
The speed of light in air and glass is $3\times {{10}^{8}}m/s$and$2\times {{10}^{8}}m/s$ respectively. A beam of light falls on a glass at an angle of $30{}^\circ $ with surface. The angle of refraction in glass is
A. $25{}^\circ 16'$
B. $35{}^\circ 26'$
C. $15{}^\circ 26'$
D. $30{}^\circ 16'$
Answer
542.1k+ views
Hint: As a first step, you could make a ray diagram just to be clear about the situation. Then you could find the refractive index of glass from given values of speed of light in the two mediums. Then, you could use Snell's law to find the angle of refraction that took place in the glass and hence the answer.
Formula used:Snell’s law,
${{n}_{a}}\sin i={{n}_{g}}\sin r$
Complete step by step answer:
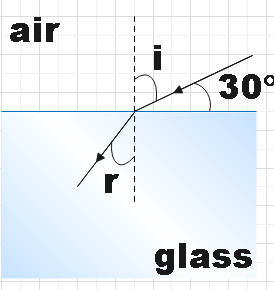
In the question, we are given the speed of light in two mediums which are air and glass.
${{v}_{a}}=3\times {{10}^{8}}m/s$
${{v}_{g}}=2\times {{10}^{8}}m/s$
The light is incident by making $30{}^\circ $ with the glass surface. So the incident angle will be,
$i=90-30=60{}^\circ $
We know that the refractive index of a medium is the speed of light with respect to the speed of light in air. So, the refractive index of glass would be,
${{n}_{g}}=\dfrac{{{v}_{a}}}{{{v}_{g}}}=\dfrac{3\times {{10}^{8}}m/s}{2\times {{10}^{8}}m/s}$
$\Rightarrow {{n}_{g}}=\dfrac{3}{2}$
Now from Snell’s law we have,
${{n}_{a}}\sin i={{n}_{g}}\sin r$
Substituting the values,
$\sin 60=\dfrac{3}{2}\sin r$
$\Rightarrow \sin r=\dfrac{2}{3}\times \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$
$\therefore r={{\sin }^{-1}}\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}=35.26{}^\circ $
Therefore, we found the refracted angle to be, $r=35.26{}^\circ $
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: One should always be careful while noting down the given angles. You shouldn’t forget that the incident angle or reflected angle, both are the angle made by the incident light with the normal and not the surface. In the question we are given the angle made with the surface and hence we have substituted accordingly.
Formula used:Snell’s law,
${{n}_{a}}\sin i={{n}_{g}}\sin r$
Complete step by step answer:

In the question, we are given the speed of light in two mediums which are air and glass.
${{v}_{a}}=3\times {{10}^{8}}m/s$
${{v}_{g}}=2\times {{10}^{8}}m/s$
The light is incident by making $30{}^\circ $ with the glass surface. So the incident angle will be,
$i=90-30=60{}^\circ $
We know that the refractive index of a medium is the speed of light with respect to the speed of light in air. So, the refractive index of glass would be,
${{n}_{g}}=\dfrac{{{v}_{a}}}{{{v}_{g}}}=\dfrac{3\times {{10}^{8}}m/s}{2\times {{10}^{8}}m/s}$
$\Rightarrow {{n}_{g}}=\dfrac{3}{2}$
Now from Snell’s law we have,
${{n}_{a}}\sin i={{n}_{g}}\sin r$
Substituting the values,
$\sin 60=\dfrac{3}{2}\sin r$
$\Rightarrow \sin r=\dfrac{2}{3}\times \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$
$\therefore r={{\sin }^{-1}}\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}=35.26{}^\circ $
Therefore, we found the refracted angle to be, $r=35.26{}^\circ $
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: One should always be careful while noting down the given angles. You shouldn’t forget that the incident angle or reflected angle, both are the angle made by the incident light with the normal and not the surface. In the question we are given the angle made with the surface and hence we have substituted accordingly.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




