
The Saliva helps in digestion of?
a. Starch
b. Proteins
c. Fibres
d. Fats
Answer
591.9k+ views
Hint: Saliva is that the watery and typically somewhat frothy substance produced within the mouths of some animals, including humans. Formed in salivary glands, saliva contains 98% water, but it contains many vital substances, involving electrolytes, mucus, antibacterial substances, and a range of enzymes. The digestive functions of saliva include moistening food and helping to make a food bolus, so it is often swallowed easily.
Complete answer:
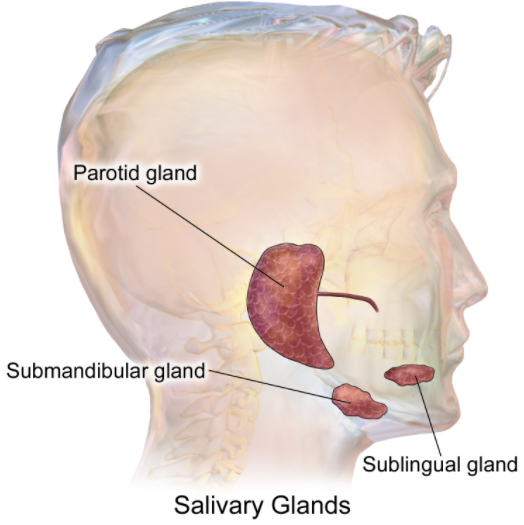
Most animals have three major pairs of salivary glands that differ within the sort of secretion they produce:
- Parotid glands produce a serious, watery secretion
- Submaxillary (mandibular) glands produce a mixed serous and secretion
- Sublingual glands secrete predominantly mucous saliva.
Saliva contains the enzyme amylase that splits several starches down into maltose and dextrin. About 30% of starch digestion takes place within the mouth cavity. Thus, the digestion of food starts within the mouth, before the food reaches the stomach. Saliva doesn't digest the proteins, fats, and fibers.
Hence, The correct answer is option (A).
Additional information:
An unusual condition identified to influence taste is that of 'Saliva Hypernatremia', or extreme amounts of sodium in saliva that's not caused by the other condition (e.g., Sjögren syndrome), causing everything to taste 'salty.
Note: Saliva is extremely important within the sense of taste. It’s the liquid medium during which chemicals are carried to taste receptor cells (mostly related to lingual papillae). Persons with small saliva habitually complain of dysgeusia (i.e. disordered taste, e.g. reduced ability to taste, or having a nasty, metallic taste in the least times).
Complete answer:
Most animals have three major pairs of salivary glands that differ within the sort of secretion they produce:
- Parotid glands produce a serious, watery secretion
- Submaxillary (mandibular) glands produce a mixed serous and secretion
- Sublingual glands secrete predominantly mucous saliva.
Saliva contains the enzyme amylase that splits several starches down into maltose and dextrin. About 30% of starch digestion takes place within the mouth cavity. Thus, the digestion of food starts within the mouth, before the food reaches the stomach. Saliva doesn't digest the proteins, fats, and fibers.
Hence, The correct answer is option (A).

Additional information:
An unusual condition identified to influence taste is that of 'Saliva Hypernatremia', or extreme amounts of sodium in saliva that's not caused by the other condition (e.g., Sjögren syndrome), causing everything to taste 'salty.
Note: Saliva is extremely important within the sense of taste. It’s the liquid medium during which chemicals are carried to taste receptor cells (mostly related to lingual papillae). Persons with small saliva habitually complain of dysgeusia (i.e. disordered taste, e.g. reduced ability to taste, or having a nasty, metallic taste in the least times).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




