
The treatment of alcohol of alkyl chlorides with aqueous $KOH$ leads to the formation of alcohols but in the presence of alcoholic $KOH$, alkenes are major products. Explain.
Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint: When alkyl chlorides are treated with aqueous $KOH$ the $KOH$ releases its. $\mathop {OH}\nolimits^ - $ ion only. This ion acts as a strong nucleophile. Due to this causes hydrolysis of alkyl chloride to their corresponding alcohols . Substitution reaction takes place.
\[\mathop {RCL}\nolimits_{} + \mathop {\mathop {OH}\nolimits^ - }\nolimits^{} \xrightarrow{{hydrolysis}}\mathop {ROH}\nolimits_{} + \mathop {Cl}\nolimits^ - \]
Complete step by step answer: Now when $KOH$ is alcoholic is doesn’t have $\mathop {OH}\nolimits^ - $ion rather it has ethoxide ion\[\mathop C\nolimits_2 \mathop H\nolimits_5 \mathop O\nolimits^ - \]. This ion is more basic than hydroxide ions. The ethoxide ion causes dehydrohalogenation to form alkenes. The ethoxide ion abstracts the beta hydrogen from alkyl chloride. Now a molecule of $KCl$ gets eliminated and alkene is formed. This reaction is an elimination reaction.
When alkyl chloride reacts with aqueous $KOH$
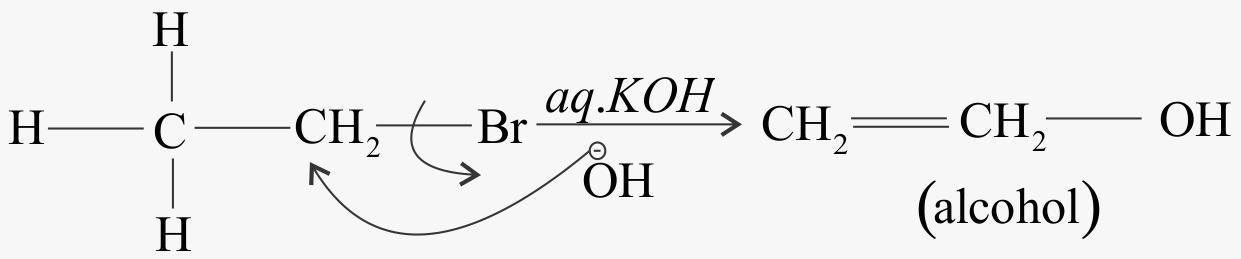
When alkyl chloride reacts with alcoholic $KOH$
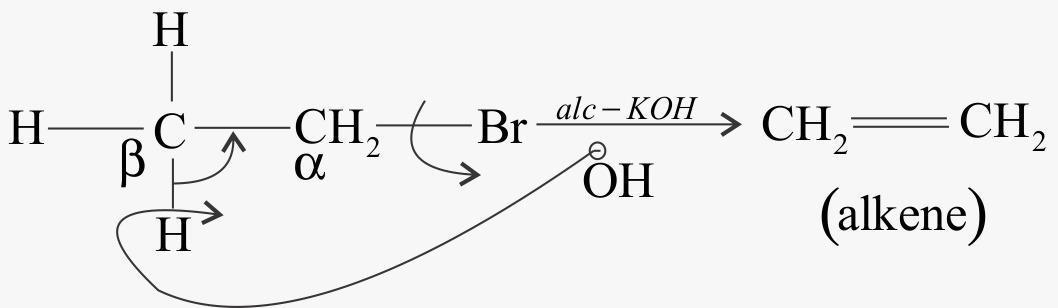
The type of elimination is beta elimination.
$\mathop {CH}\nolimits_3 - \mathop {CHCl}\nolimits_{} - \mathop {CH}\nolimits_3 + \mathop {KOH}\nolimits_{} \to \mathop {CH}\nolimits_3 - \mathop {CH}\nolimits_{} \doteq \mathop {CH}\nolimits_2 + \mathop {KCl}\nolimits_{} + \mathop H\nolimits_2 \mathop O\nolimits_{} $
It is a single step bimolecular elimination reaction
Note: Haloalkanes having two or more types of beta hydrogen atoms on dehydrohalogenation gives more than one alkene. Major product is decided by Saytzeff’s rule which states that haloalkanes on heating with alcoholic $KOH$ give more substituted alkene as a major product.
When a bulky base like propoxide ion is used then less substituted alkene is the major product because bulky groups find it easier to remove protons from less sterically hindered beta carbon atoms.
\[\mathop {RCL}\nolimits_{} + \mathop {\mathop {OH}\nolimits^ - }\nolimits^{} \xrightarrow{{hydrolysis}}\mathop {ROH}\nolimits_{} + \mathop {Cl}\nolimits^ - \]
Complete step by step answer: Now when $KOH$ is alcoholic is doesn’t have $\mathop {OH}\nolimits^ - $ion rather it has ethoxide ion\[\mathop C\nolimits_2 \mathop H\nolimits_5 \mathop O\nolimits^ - \]. This ion is more basic than hydroxide ions. The ethoxide ion causes dehydrohalogenation to form alkenes. The ethoxide ion abstracts the beta hydrogen from alkyl chloride. Now a molecule of $KCl$ gets eliminated and alkene is formed. This reaction is an elimination reaction.
When alkyl chloride reacts with aqueous $KOH$

When alkyl chloride reacts with alcoholic $KOH$

The type of elimination is beta elimination.
$\mathop {CH}\nolimits_3 - \mathop {CHCl}\nolimits_{} - \mathop {CH}\nolimits_3 + \mathop {KOH}\nolimits_{} \to \mathop {CH}\nolimits_3 - \mathop {CH}\nolimits_{} \doteq \mathop {CH}\nolimits_2 + \mathop {KCl}\nolimits_{} + \mathop H\nolimits_2 \mathop O\nolimits_{} $
It is a single step bimolecular elimination reaction
Note: Haloalkanes having two or more types of beta hydrogen atoms on dehydrohalogenation gives more than one alkene. Major product is decided by Saytzeff’s rule which states that haloalkanes on heating with alcoholic $KOH$ give more substituted alkene as a major product.
When a bulky base like propoxide ion is used then less substituted alkene is the major product because bulky groups find it easier to remove protons from less sterically hindered beta carbon atoms.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




