
The transcription unit extends from
(A) TATA box to start point
(B) TATA box to stop codon
(C) Start point to stop codon
(D) 35 sequence to start point
Answer
575.7k+ views
Hint: Transcription is a process in which the DNA of an organism is transcribed into RNA with the help of RNA polymerase. For a gene to be translated, this is the first step. A number of coding and non-coding genes are involved in the regulation of transcription.
Complete answer:
First, let us understand the process of transcription in detail. To begin transcription, the DNA unwinds near the gene of interest creating a transcription bubble. The following steps can be dividing into following stages:
Initiation: This step is where transcription is initiated by RNA polymerase by binding to the promoter region. This is the recognition site, which helps in identifying the correct gene. The transcription begins from the start codon.
Elongation: The RNA polymerase bound to the DNA strand starts adding complementary nucleotides to the template DNA strand in 3’ to 5’ direction.
Termination: The RNA will continue adding nucleotides until it reaches the stop codon. At the stop codon, transcription is terminated.
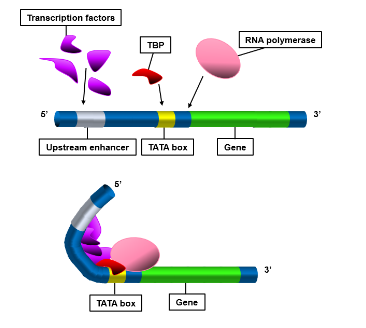
Now let us identify the transcription unit. From the picture above, we can observe the different components involved.To transcribe a gene of interest, a sequence of non-coding DNA is involved to regulate the process. The TATA box is a component in the core promoter sequence of eukaryotes, which functions for this purpose. As I mentioned earlier, the initiation starts at the promoter site and ends at the stop codon. So, the transcription site should contain a promoter, a gene of interest and stop codon.
Thus, the transcription unit extends from (B) TATA box to stop codon.
Note: If a gene encodes a protein, after transcription the mRNA (messenger RNA) produced will further be translated by ribosomes into proteins which is a process called translation. On the other hand, the gene transcribed might also be a non-coding RNA such as tRNA (transfer RNA), mRNA, microRNA or rRNA (ribosomal RNA).
Complete answer:
First, let us understand the process of transcription in detail. To begin transcription, the DNA unwinds near the gene of interest creating a transcription bubble. The following steps can be dividing into following stages:
Initiation: This step is where transcription is initiated by RNA polymerase by binding to the promoter region. This is the recognition site, which helps in identifying the correct gene. The transcription begins from the start codon.
Elongation: The RNA polymerase bound to the DNA strand starts adding complementary nucleotides to the template DNA strand in 3’ to 5’ direction.
Termination: The RNA will continue adding nucleotides until it reaches the stop codon. At the stop codon, transcription is terminated.

Now let us identify the transcription unit. From the picture above, we can observe the different components involved.To transcribe a gene of interest, a sequence of non-coding DNA is involved to regulate the process. The TATA box is a component in the core promoter sequence of eukaryotes, which functions for this purpose. As I mentioned earlier, the initiation starts at the promoter site and ends at the stop codon. So, the transcription site should contain a promoter, a gene of interest and stop codon.
Thus, the transcription unit extends from (B) TATA box to stop codon.
Note: If a gene encodes a protein, after transcription the mRNA (messenger RNA) produced will further be translated by ribosomes into proteins which is a process called translation. On the other hand, the gene transcribed might also be a non-coding RNA such as tRNA (transfer RNA), mRNA, microRNA or rRNA (ribosomal RNA).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




