
The sum of the focal distances from any point on the ellipse \[9{x^2} + 16{y^2} = 144\] is
1. \[3\]
2. \[6\]
3. \[8\]
4. \[4\]
Answer
495.3k+ views
Hint: We are given the equation of an ellipse and we are asked to find the sum of the focal distances from any point on the given ellipse. Firstly we need to keep in mind the definition of an ellipse. An ellipse is a curve consisting of two focal points, such that all the points lying on the curve have the sum of the two distances from the focal points as constant. We have to find this constant distance of each point of the ellipse from the two foci.
Complete step-by-step solution:
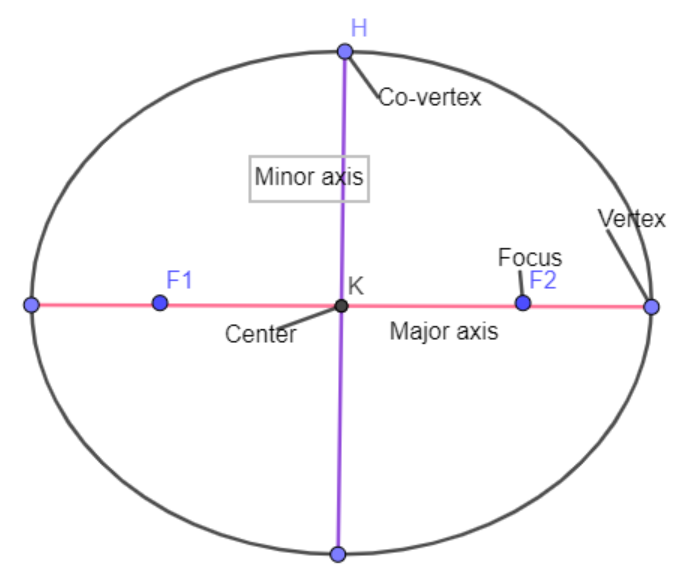
We are given the equation of ellipse as \[9{x^2} + 16{y^2} = 144\]
Converting it to the standard form of the equation of ellipse we get ,
\[\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{16}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{9} = 1\]
Comparing it with the general equation of ellipse i.e. \[\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1\] we get \[a = 4\] and \[b = 3\]
Now, we know that the sum of focal distances of a point on an ellipse is constant and equal to the length of the major axis of that particular ellipse i.e. sum of focal distance of any point on an ellipse \[ = 2a\]
So. substituting the known value of a, we get,
\[ = 2 \times 4 = 8\]
Therefore option (3) is the correct answer.
Note: In order to solve such types of questions one must have a grip over the concept of ellipses , related terms and the respective formulas. Major axis is denoted by a and is the greatest length of any ellipse passing through the center from one end to the other, at the broad part of the ellipse. On the other hand, the minor axis is denoted by b and is the shortest diameter of the ellipse, crossing through the center at the narrowest part. Half of the major axis is called semi-major axis and half of the minor axis is called semi-minor axis.
Complete step-by-step solution:

We are given the equation of ellipse as \[9{x^2} + 16{y^2} = 144\]
Converting it to the standard form of the equation of ellipse we get ,
\[\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{16}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{9} = 1\]
Comparing it with the general equation of ellipse i.e. \[\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1\] we get \[a = 4\] and \[b = 3\]
Now, we know that the sum of focal distances of a point on an ellipse is constant and equal to the length of the major axis of that particular ellipse i.e. sum of focal distance of any point on an ellipse \[ = 2a\]
So. substituting the known value of a, we get,
\[ = 2 \times 4 = 8\]
Therefore option (3) is the correct answer.
Note: In order to solve such types of questions one must have a grip over the concept of ellipses , related terms and the respective formulas. Major axis is denoted by a and is the greatest length of any ellipse passing through the center from one end to the other, at the broad part of the ellipse. On the other hand, the minor axis is denoted by b and is the shortest diameter of the ellipse, crossing through the center at the narrowest part. Half of the major axis is called semi-major axis and half of the minor axis is called semi-minor axis.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




