
The tangent to the curve \[y = {e^{2x}}\] at the point \[\left( {0,1} \right)\] meets \[x\]–axis at?
A. \[\left( {0,1} \right)\]
B. \[\left( { - \dfrac{1}{2},0} \right)\]
C. \[\left( {2,0} \right)\]
D. \[\left( {0,2} \right)\]
Answer
595.2k+ views
Hint: First, we will find the derivative of the given curve to compute the slope of the tangent at a given point. Then take the point-slope form of the equation of the line, that is, \[y - {y_0} = \dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}}\left( {x - {x_0}} \right)\] and substitute the values of \[{x_0}\] and \[{y_0}\] from given point in the point-slope form of the equation. Take \[y = 0\] in the obtained equation where the point meets the \[x\]–axis to find the required result.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Given that the equation of curve is \[y = {e^{2x}}\].
We know that the given curve passes through the point \[\left( {0,1} \right)\].
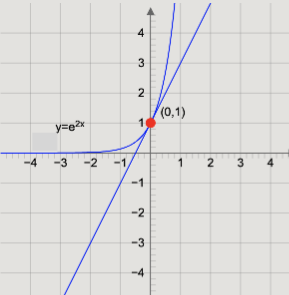
Now, we will find the derivative of the curve \[y = {e^{2x}}\] to find the slope of the tangent to the curve.
\[
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = \dfrac{d}{{dx}}\left( {{e^{2x}}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = {e^{2x}} \cdot \dfrac{d}{{dx}}\left( {2x} \right) \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = {e^{2x}} \cdot 2 \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = 2{e^{2x}} \\
\]
Computing the slope of the tangent at point \[\left( {0,1} \right)\], we get
\[
{\left. {\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}}} \right|_{x = 0}} = {\left. {2{e^{2x}}} \right|_{x = 0}} \\
= 2{e^{2\left( 0 \right)}} \\
= 2 \cdot 1 \\
= 2 \\
\]
It is known that the point-slope form of the equation of a straight line is \[y - {y_0} = \dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}}\left( {x - {x_0}} \right)\], where \[\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}}\] is the slope of the line and passes through the point \[\left( {{x_0},{y_0}} \right)\].
Substituting the above value in the point-slope form of the equation at point \[\left( {0,1} \right)\], we get
\[
y - 1 = 2\left( {x - 0} \right) \\
y - 1 = 2x \\
\]
Since, we know that the tangent to the curve \[y = {e^{2x}}\] at the point meets \[x\]–axis is \[y = 0\].
Replacing 0 for \[y\] in the above equation of tangent, we get
\[
\Rightarrow 0 = 2x + 1 \\
\Rightarrow 2x = - 1 \\
\Rightarrow x = - \dfrac{1}{2} \\
\]
So, we found that the required point is \[\left( { - \dfrac{1}{2},0} \right)\].
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note: While solving these types of questions always remember to plot these questions using diagrams. This will make solving such questions easier. In this question, first of all, note that the derivative of the curve is also a slope of the equation of the line. Also, in this question, some students take the slope of the tangent as the \[y\]–coordinate for the required point which is wrong, we have to find the equation of the slope and then substitute \[y = 0\] where it meets \[x\]-axis.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Given that the equation of curve is \[y = {e^{2x}}\].
We know that the given curve passes through the point \[\left( {0,1} \right)\].

Now, we will find the derivative of the curve \[y = {e^{2x}}\] to find the slope of the tangent to the curve.
\[
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = \dfrac{d}{{dx}}\left( {{e^{2x}}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = {e^{2x}} \cdot \dfrac{d}{{dx}}\left( {2x} \right) \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = {e^{2x}} \cdot 2 \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = 2{e^{2x}} \\
\]
Computing the slope of the tangent at point \[\left( {0,1} \right)\], we get
\[
{\left. {\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}}} \right|_{x = 0}} = {\left. {2{e^{2x}}} \right|_{x = 0}} \\
= 2{e^{2\left( 0 \right)}} \\
= 2 \cdot 1 \\
= 2 \\
\]
It is known that the point-slope form of the equation of a straight line is \[y - {y_0} = \dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}}\left( {x - {x_0}} \right)\], where \[\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}}\] is the slope of the line and passes through the point \[\left( {{x_0},{y_0}} \right)\].
Substituting the above value in the point-slope form of the equation at point \[\left( {0,1} \right)\], we get
\[
y - 1 = 2\left( {x - 0} \right) \\
y - 1 = 2x \\
\]
Since, we know that the tangent to the curve \[y = {e^{2x}}\] at the point meets \[x\]–axis is \[y = 0\].
Replacing 0 for \[y\] in the above equation of tangent, we get
\[
\Rightarrow 0 = 2x + 1 \\
\Rightarrow 2x = - 1 \\
\Rightarrow x = - \dfrac{1}{2} \\
\]
So, we found that the required point is \[\left( { - \dfrac{1}{2},0} \right)\].
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note: While solving these types of questions always remember to plot these questions using diagrams. This will make solving such questions easier. In this question, first of all, note that the derivative of the curve is also a slope of the equation of the line. Also, in this question, some students take the slope of the tangent as the \[y\]–coordinate for the required point which is wrong, we have to find the equation of the slope and then substitute \[y = 0\] where it meets \[x\]-axis.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




