
The sporophyte of Funaria begins development within
(a) Antheridia
(b) Capsule
(c) Protonema
(d) Archegonium
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: Funaria sporophyte has an embedded foot, an elongated curved seta, and a pyriform terminal capsule. The sporophyte of funaria begins its development within the female reproductive organ. It acts as a fertilization site as well.
Complete step by step answer:
Funaria's sporophyte starts to evolve within the Archegonium. A mature archegonium has the form of a flask, borne on a short stalk. It has a basal swollen venter portion and an elongated neck. A two-layered jacket covers the venter, while the jacket around the neck is lined singly.
The antherozoids pass the vicinity of the archegonial neck during heavy rains and swim down to the center. Any antherozoid fuses to form a zygote (2n) with an embryo. The egg will remain in the archegonium even after fertilization until it develops into a sporophyte. The spore-forming form of the plant is a sporophyte. The zygote soon secretes a wall of cells and becomes the oospore. The oospore separates and redivides into embryos. The embryo then becomes a sporophyte or sporogonium. Once the sporophyte is fully developed, it is released from the archegonium.
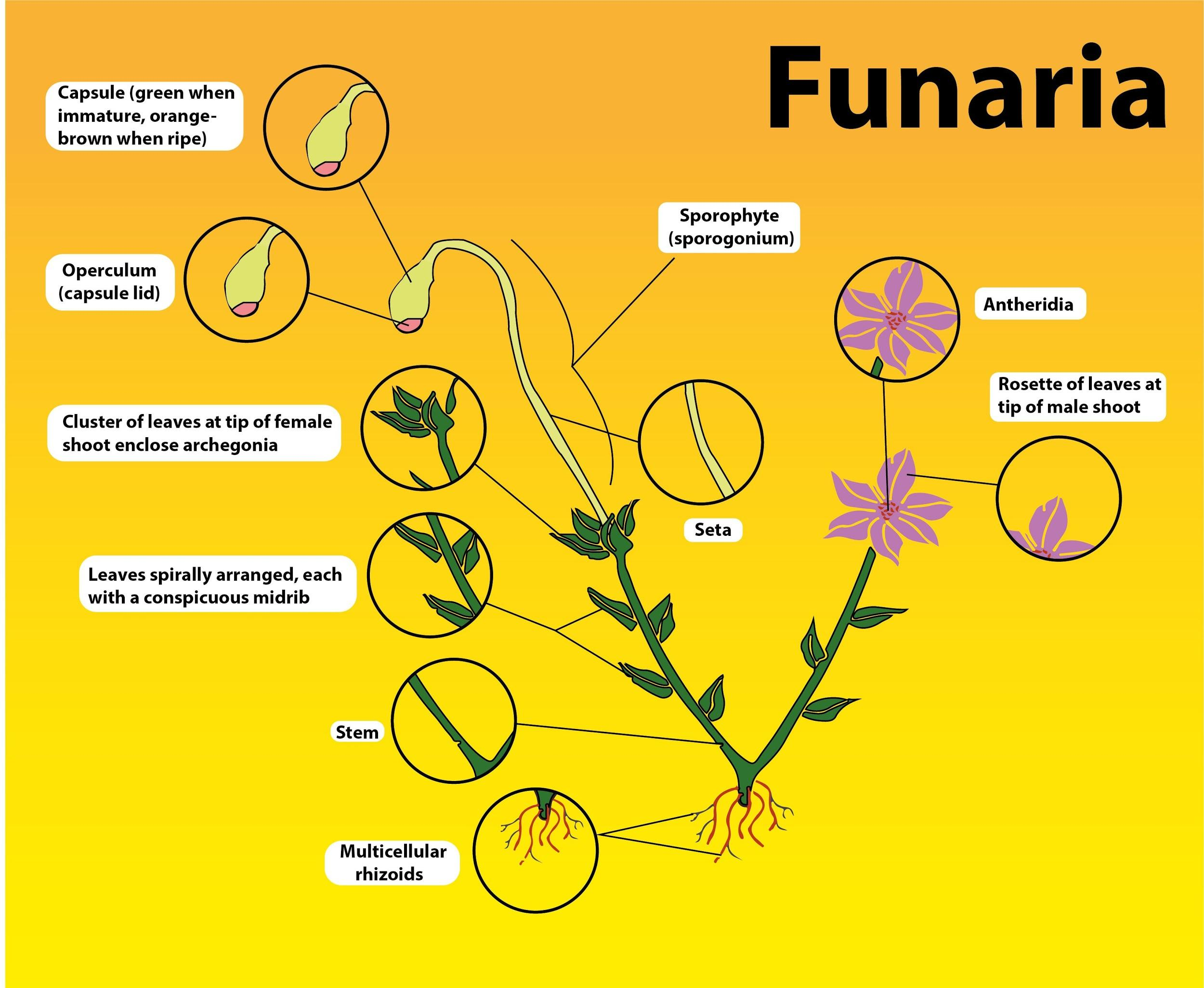
Funaria is usually referred to as 'cord moss.' It is distributed worldwide. The Common Species is Funaria hygrometrica. It grows on rocks, trunks of trees, damp walls, and wet soils in dense tufts. They assist in the soil-forming process. That process is called Pedogenesis.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Archegonium’.
Note: In Funaria the sexual reproduction is oogamous. The male reproductive system is known as antheridium and the archegonium is the female reproductive system. Funaria is monoecious (male and female sex organs are present on the same thallus) and autoicous (the development of antheridia and archegonia on different branches of the same thallus). In terminal clusters, the sex organs are borne on leafy gametophores.
Complete step by step answer:
Funaria's sporophyte starts to evolve within the Archegonium. A mature archegonium has the form of a flask, borne on a short stalk. It has a basal swollen venter portion and an elongated neck. A two-layered jacket covers the venter, while the jacket around the neck is lined singly.
The antherozoids pass the vicinity of the archegonial neck during heavy rains and swim down to the center. Any antherozoid fuses to form a zygote (2n) with an embryo. The egg will remain in the archegonium even after fertilization until it develops into a sporophyte. The spore-forming form of the plant is a sporophyte. The zygote soon secretes a wall of cells and becomes the oospore. The oospore separates and redivides into embryos. The embryo then becomes a sporophyte or sporogonium. Once the sporophyte is fully developed, it is released from the archegonium.

Funaria is usually referred to as 'cord moss.' It is distributed worldwide. The Common Species is Funaria hygrometrica. It grows on rocks, trunks of trees, damp walls, and wet soils in dense tufts. They assist in the soil-forming process. That process is called Pedogenesis.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Archegonium’.
Note: In Funaria the sexual reproduction is oogamous. The male reproductive system is known as antheridium and the archegonium is the female reproductive system. Funaria is monoecious (male and female sex organs are present on the same thallus) and autoicous (the development of antheridia and archegonia on different branches of the same thallus). In terminal clusters, the sex organs are borne on leafy gametophores.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




