
The temperature $ (T) $ dependence of resistivity $ (\rho ) $ of a semiconductor is represented by:
A)
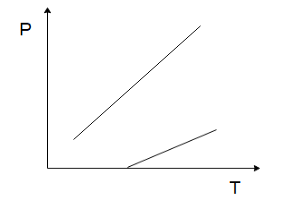
B)
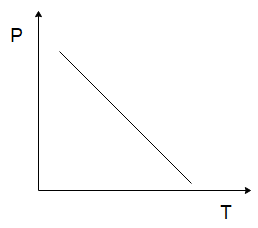
C)
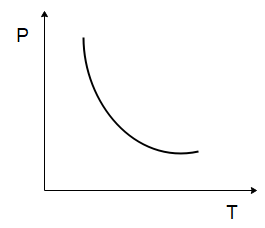
D)
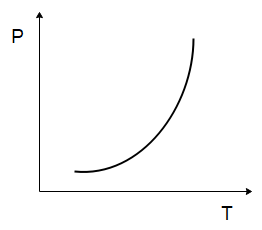




Answer
561k+ views
Hint: The resistivity of a substance is a quantitative measurement of the tendency of the substance to prevent current flowing from it. The resistivity of the substance is directly proportional to the resistance of the substance.
Complete answer:
The resistance of a substance is decided by the number of charge carriers in the substance and how they are affected by the change in temperature. The number of charge carriers in semiconductors is more than that of insulators but is less than that of conductors. This implies that for a given temperature, the resistivity of a semiconductor is less than that of insulators but higher than that of metals.
Now, when the temperature of the semiconductor is increased, the electrons start vibrating due to thermal energy. This leads to the generation of more free electrons and more holes. These carriers are generated by the thermal breaking of bonds inside the substance. Thus, as the temperature rises, a greater number of covalent bonds break in the substance, releasing more electrons which lower the resistivity rapidly as there are now more free charges available to carry the current. This temperature dependence is usually exponential which makes semiconductors very useful in electronic circuits detecting small temperature changes.
Hence the correct choice will be option (B).
Note:
To answer such questions, we must be aware of the current-carrying mechanism in a semiconductor and how it will be affected by thermal energy. The decreasing resistivity of semiconductors with increasing temperatures can also be thought of as it has a negative temperature coefficient of resistance.
Complete answer:
The resistance of a substance is decided by the number of charge carriers in the substance and how they are affected by the change in temperature. The number of charge carriers in semiconductors is more than that of insulators but is less than that of conductors. This implies that for a given temperature, the resistivity of a semiconductor is less than that of insulators but higher than that of metals.
Now, when the temperature of the semiconductor is increased, the electrons start vibrating due to thermal energy. This leads to the generation of more free electrons and more holes. These carriers are generated by the thermal breaking of bonds inside the substance. Thus, as the temperature rises, a greater number of covalent bonds break in the substance, releasing more electrons which lower the resistivity rapidly as there are now more free charges available to carry the current. This temperature dependence is usually exponential which makes semiconductors very useful in electronic circuits detecting small temperature changes.
Hence the correct choice will be option (B).
Note:
To answer such questions, we must be aware of the current-carrying mechanism in a semiconductor and how it will be affected by thermal energy. The decreasing resistivity of semiconductors with increasing temperatures can also be thought of as it has a negative temperature coefficient of resistance.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




