options are A and C.
Note: The weight of the liquid taken here is not exactly accurate. We have not taken into account the weight of liquid present above height l. It could be taken into account if we know the value of $\theta $ (volume of partial sphere can be calculated from it). But generally this part of liquid is neglected.
Complete step by step solution:
When a capillary is dipped in a liquid, the force of surface tension lifts the liquid upward. As there is no other force to balance it, the liquid starts rising. As it happens the weight of the raised liquid starts countering force due to surface tension. After a specific length the force due to surface tension is balanced by weight of liquid. So, the liquid stops rising. Hence, we can say that the weight of liquid must be equal to force due to surface tension.
Let us consider a capillary, the liquid has raised its final length l, T is surface tension of liquid, r is radius of capillary, $\rho $is density of liquid and $\theta $is the contact angle (angle made by liquid with the walls of capillary).
The liquid forms a cylinder of radius r and height l. Weight of the liquid can be written as product of density and volume
$W = \rho \times \pi {r^2}l$
Force due to surface tension can be written as a product of surface tension and the length where it’s acting. The length where its acting is equal to $2\pi r$ as it is acting on complete circumference or tube. So the magnitude of this force will be
\[T \times 2\pi r\]
But this force is acting along the contact angle and only a component of it will balance the weight. And that component will be
\[T \times 2\pi r\cos \theta \]

So we can say that
\[T \times 2\pi r\cos \theta = \rho \times \pi {r^2}l\]
On solving for l, we get
$l = \dfrac{{2T\cos \theta }}{{\rho gr}}$
So the rise of a liquid in a capillary tube depends on surface tension of liquid, contact angle, density of liquid and inner radius of capillary.
Contact angle depends on material of capillary tube.
So the correct options are A and C.
Note: The weight of the liquid taken here is not exactly accurate. We have not taken into account the weight of liquid present above height l. It could be taken into account if we know the value of $\theta $ (volume of partial sphere can be calculated from it). But generally this part of liquid is neglected.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




