
The structure of $\text{Xe}{{\text{F}}_{\text{4}}}$ is
A) Planar
B) Tetrahedral
C) Square Planar
D) Pyramidal
Answer
528.9k+ views
Hint: To solve the given question, we first need to know the hybridization of xenon tetrafluoride or $XeF_4$ with this information we can proceed to find out the hybridization of the central atom and similarly find the structure of $\text{Xe}{{\text{F}}_{\text{4}}}$.
Complete step by step answer:
The central atom in Xe has 4 bond pairs of electrons and two lone pairs of electrons. It undergoes $\text{s}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}{{\text{d}}^{\text{2}}}$hybridization which results in octahedral electron geometry. This also results in the square planar molecular geometry.
The hybridization of $\text{Xe}{{\text{F}}_{\text{4}}}$ molecule.
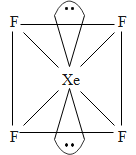
The two lone pairs that are present on the opposite corners of an octahedron. This is because of the fact that it will minimize the repulsion between them.
Here is the diagram of the structure of $\text{Xe}{{\text{F}}_{\text{4}}}$
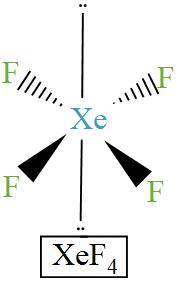
Hence, the correct answer is Option C.
Note: We can define hybridization as the idea of atomic orbitals to choose from newly hybridized orbitals. This, in turn, influences the molecular geometry and bonding properties of a molecule. Hybridization also defines the expansion of valence bond theory and this concept illustrates various compounds with $\text{s}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$, $\text{s}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}$ and $\text{sp}$ kinds of hybridization. To define the hybridization of a particular molecule, we need to first clarify the spin direction of each electron in the molecule and similarly, we need to arrange the electrons in various energy shells such as s, p, d, f. After we attain a stable hybridization of a molecule, we can determine its pi ($\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ }$) and sigma ($\text{ }\!\!\sigma\!\!\text{ }$) bonds and hence we can determine the structure that the molecule possesses.
Complete step by step answer:
The central atom in Xe has 4 bond pairs of electrons and two lone pairs of electrons. It undergoes $\text{s}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}{{\text{d}}^{\text{2}}}$hybridization which results in octahedral electron geometry. This also results in the square planar molecular geometry.
The hybridization of $\text{Xe}{{\text{F}}_{\text{4}}}$ molecule.

The two lone pairs that are present on the opposite corners of an octahedron. This is because of the fact that it will minimize the repulsion between them.
Here is the diagram of the structure of $\text{Xe}{{\text{F}}_{\text{4}}}$

Hence, the correct answer is Option C.
Note: We can define hybridization as the idea of atomic orbitals to choose from newly hybridized orbitals. This, in turn, influences the molecular geometry and bonding properties of a molecule. Hybridization also defines the expansion of valence bond theory and this concept illustrates various compounds with $\text{s}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$, $\text{s}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}$ and $\text{sp}$ kinds of hybridization. To define the hybridization of a particular molecule, we need to first clarify the spin direction of each electron in the molecule and similarly, we need to arrange the electrons in various energy shells such as s, p, d, f. After we attain a stable hybridization of a molecule, we can determine its pi ($\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ }$) and sigma ($\text{ }\!\!\sigma\!\!\text{ }$) bonds and hence we can determine the structure that the molecule possesses.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




