
The S.I unit of electric field intensity is?
Answer
529.8k+ views
Hint: In this question, we will use the basics of the Electric field to get the required answer. Further we will observe that the electric field depends on the potential of the conductor. Also, we will see the concept that the potential on the surface of a charged conductor is constant, which means there is no electric field observed.
Formula used:
$E \propto \dfrac{F}{q}$
$E = - gradV$
Complete answer:
As we know, the electric field is defined as the electric force per unit charge:
$E \propto \dfrac{F}{q}$
Here, F is force exerted or experienced by the object and q is the charge on the object. So, if the electric field at a particular point is known and force is known we can get the charge or if the charge is known we can get the force experienced by the point charge.
Electric field is radially outward from a positive charge and it is radially inward to a negative point charge. S.I unit of electric field is Newton per coulomb.
Therefore, the S.I unit of electric field is N/C.
Additional information:
As we know, the direction of electric field E is taken to be the direction of force it would exert on the positive test charge.
Following is a diagram of charge flowing in a conductor with electric field direction.
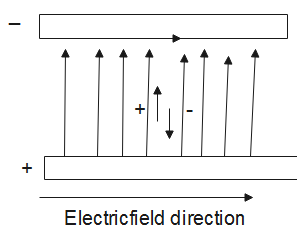
Also, we know that the electric field is defined as the gradient of potential (V):
$E = - gradV$
Since, we know that the surface of the charged conductor has a constant potential. Therefore, there is no field along the surface of the charged conductor. This shows that the electrostatic field at the surface of the charged conductor should be normal to the surface at every point.
Also, potential (V) is defined as the amount of work needed to move one unit of electric charge from a reference point to a specific point in an electric field. S.I unit of potential is Volts or joules per coulomb.
Note:
Electric field is a vector quantity. It has both magnitude and direction. Electric field is not negative; the negative sign shows the opposite direction of the field. Electric field inside a conductor is zero, because charges are not present inside the conductor, they are present on the surface of the conductor.
Formula used:
$E \propto \dfrac{F}{q}$
$E = - gradV$
Complete answer:
As we know, the electric field is defined as the electric force per unit charge:
$E \propto \dfrac{F}{q}$
Here, F is force exerted or experienced by the object and q is the charge on the object. So, if the electric field at a particular point is known and force is known we can get the charge or if the charge is known we can get the force experienced by the point charge.
Electric field is radially outward from a positive charge and it is radially inward to a negative point charge. S.I unit of electric field is Newton per coulomb.
Therefore, the S.I unit of electric field is N/C.
Additional information:
As we know, the direction of electric field E is taken to be the direction of force it would exert on the positive test charge.
Following is a diagram of charge flowing in a conductor with electric field direction.

Also, we know that the electric field is defined as the gradient of potential (V):
$E = - gradV$
Since, we know that the surface of the charged conductor has a constant potential. Therefore, there is no field along the surface of the charged conductor. This shows that the electrostatic field at the surface of the charged conductor should be normal to the surface at every point.
Also, potential (V) is defined as the amount of work needed to move one unit of electric charge from a reference point to a specific point in an electric field. S.I unit of potential is Volts or joules per coulomb.
Note:
Electric field is a vector quantity. It has both magnitude and direction. Electric field is not negative; the negative sign shows the opposite direction of the field. Electric field inside a conductor is zero, because charges are not present inside the conductor, they are present on the surface of the conductor.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




