
The square planar shape is ____.
(A) $sp$
(B) $ds{{p}^{3}}$
(C) $ds{{p}^{2}}$
(D) $s{{p}^{3}}$
Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint: An attempt to this question can be made by determining the postulates of valence bond theory. With this you can understand hybridisation of a complex. Try to draw the structure of the compounds having the respective hybridisation in the options. Based on that you can determine the hybridisation having square planar geometry.
Complete step by step answer:
The hybridization of atomic orbitals give rise to hybrid orbitals that are responsible for the formation of molecules. These hybrid orbitals have characteristic geometry from their time of formation. But there are some factors that can influence the geometry and therefore change the overall shape of molecules. Some of these factors are, number and position of lone pairs, type of substituent attached to the central atom etc.
Square planar is one of the shapes that represent a specific hybridisation of the atoms. It is a planar structure, which contains one central atom bonded to 4 substituents. The hybridization that is required for this shape is $ds{{p}^{2}}$. As you can see, it is an inner orbital complex. Let us know more about this.
It is a fact that the energy of 3d-orbitals is either similar to 3s and 3p or 4s and 4p. This makes the d-orbitals hybridize with both the groups. If they hybridize with the former group, they form inner orbital complexes, as the principal quantum number is the same for all the orbitals involved. The hybridization of 3d orbitals with 4s and 4p orbitals is termed as outer orbital complexes, as the principal quantum number of the orbitals except the d-orbitals is one unit higher.
Chemical compounds which exhibit this type of molecular geometry are- ${{\left[ Ni{{\left( CN \right)}_{4}} \right]}^{2-}}$ and ${{\left[ Pt{{\left( Cl \right)}_{4}} \right]}^{2-}}$. Structure of the latter is as below:
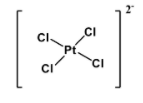
So the answer is option C.
Note: Square planar shape is also possible if the hybridization of the central atom is $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$ with two lone pairs at the axial positions. As for example, the molecule $Xe{{F}_{4}}$exhibits a square planar shape and has two lone pairs.
Complete step by step answer:
The hybridization of atomic orbitals give rise to hybrid orbitals that are responsible for the formation of molecules. These hybrid orbitals have characteristic geometry from their time of formation. But there are some factors that can influence the geometry and therefore change the overall shape of molecules. Some of these factors are, number and position of lone pairs, type of substituent attached to the central atom etc.
Square planar is one of the shapes that represent a specific hybridisation of the atoms. It is a planar structure, which contains one central atom bonded to 4 substituents. The hybridization that is required for this shape is $ds{{p}^{2}}$. As you can see, it is an inner orbital complex. Let us know more about this.
It is a fact that the energy of 3d-orbitals is either similar to 3s and 3p or 4s and 4p. This makes the d-orbitals hybridize with both the groups. If they hybridize with the former group, they form inner orbital complexes, as the principal quantum number is the same for all the orbitals involved. The hybridization of 3d orbitals with 4s and 4p orbitals is termed as outer orbital complexes, as the principal quantum number of the orbitals except the d-orbitals is one unit higher.
Chemical compounds which exhibit this type of molecular geometry are- ${{\left[ Ni{{\left( CN \right)}_{4}} \right]}^{2-}}$ and ${{\left[ Pt{{\left( Cl \right)}_{4}} \right]}^{2-}}$. Structure of the latter is as below:

So the answer is option C.
Note: Square planar shape is also possible if the hybridization of the central atom is $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$ with two lone pairs at the axial positions. As for example, the molecule $Xe{{F}_{4}}$exhibits a square planar shape and has two lone pairs.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




