
The tangent and the normal lines at the point $\left( \sqrt{3,}1 \right)$ to the circle ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=4$ and the x-axis form a triangle. The area of this triangle (in square units) is:
(a) $\dfrac{1}{3}$
(b) $\dfrac{4}{\sqrt{3}}$
(c) $\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}$
(d) $\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{3}}$
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: The equation of tangent at $\left( \sqrt{3,}1 \right)$ to the circle ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=4$ is $\dfrac{y-1}{x-\sqrt{3}}={{\left[ \dfrac{dy}{dx} \right]}_{\left( \sqrt{3},1 \right)}}$. The tangent cuts the x-axis, so we can find the intersecting point of tangent and x-axis by putting $y=0$.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us draw a circle with centre $O\left( 0,0 \right)$.
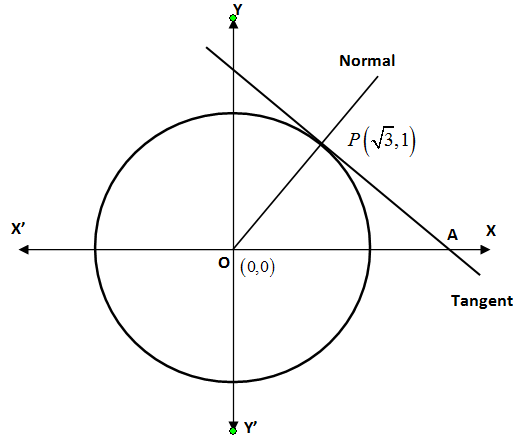
Here you can see that it is given that the tangent and the normal to the circle intersect at a point$\left( \sqrt{3,}1 \right)$. Let us take this point as $P\left( \sqrt{3,}1 \right)$. The tangent will intersect x-axis at point A.
Let us find the equation of the tangent to the circle ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=4$. As the tangent meet the circle at point$P\left( \sqrt{3,}1 \right)$, so first we will find the slope of the tangent at $P\left( \sqrt{3,}1 \right)$.
The slope of the tangent at the point $Q\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ is ${{\left( \dfrac{dy}{dx} \right)}_{\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)}}$. Here we have the equation of the circle as ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=4$.
If $z={{x}^{n}}$, then $\dfrac{dz}{dx}=n{{x}^{n-1}}$; and if $z=n$, $\dfrac{dz}{dx}=0$, where $n$ is a real number.
Now let us find differentiation of the equation ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=4$with respect to $x$.
Then, $2{{x}^{2-1}}+2{{y}^{2-1}}\dfrac{dy}{dx}=0$
$\Rightarrow 2x+2y\dfrac{dy}{dx}=0$
$\Rightarrow 2\left( x+y\dfrac{dy}{dx} \right)=0$
$\Rightarrow \left( x+y\dfrac{dy}{dx} \right)=0$
\[\Rightarrow y\dfrac{dy}{dx}=-x\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{-x}{y}\]
At point $P\left( \sqrt{3,}1 \right)$, we have $x=\sqrt{3}$ and $y=1$.
So we have \[{{\left( \dfrac{dy}{dx} \right)}_{\left( \sqrt{3},1 \right)}}=-\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{1}=-\sqrt{3}\].
We know that equation of tangent at point $Q\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ is $\dfrac{y-{{y}_{1}}}{x-{{x}_{1}}}={{\left( \dfrac{dy}{dx} \right)}_{\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)}}$.
So equation of tangent at point $P\left( \sqrt{3,}1 \right)$ will be
$\dfrac{y-1}{x-\sqrt{3}}=-\sqrt{3}$
$\Rightarrow y-1=-\sqrt{3}x+3$
\[\Rightarrow \sqrt{3}x+y=4\] (1)
As the tangent cuts x-axis at $A$, so at $A$, $y=0$. Since the tangent cuts x-axis at $A$, therefore we shall put $y=0$in equation (1). Then,
$\Rightarrow \sqrt{3}x+0=4$
\[\Rightarrow \sqrt{3}x=4\]
$\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{4}{\sqrt{3}}$
At point A, $x=\dfrac{4}{\sqrt{3}}$and $y=0$, therefore the coordinate of A is $A\left( \dfrac{4}{\sqrt{3}},0 \right)$.
Now let us find $OP$and $AP$to find the area of triangle $\Delta OAP$ as $OP\bot AP$. Thus $OP$ is the height of $\Delta OAP$ and $AP$ is the base of $\Delta OAP$.
Now,
$OP=\sqrt{{{\left( 3 \right)}^{2}}+{{1}^{2}}}=\sqrt{3+1}=\sqrt{4}=2units$.
\[\begin{align}
& AP=\sqrt{{{\left( \sqrt{3}-\dfrac{4}{\sqrt{3}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 1-0 \right)}^{2}}}=\sqrt{{{\left( \dfrac{3-4}{\sqrt{3}} \right)}^{2}}+{{1}^{2}}} \\
& \\
\end{align}\]
\[=\sqrt{{{\left( -\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}} \right)}^{2}}+1}\]
\[=\sqrt{\dfrac{1}{3}+1}\]
\[=\sqrt{\dfrac{1+3}{3}}\]
\[=\sqrt{\dfrac{4}{3}}\]
\[=\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{3}}units\]
$\therefore ar\left( \Delta OAP \right)=$ $\dfrac{1}{2}\times $base $\times $ height
$=\dfrac{1}{2}\times AP\times OP$
$=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \dfrac{2}{\sqrt{3}}\times 2$ sq. units
$=\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{3}}$ sq. units
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: The student must not get confused with tangent and normal. The tangent is a straight line that just touches the curve at a given point. The normal is a straight line which is perpendicular to the tangent. The student might get wrong in recognizing the base and height of triangle$\Delta OAP$. The line which is perpendicular to the tangent is height and the tangent is the base.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us draw a circle with centre $O\left( 0,0 \right)$.

Here you can see that it is given that the tangent and the normal to the circle intersect at a point$\left( \sqrt{3,}1 \right)$. Let us take this point as $P\left( \sqrt{3,}1 \right)$. The tangent will intersect x-axis at point A.
Let us find the equation of the tangent to the circle ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=4$. As the tangent meet the circle at point$P\left( \sqrt{3,}1 \right)$, so first we will find the slope of the tangent at $P\left( \sqrt{3,}1 \right)$.
The slope of the tangent at the point $Q\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ is ${{\left( \dfrac{dy}{dx} \right)}_{\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)}}$. Here we have the equation of the circle as ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=4$.
If $z={{x}^{n}}$, then $\dfrac{dz}{dx}=n{{x}^{n-1}}$; and if $z=n$, $\dfrac{dz}{dx}=0$, where $n$ is a real number.
Now let us find differentiation of the equation ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=4$with respect to $x$.
Then, $2{{x}^{2-1}}+2{{y}^{2-1}}\dfrac{dy}{dx}=0$
$\Rightarrow 2x+2y\dfrac{dy}{dx}=0$
$\Rightarrow 2\left( x+y\dfrac{dy}{dx} \right)=0$
$\Rightarrow \left( x+y\dfrac{dy}{dx} \right)=0$
\[\Rightarrow y\dfrac{dy}{dx}=-x\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{-x}{y}\]
At point $P\left( \sqrt{3,}1 \right)$, we have $x=\sqrt{3}$ and $y=1$.
So we have \[{{\left( \dfrac{dy}{dx} \right)}_{\left( \sqrt{3},1 \right)}}=-\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{1}=-\sqrt{3}\].
We know that equation of tangent at point $Q\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ is $\dfrac{y-{{y}_{1}}}{x-{{x}_{1}}}={{\left( \dfrac{dy}{dx} \right)}_{\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)}}$.
So equation of tangent at point $P\left( \sqrt{3,}1 \right)$ will be
$\dfrac{y-1}{x-\sqrt{3}}=-\sqrt{3}$
$\Rightarrow y-1=-\sqrt{3}x+3$
\[\Rightarrow \sqrt{3}x+y=4\] (1)
As the tangent cuts x-axis at $A$, so at $A$, $y=0$. Since the tangent cuts x-axis at $A$, therefore we shall put $y=0$in equation (1). Then,
$\Rightarrow \sqrt{3}x+0=4$
\[\Rightarrow \sqrt{3}x=4\]
$\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{4}{\sqrt{3}}$
At point A, $x=\dfrac{4}{\sqrt{3}}$and $y=0$, therefore the coordinate of A is $A\left( \dfrac{4}{\sqrt{3}},0 \right)$.
Now let us find $OP$and $AP$to find the area of triangle $\Delta OAP$ as $OP\bot AP$. Thus $OP$ is the height of $\Delta OAP$ and $AP$ is the base of $\Delta OAP$.
Now,
$OP=\sqrt{{{\left( 3 \right)}^{2}}+{{1}^{2}}}=\sqrt{3+1}=\sqrt{4}=2units$.
\[\begin{align}
& AP=\sqrt{{{\left( \sqrt{3}-\dfrac{4}{\sqrt{3}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 1-0 \right)}^{2}}}=\sqrt{{{\left( \dfrac{3-4}{\sqrt{3}} \right)}^{2}}+{{1}^{2}}} \\
& \\
\end{align}\]
\[=\sqrt{{{\left( -\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}} \right)}^{2}}+1}\]
\[=\sqrt{\dfrac{1}{3}+1}\]
\[=\sqrt{\dfrac{1+3}{3}}\]
\[=\sqrt{\dfrac{4}{3}}\]
\[=\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{3}}units\]
$\therefore ar\left( \Delta OAP \right)=$ $\dfrac{1}{2}\times $base $\times $ height
$=\dfrac{1}{2}\times AP\times OP$
$=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \dfrac{2}{\sqrt{3}}\times 2$ sq. units
$=\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{3}}$ sq. units
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: The student must not get confused with tangent and normal. The tangent is a straight line that just touches the curve at a given point. The normal is a straight line which is perpendicular to the tangent. The student might get wrong in recognizing the base and height of triangle$\Delta OAP$. The line which is perpendicular to the tangent is height and the tangent is the base.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




