
The sporophyte of Funaria begins development within
A) Antheridia
B) Capsule
C) Protonema
D) Archegonium
Answer
590.7k+ views
Hint: This structure is flask-shaped, which is borne on a short stalk having a basal swollen part of venter and elongated neck.
Complete Answer:
The zygote is the first cell of the sporophytic phase of Funaria. The development of sporophyte occurs within the center of the archegonium. The sporophyte is semi-parasitic in nature, the mature sporophyte can be differentiated into three distinct parts—foot, seta, and capsule.
Additional information:
Development of Sporophyte: - In Funaria soon after fertilization, the zygote secretes a wall around it and enlarges in size. It starts dividing by a transverse wall forming an upper epibasal cell and lower hypo basal cell.
- The epibasal cell further divides by two intersecting oblique walls. This results in the differentiation of an apical cell with two cutting faces in the epibasal cell.
- Similarly, the hypo basal cell differentiates an apical cell. These two apical cells result in the differentiation of the entire sporophyte. Therefore, the development of embryo sporophyte is bi-apical.
- The epibasal apical cell on maturation develops into the capsule and upper portion of the seta while the hypo basal apical cell develops into the foot and remaining part of the seta.
- Both apical cells cut out alternate segments resulting in the elongated filamentous structure of young sporogonium.
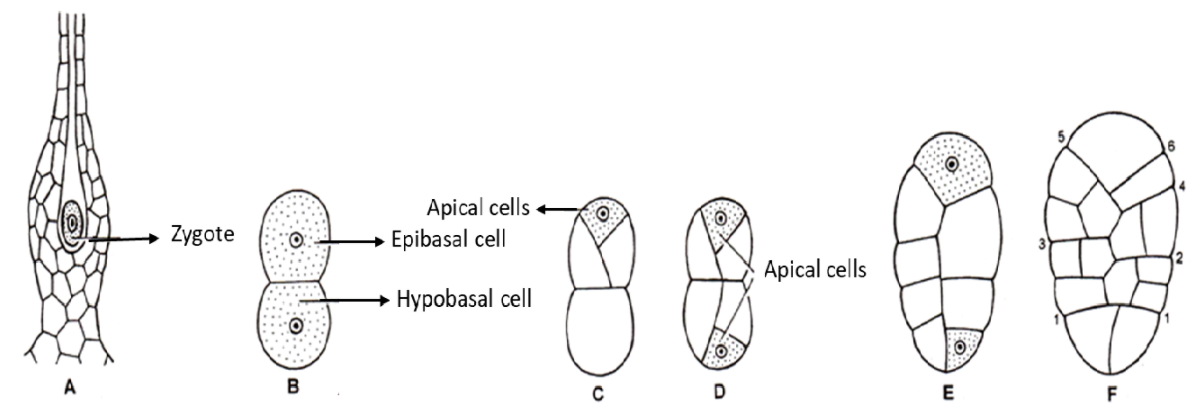
Fig: Early stages in the development of the sporophyte
- Antheridium is the male part of the plant.
- A branched, filamentous and multicellular structure produced from the spores on germination is called protonema.
So, the correct answer is ‘Archegonium’.
Note: - In Funaria, the sex organs, antheridia, and archegonia develop at the apices of separate erect branches, called as gametophores.
- The plant body is gametophyte in Funaria and involves two different stages namely the Juvenile stage represented by primary protonema and the leafy gametophyte which represents the adult form.
Complete Answer:
The zygote is the first cell of the sporophytic phase of Funaria. The development of sporophyte occurs within the center of the archegonium. The sporophyte is semi-parasitic in nature, the mature sporophyte can be differentiated into three distinct parts—foot, seta, and capsule.
Additional information:
Development of Sporophyte: - In Funaria soon after fertilization, the zygote secretes a wall around it and enlarges in size. It starts dividing by a transverse wall forming an upper epibasal cell and lower hypo basal cell.
- The epibasal cell further divides by two intersecting oblique walls. This results in the differentiation of an apical cell with two cutting faces in the epibasal cell.
- Similarly, the hypo basal cell differentiates an apical cell. These two apical cells result in the differentiation of the entire sporophyte. Therefore, the development of embryo sporophyte is bi-apical.
- The epibasal apical cell on maturation develops into the capsule and upper portion of the seta while the hypo basal apical cell develops into the foot and remaining part of the seta.
- Both apical cells cut out alternate segments resulting in the elongated filamentous structure of young sporogonium.

Fig: Early stages in the development of the sporophyte
- Antheridium is the male part of the plant.
- A branched, filamentous and multicellular structure produced from the spores on germination is called protonema.
So, the correct answer is ‘Archegonium’.
Note: - In Funaria, the sex organs, antheridia, and archegonia develop at the apices of separate erect branches, called as gametophores.
- The plant body is gametophyte in Funaria and involves two different stages namely the Juvenile stage represented by primary protonema and the leafy gametophyte which represents the adult form.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




