
The smallest animal egg is that of:
(a) Ostrich
(b) Human female
(c) Duck
(d) Hen
Answer
595.8k+ views
Hint: The smallest animal cell also contains the smallest percentage of yolk because it exhibits an alternate main supply of nutrients to the developing embryo. Also, in the organism in which it is found, it is the largest of all the cells.
Complete step-by-step answer:
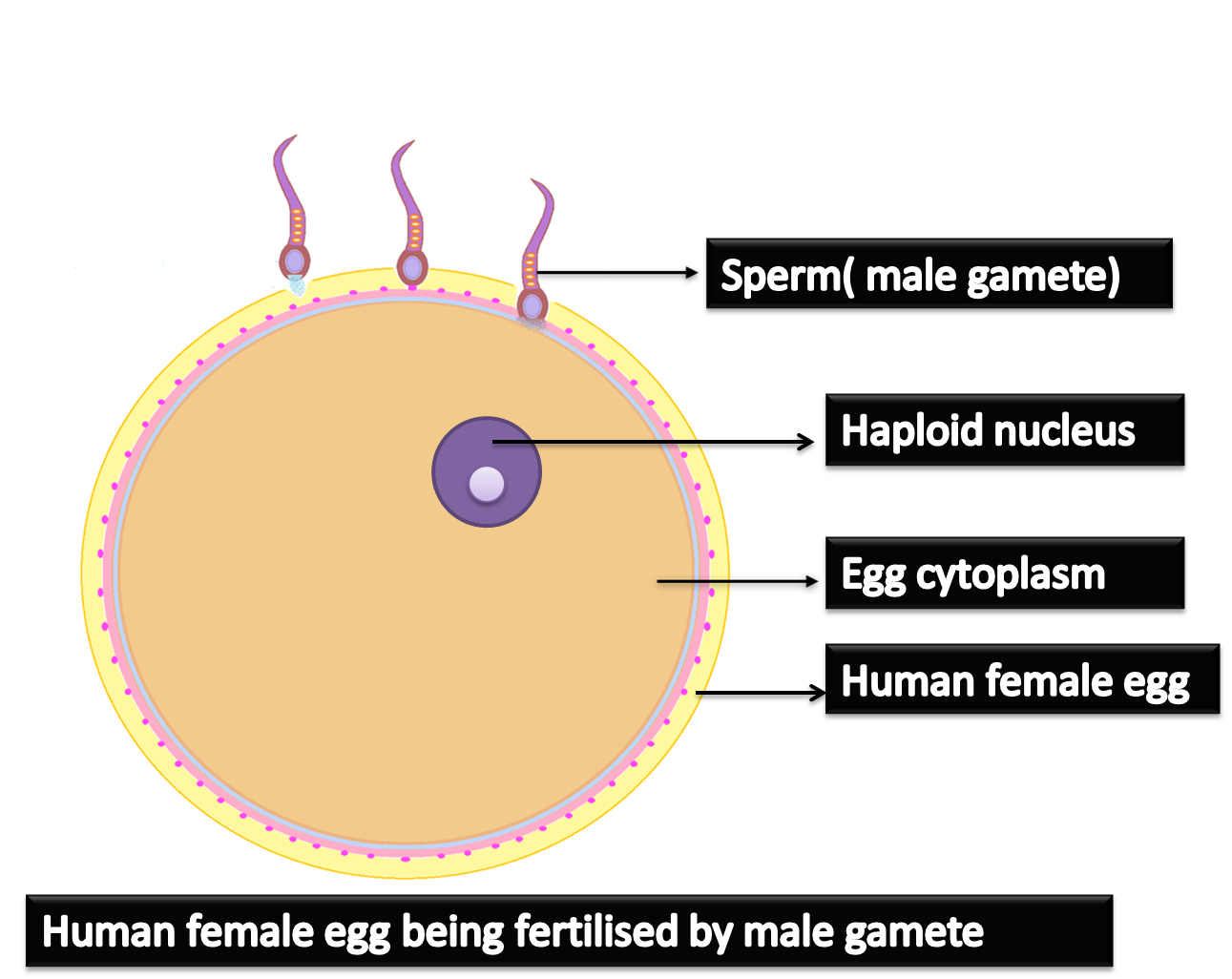
Human egg is barely over 0.1mm or 100µm in diameter. It is the smallest egg cell. In general, eggs are large-sized cells because they store food for the development of the embryo. Avian (birds)eggs are the largest. They are in centimetres. Among them, the ostrich egg is the largest and weighs around 1.3 kg.
Additional Information:
In birds such as ostrich, duck and hen, after internal fertilisation, the eggs are released from the female’s body. They are laid in a nest. After birds have laid their eggs, they keep the eggs warm through their body heat. This process is known as incubation. It is necessary for proper and complete development of the embryo in the eggs. The yolk which occupies a major portion in avian eggs provides nourishment to the embryo. Also, many minute semi-permeable pores are present on the shell for the exchange of gases as well as moisture to prevent desiccation of the eggs.
The human egg is also known as an ovum. It is the largest cell in a human body and can be seen with the naked eye. After internal fertilization in the female’s body, a zygote is formed. After a series of divisions, an embryo is formed which gets embedded in the uterus of the female. Human egg cell does not contain much yolk as the nutrients of the embryo is fulfilled from the mother via the placenta.
So, the correct answer is ‘Human female.’
Note: In reptiles, insects and birds, an egg is a fertilized zygote and is released from the mother’s body with little or no development at all. Such types of animals are known as oviparous animals. They lay eggs with hard calcareous shells to protect the embryo from predators as well as to survive extreme habitats or environments. In contrast, viviparous animals are the ones in which the embryonic development of the young ones takes place inside the mother’s body, specifically in her uterus.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Human egg is barely over 0.1mm or 100µm in diameter. It is the smallest egg cell. In general, eggs are large-sized cells because they store food for the development of the embryo. Avian (birds)eggs are the largest. They are in centimetres. Among them, the ostrich egg is the largest and weighs around 1.3 kg.

Additional Information:
In birds such as ostrich, duck and hen, after internal fertilisation, the eggs are released from the female’s body. They are laid in a nest. After birds have laid their eggs, they keep the eggs warm through their body heat. This process is known as incubation. It is necessary for proper and complete development of the embryo in the eggs. The yolk which occupies a major portion in avian eggs provides nourishment to the embryo. Also, many minute semi-permeable pores are present on the shell for the exchange of gases as well as moisture to prevent desiccation of the eggs.
The human egg is also known as an ovum. It is the largest cell in a human body and can be seen with the naked eye. After internal fertilization in the female’s body, a zygote is formed. After a series of divisions, an embryo is formed which gets embedded in the uterus of the female. Human egg cell does not contain much yolk as the nutrients of the embryo is fulfilled from the mother via the placenta.
So, the correct answer is ‘Human female.’
Note: In reptiles, insects and birds, an egg is a fertilized zygote and is released from the mother’s body with little or no development at all. Such types of animals are known as oviparous animals. They lay eggs with hard calcareous shells to protect the embryo from predators as well as to survive extreme habitats or environments. In contrast, viviparous animals are the ones in which the embryonic development of the young ones takes place inside the mother’s body, specifically in her uterus.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




