
The structure absent in Frog’s testis is
(a) Seminiferous tubules
(b) Seminal vesicles
(c) Sertoli cells
(d) None of the above
Answer
583.8k+ views
Hint: Testes represent the male reproductive organ in males. The structure that is absent in the frog’s testis performs the function of nutritional support to the developing spermatozoa in the testes of human males.
Complete step by step answer:
The sexes in frogs are separate and they exhibit sexual dimorphism i.e the male and female can be distinguished morphologically. The male reproductive system of Frog consists of a pair of the testis lying anterior- ventrally to the kidneys. The internal cavity of testes is filled with coiled seminiferous tubules where sperms are produced by spermatogenesis. The tubules are interspersed with interstitial tissues secreting a male sex hormone to produce secondary sexual characters in males. No Sertoli cells or nurse cells are present in the testis.
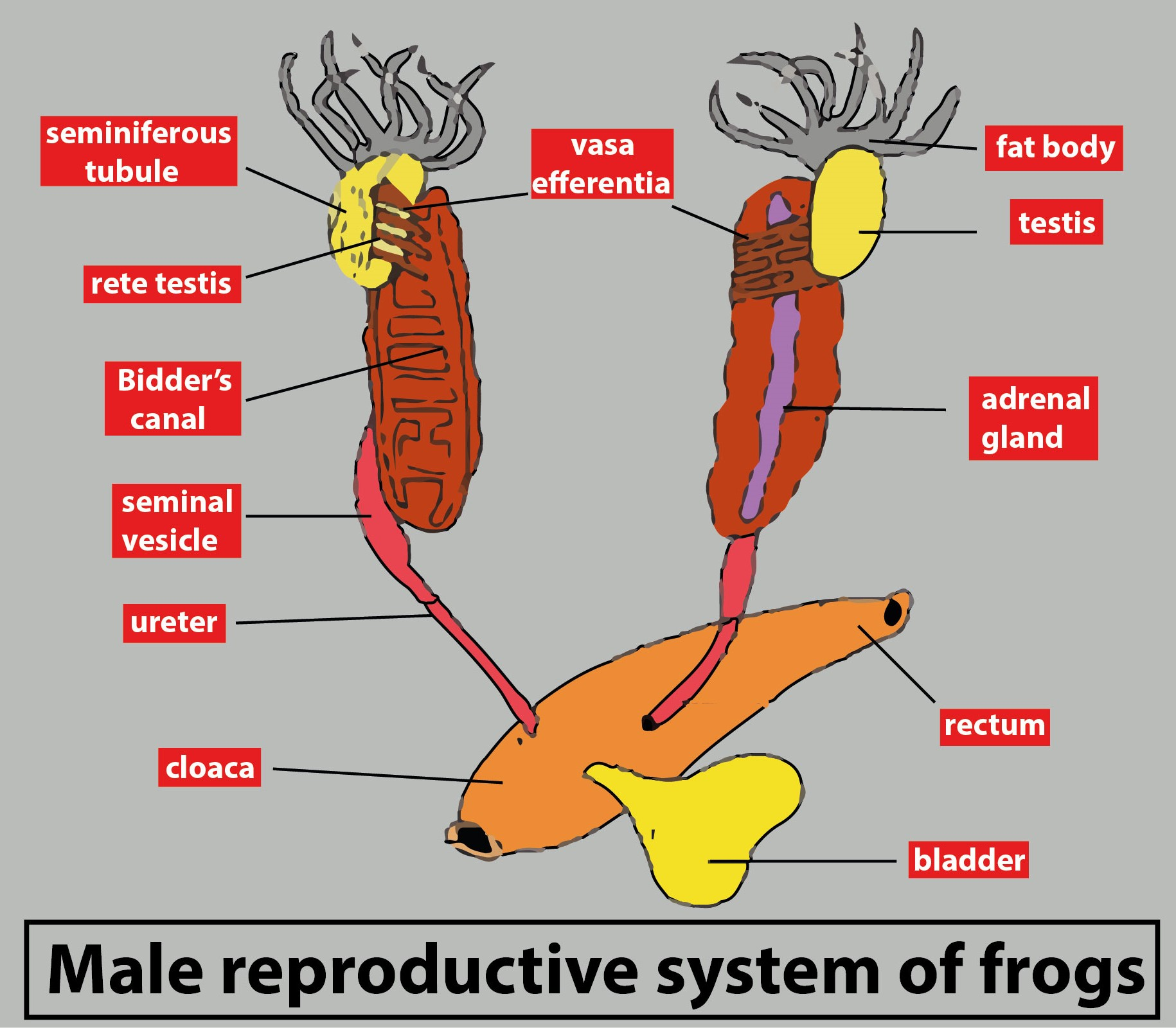
So, the correct answer is ‘Sertoli cells.’
Additional Information:
- The sperms produced in the testes travel through tubules named ‘vasa efferentia’ which opens into Bidder’s canal.
- From Bidder’s canal, the sperms are carried to the transverse collecting tubules before it reaches the urogenital tract.
- The urogenital tract is a common tract for both urine and sperms. Before opening into the cloaca, it dilates to form a seminal vesicle to store the sperms temporarily.
- During amplexus i.e mating in frogs, the sperms leave the seminal vesicle, and through the cloaca, sheds into the water via the cloacal aperture. Cloaca is a common chamber for the discharge of fecal matter, urine, and sperms.
Note:
- Frogs show sexual dimorphism where both female and male can be differentiated morphologically too. - Male has vocal sacs and amplexusory pads. Both are usually functional during the mating season where the males use vocal sacs to croak so as to call the female.
- The amplexusory pads are used to grip the female during copulation.
Complete step by step answer:
The sexes in frogs are separate and they exhibit sexual dimorphism i.e the male and female can be distinguished morphologically. The male reproductive system of Frog consists of a pair of the testis lying anterior- ventrally to the kidneys. The internal cavity of testes is filled with coiled seminiferous tubules where sperms are produced by spermatogenesis. The tubules are interspersed with interstitial tissues secreting a male sex hormone to produce secondary sexual characters in males. No Sertoli cells or nurse cells are present in the testis.

So, the correct answer is ‘Sertoli cells.’
Additional Information:
- The sperms produced in the testes travel through tubules named ‘vasa efferentia’ which opens into Bidder’s canal.
- From Bidder’s canal, the sperms are carried to the transverse collecting tubules before it reaches the urogenital tract.
- The urogenital tract is a common tract for both urine and sperms. Before opening into the cloaca, it dilates to form a seminal vesicle to store the sperms temporarily.
- During amplexus i.e mating in frogs, the sperms leave the seminal vesicle, and through the cloaca, sheds into the water via the cloacal aperture. Cloaca is a common chamber for the discharge of fecal matter, urine, and sperms.
Note:
- Frogs show sexual dimorphism where both female and male can be differentiated morphologically too. - Male has vocal sacs and amplexusory pads. Both are usually functional during the mating season where the males use vocal sacs to croak so as to call the female.
- The amplexusory pads are used to grip the female during copulation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




