
The transfer ratio $\beta $ of a transistor is 50. The input resistance of the transistor used in the common emitter configuration is $2K\Omega $. The peak value of the collector A.C current for an A.C input voltage of 0.02V is,
A.)$200\mu A$
B.)$0.01mA$
C.)$0.25mA$
D.)$500\mu A$
Answer
596.1k+ views
Hint: The current transfer ratio of a common-emitter ratio is the ratio of the collector current to the base current. We can find the base current by dividing the peak value input voltage by the input resistance. From the current transfer ratio, we can find the value of the peak collector current in the circuit.
Equation Used:
The current transfer ratio ($\beta $) in a common emitter configuration is usually expressed as,
$\beta =\dfrac{{{I}_{c}}}{{{I}_{b}}}$
Where
${{I}_{c}}$ is the peak collector current.
${{I}_{b}}$ is the peak base current.
The base current of the circuit can be found out by,
${{I}_{b}}=\dfrac{{{V}_{i}}}{{{R}_{i}}}$
Complete step by step answer:
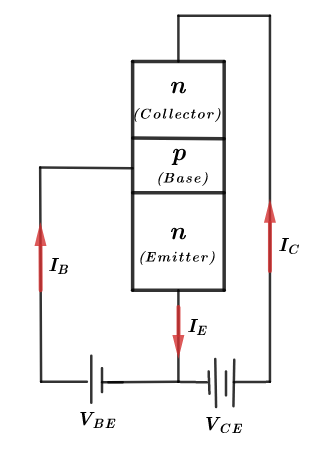
So, in our question, it is given that the current transfer ratio in the common-emitter configuration is 50. The current transfer ratio ($\beta $) in a common emitter configuration is usually expressed as,
$\beta =\dfrac{{{I}_{c}}}{{{I}_{b}}}$
Where
${{I}_{c}}$ is the peak collector current.
${{I}_{b}}$ is the peak base current.
The input resistance in the given configuration is $2K\Omega $ , and the input voltage is 0.02V. So the base current of the circuit can be found out by,
${{I}_{b}}=\dfrac{{{V}_{i}}}{{{R}_{i}}}$
$\Rightarrow {{I}_{b}}=\dfrac{0.02V}{2K\Omega }$
$\therefore {{I}_{b}}=0.01mA$
We now have calculated the base current. So, the peak collector current can be calculated from the current ratio,
$\begin{align}
& \beta =\dfrac{{{I}_{c}}}{{{I}_{b}}} \\
& \Rightarrow 50=\dfrac{{{I}_{c}}}{0.01mA} \\
\end{align}$
$\therefore {{I}_{c}}=0.5mA$
So, the peak collector current of the common-emitter configuration is $500\mu A$.
So, the answer to the question is option (D).
Note:
A transistor is an electronic device that has three terminals and is usually used to amplify or switch electronic signals. It is a semiconductor device, in which both n-type and p-type materials are present. The three terminals are the emitter, base and the collector terminals.
The transistor is made up of a combination of 3 regions. The emitter region which is the most doped region out of the three regions. Then comes the base region, which slightly doped and very narrow in size. Finally, there is the collector region which is moderately doped when compared to the emitter and much larger than the base region.
The transistor can have various combinations of configurations. It can have a common base configuration in which the base is the common terminal for input and output or a common emitter configuration in which the emitter is the common terminal or the common collector configuration.
Equation Used:
The current transfer ratio ($\beta $) in a common emitter configuration is usually expressed as,
$\beta =\dfrac{{{I}_{c}}}{{{I}_{b}}}$
Where
${{I}_{c}}$ is the peak collector current.
${{I}_{b}}$ is the peak base current.
The base current of the circuit can be found out by,
${{I}_{b}}=\dfrac{{{V}_{i}}}{{{R}_{i}}}$
Complete step by step answer:

So, in our question, it is given that the current transfer ratio in the common-emitter configuration is 50. The current transfer ratio ($\beta $) in a common emitter configuration is usually expressed as,
$\beta =\dfrac{{{I}_{c}}}{{{I}_{b}}}$
Where
${{I}_{c}}$ is the peak collector current.
${{I}_{b}}$ is the peak base current.
The input resistance in the given configuration is $2K\Omega $ , and the input voltage is 0.02V. So the base current of the circuit can be found out by,
${{I}_{b}}=\dfrac{{{V}_{i}}}{{{R}_{i}}}$
$\Rightarrow {{I}_{b}}=\dfrac{0.02V}{2K\Omega }$
$\therefore {{I}_{b}}=0.01mA$
We now have calculated the base current. So, the peak collector current can be calculated from the current ratio,
$\begin{align}
& \beta =\dfrac{{{I}_{c}}}{{{I}_{b}}} \\
& \Rightarrow 50=\dfrac{{{I}_{c}}}{0.01mA} \\
\end{align}$
$\therefore {{I}_{c}}=0.5mA$
So, the peak collector current of the common-emitter configuration is $500\mu A$.
So, the answer to the question is option (D).
Note:
A transistor is an electronic device that has three terminals and is usually used to amplify or switch electronic signals. It is a semiconductor device, in which both n-type and p-type materials are present. The three terminals are the emitter, base and the collector terminals.
The transistor is made up of a combination of 3 regions. The emitter region which is the most doped region out of the three regions. Then comes the base region, which slightly doped and very narrow in size. Finally, there is the collector region which is moderately doped when compared to the emitter and much larger than the base region.
The transistor can have various combinations of configurations. It can have a common base configuration in which the base is the common terminal for input and output or a common emitter configuration in which the emitter is the common terminal or the common collector configuration.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

RNA and DNA are chiral molecules their chirality is class 12 chemistry CBSE




