
The Ti plasmid is often used for making transgenic plants. This plasmid is found in:
A. Yeast as a 2 μm plasmid
B. Azotobacter
C. Rhizobium of the roots of leguminous plants
D. Agrobacterium
Answer
579.3k+ views
Hint: Ti plasmid is found in soil bacteria that induce tumour formation in plants. It is used to transfer a specific segment of DNA(T-DNA) in the host cell/genome.
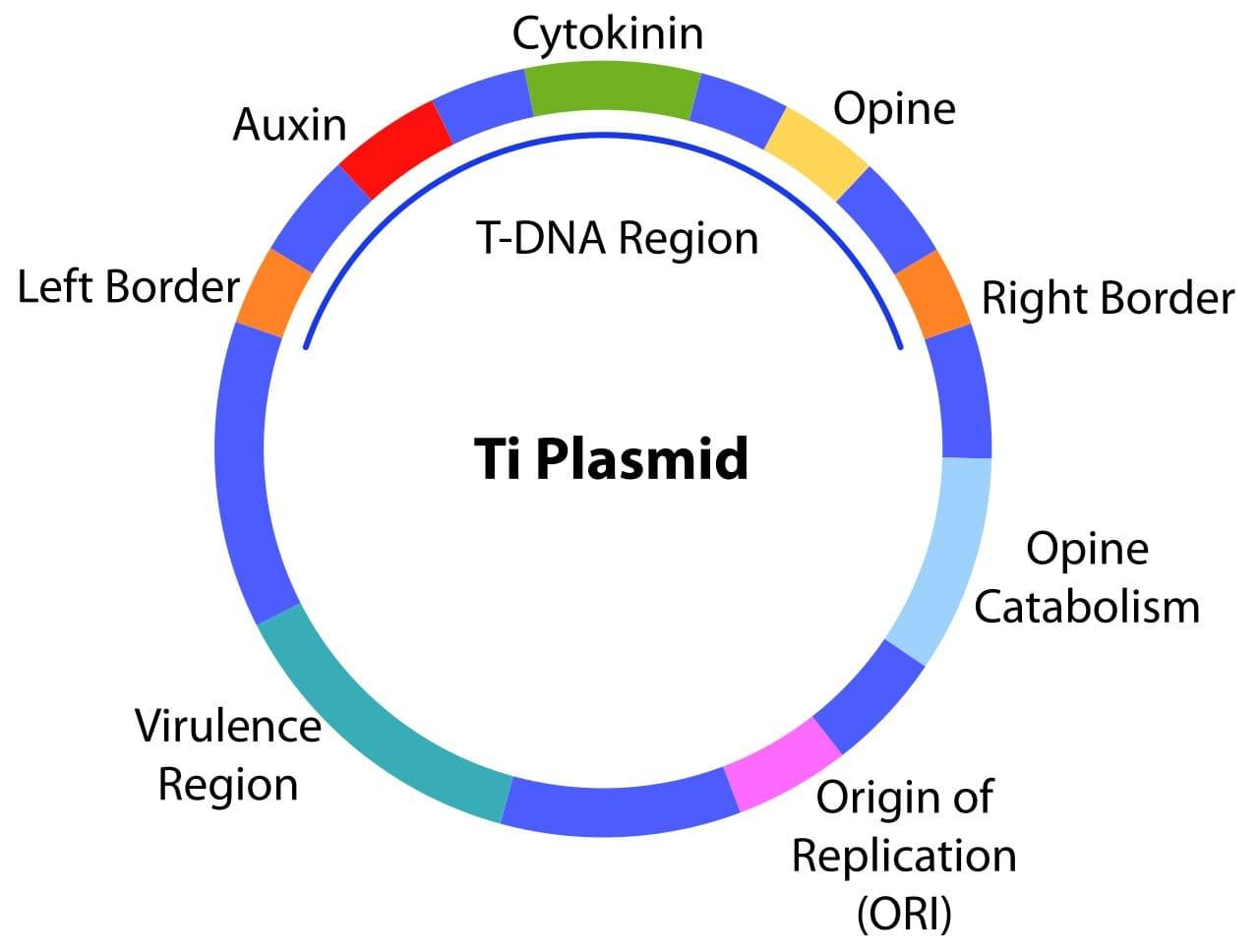
Step by step answer:Agrobacterium tumefaciens is a bacterium found in soil. It is pathogenic for plants and carries Ti plasmid. The Ti or tumor-inducing plasmid carries the genes that can induce tumor formation in plants. It is able to transfer a specific segment of the plasmid into the nucleus of infected cells. This segment is called T-DNA. The transferred T-DNA integrates into the host genome. As the transcription occurs in the host genome, T-DNA also gets transcribed. The ability of the bacterium Agrobacterium tumefaciens to transfer T-DNA in the host genome is made use of in genetic engineering. This principle is used to transfer the desired DNA segment, carrying the gene of the interest into the genome of the target organisms. Azotobacter is a genus of aerobic soil bacteria involved in the fixation of atmospheric nitrogen. They do not carry the Ti plasmid and hence cannot induce tumor formation in plants. From yeast, 4 types of plasmid vectors have been developed, viz. Yeast Episomal Plasmids (YEPs), Yeast Replicating Plasmids (YRPs), Yeast Centromere Plasmids (YCPs), and Yeast Artificial Chromosomes (YACs). These plasmids have unique restriction sites and can replicate within E. coli at high copy number but they do not carry Ti plasmid and cannot induce tumors in plant cells. In Rhizobium the roots of leguminous plants remain in a symbiotic relationship. They also fix atmospheric nitrogen.
So, the correct answer is D, i.e.,Agrobacterium
Note: The T-DNA segment contains right and left border sequences along with plant hormone coding genes, e.g. auxin, cytokinin, etc. These auxin and cytokinin are plant growth hormones that help the plant to promote its growth.
Step by step answer:Agrobacterium tumefaciens is a bacterium found in soil. It is pathogenic for plants and carries Ti plasmid. The Ti or tumor-inducing plasmid carries the genes that can induce tumor formation in plants. It is able to transfer a specific segment of the plasmid into the nucleus of infected cells. This segment is called T-DNA. The transferred T-DNA integrates into the host genome. As the transcription occurs in the host genome, T-DNA also gets transcribed. The ability of the bacterium Agrobacterium tumefaciens to transfer T-DNA in the host genome is made use of in genetic engineering. This principle is used to transfer the desired DNA segment, carrying the gene of the interest into the genome of the target organisms. Azotobacter is a genus of aerobic soil bacteria involved in the fixation of atmospheric nitrogen. They do not carry the Ti plasmid and hence cannot induce tumor formation in plants. From yeast, 4 types of plasmid vectors have been developed, viz. Yeast Episomal Plasmids (YEPs), Yeast Replicating Plasmids (YRPs), Yeast Centromere Plasmids (YCPs), and Yeast Artificial Chromosomes (YACs). These plasmids have unique restriction sites and can replicate within E. coli at high copy number but they do not carry Ti plasmid and cannot induce tumors in plant cells. In Rhizobium the roots of leguminous plants remain in a symbiotic relationship. They also fix atmospheric nitrogen.

So, the correct answer is D, i.e.,Agrobacterium
Note: The T-DNA segment contains right and left border sequences along with plant hormone coding genes, e.g. auxin, cytokinin, etc. These auxin and cytokinin are plant growth hormones that help the plant to promote its growth.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




