
The structures of four molecules are shown. Which molecule belongs to the same homologous series?
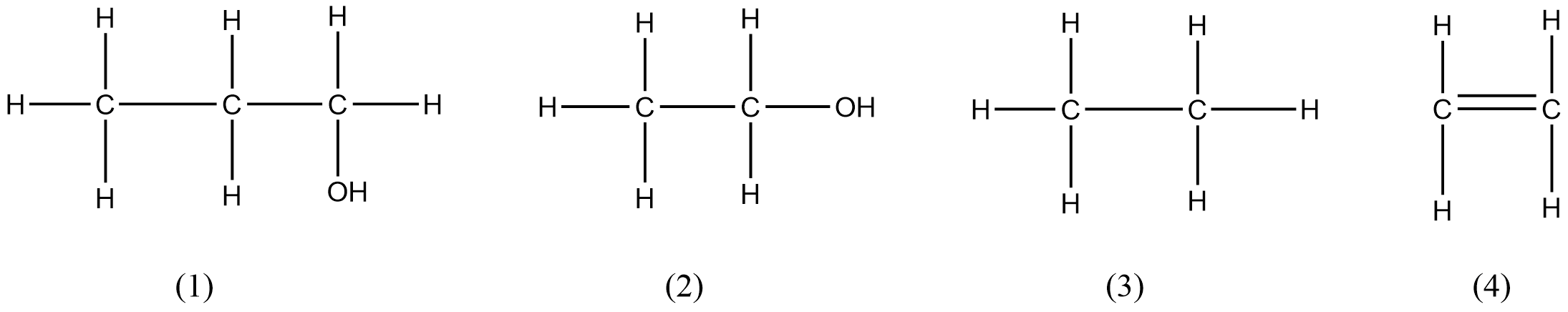
A.$1$ and $2$
B.$1$ and $3$
C.$2$ and $4$
D.$3$ and $4$

Answer
561k+ views
Hint: In Organic chemistry, homologous series is a series which consist of molecules of similar structure and same functional group. They also show similarity in chemical properties.
Complete step by step answer:
The key-points about homologous series are,
-They are a group or series of organic compounds each containing a characteristic functional group and similar structure.
-The members of homologous series are called homologous.
-Homologues show similar chemical properties.
-Homologous series can be represented by a general molecular formula.
-The successive members of homologous series differ from each other by a $ - C{H_2}$ unit.
Examples of homologous series are alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, haloalkanes etc.
From the given structures, structure $1$ and $2$ are alcohols. They contain the same functional group and differ from each other by a $ - C{H_2}$ unit. Hence they belong to the same homologous series.
-Molecules $1$ and $3$ are alcohol and alkane respectively. Hence they belong to different homologous series.
-Molecules $1$ and $4$ are alcohol and alkene respectively. Hence they belong to different homologous series.
-Molecules $2$ and $3$ are alcohol and alkane respectively. Hence they belong to different homologous series.
-Molecules $2$ and $4$ are alcohol and alkene respectively. Hence they belong to different homologous series.
-Molecules $3$ and $4$ are alkane and alkene respectively. Hence they belong to different homologous series.
Therefore option A is correct.
Note:
The general molecular formula of each type of compound given are,
Alkane - ${C_n}{H_{2n + 2}}$
Alkene - ${C_n}{H_{2n}}$
Alcohol - ${C_n}{H_{2n + 1}}OH$
This question can also be solved by writing the molecular formula of each compound given and comparing with the above formulae. The compounds which have similar formulas will belong to the same homologous series.
Complete step by step answer:
The key-points about homologous series are,
-They are a group or series of organic compounds each containing a characteristic functional group and similar structure.
-The members of homologous series are called homologous.
-Homologues show similar chemical properties.
-Homologous series can be represented by a general molecular formula.
-The successive members of homologous series differ from each other by a $ - C{H_2}$ unit.
Examples of homologous series are alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, haloalkanes etc.
From the given structures, structure $1$ and $2$ are alcohols. They contain the same functional group and differ from each other by a $ - C{H_2}$ unit. Hence they belong to the same homologous series.
-Molecules $1$ and $3$ are alcohol and alkane respectively. Hence they belong to different homologous series.
-Molecules $1$ and $4$ are alcohol and alkene respectively. Hence they belong to different homologous series.
-Molecules $2$ and $3$ are alcohol and alkane respectively. Hence they belong to different homologous series.
-Molecules $2$ and $4$ are alcohol and alkene respectively. Hence they belong to different homologous series.
-Molecules $3$ and $4$ are alkane and alkene respectively. Hence they belong to different homologous series.
Therefore option A is correct.
Note:
The general molecular formula of each type of compound given are,
Alkane - ${C_n}{H_{2n + 2}}$
Alkene - ${C_n}{H_{2n}}$
Alcohol - ${C_n}{H_{2n + 1}}OH$
This question can also be solved by writing the molecular formula of each compound given and comparing with the above formulae. The compounds which have similar formulas will belong to the same homologous series.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




