
The superior vena cava of precaval veins collect blood from
A. Trunk and hind limbs
B. Forelimbs and hind limbs
C. Head and forelimbs
D. Head and hind limbs
Answer
568.8k+ views
Hint: The superior vena cava, as its name suggests, it is the superior of the two venae cavae of the heart. These are great venous trunks that pour deoxygenated blood from the circulatory system to the right atrium of the heart. The pre-caval veins are situated before the venae cavae and collect the blood from the upper body for superior vena cava.
Complete answer: The circulatory system of the human is a complex system of various individual units working together. The venous trunks of the heart collect deoxygenated blood from the body. It pours unfiltered blood to the right atrium of the heart. It is made of two main venae cavae. One of them is the superior vena cava. It has a large diameter but a shorter length. Thus, for blood collection, various pre-caval veins are joined to it. These veins collect deoxygenated blood from the upper portion of the body. Each of the pre-caval veins is formed by a combination of external jugular, internal jugular, subclavian, and anterior intercostal veins. The deoxygenated blood from the head, tongue, and the muscles of the jaw are collected by external jugular veins. Blood from the muscles of the neck and the brain is collected by the internal jugular veins. Blood from shoulders and forelimbs is received by the subclavian vein and this is connected to the external jugular vein. The intercostal vein is connected to the right pre-caval. It collects blood from anterior intercostal spaces and an azygos vein. All of these bring blood from the posterior intercostal and the lumbar region.
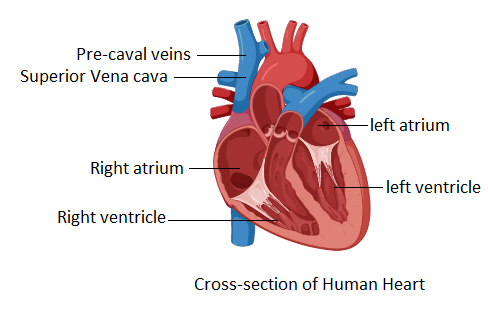
Both of the left and right precaval veins pour blood into the right auricle of the heart. Thus, we can conclude that the superior vena cava of precaval veins collect blood from the head and forelimbs of the upper body.
So, the correct answer is option C.
Note: Damage to superior vena cava refers to the partial or complete obstruction of superior vena cava. Lung cancer, metastatic cancer, or lymphoma is related to superior vena cava obstruction. This can lead to enlarged veins in the head and neck that can cause breathlessness, cough, difficulty in swallowing, and chest pain. Chemotherapy and radiotherapy can be effective treatments.
Complete answer: The circulatory system of the human is a complex system of various individual units working together. The venous trunks of the heart collect deoxygenated blood from the body. It pours unfiltered blood to the right atrium of the heart. It is made of two main venae cavae. One of them is the superior vena cava. It has a large diameter but a shorter length. Thus, for blood collection, various pre-caval veins are joined to it. These veins collect deoxygenated blood from the upper portion of the body. Each of the pre-caval veins is formed by a combination of external jugular, internal jugular, subclavian, and anterior intercostal veins. The deoxygenated blood from the head, tongue, and the muscles of the jaw are collected by external jugular veins. Blood from the muscles of the neck and the brain is collected by the internal jugular veins. Blood from shoulders and forelimbs is received by the subclavian vein and this is connected to the external jugular vein. The intercostal vein is connected to the right pre-caval. It collects blood from anterior intercostal spaces and an azygos vein. All of these bring blood from the posterior intercostal and the lumbar region.

Both of the left and right precaval veins pour blood into the right auricle of the heart. Thus, we can conclude that the superior vena cava of precaval veins collect blood from the head and forelimbs of the upper body.
So, the correct answer is option C.
Note: Damage to superior vena cava refers to the partial or complete obstruction of superior vena cava. Lung cancer, metastatic cancer, or lymphoma is related to superior vena cava obstruction. This can lead to enlarged veins in the head and neck that can cause breathlessness, cough, difficulty in swallowing, and chest pain. Chemotherapy and radiotherapy can be effective treatments.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




