
The tRNA anticodon 3-UAC-5 will pair with the mRNA codon
A) 5-AUU-3
B) 5-UAC-3
C) 5-AUG-3
D) 3-GUA-5
Answer
589.8k+ views
Hint: Just like all other intermolecular interactions between nucleic acids, the anticodon-codon interactions also follow Chargaff’s base-pairing rules. According to this rule, A always pairs with T (U in RNA) and G always pairs with C and vice-versa.
Complete Answer:
Transfer RNA (tRNA) is an adaptor molecule that reads the information encoded in the mRNA and transfers the appropriate amino acid to a growing polypeptide chain during protein synthesis. The tRNA consists of a single strand of RNA folded into a three dimensional structure.
The hydrogen-bonding pattern of tRNA forms a cloverleaf structure with four arms
1. The acceptor arm or amino acid arm that carries a specific amino acid residue at the 3’ end of the tRNA
2. The TΨC arm which contains ribothymidine (T), pseudouridine (Ψ) and cytidine (C) which has an unusual carbon–carbon bond between the base and ribose
3. The anticodon arm which contains the anticodon. Anticodon is a nucleotide triplet that interacts with a particular codon in mRNA through hydrogen bonding of complementary bases.
4. The D arm, which contains dihydrouridine (D), a nucleotide which is not usually present in RNAs.
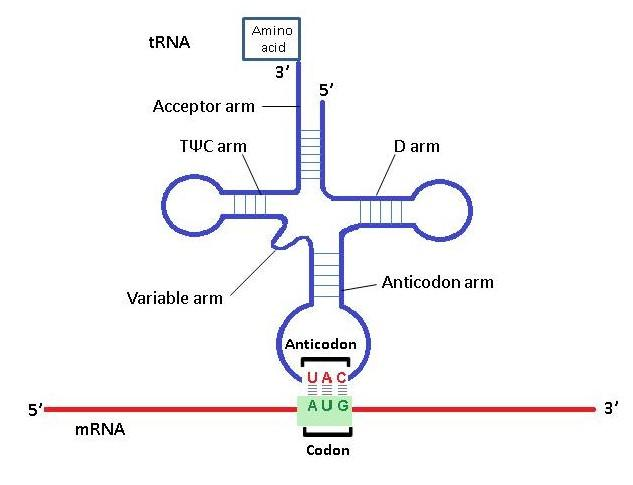
Fig: Clover leaf model of tRNA
- Only a specific tRNA molecule contains the suitable anticodon for a particular codon in the mRNA, and each tRNA molecule can be activated with only one specific amino acid. Therefore, each codon specifies only one amino acid.
- In every cell, there is at least one species of tRNA corresponding to each of the 20 amino acids required for protein synthesis.
- For a particular amino acid, the codon of the mRNA and the anticodon of tRNA molecules are complementary to each other and the alignment of the two RNAs is antiparallel, i.e., the tRNA anticodon (in 3’-5’ direction) base-pairs with mRNA codon (in 5’-3’ direction) specifically via base-pairing rules.
- According to Chargaff’s base-pairing rules and antiparallel alignment of anticodon and codon, we can say that the tRNA anticodon 3’-UAC-5’ will pair with the mRNA codon 5’-AUG-3’. This codon AUG is the initiation codon and it codes for formyl-Methionine.
Thus, the correct answer is C i.e., 5’-AUG-3’.
Note: Clover leaf model of tRNA was given by Robert Holley. According to this model, apart from the four arms discussed above there is an extra arm which is very short and known as variable arm. The function of this arm is to recognize the specific enzyme required for the activation of the tRNA.
Complete Answer:
Transfer RNA (tRNA) is an adaptor molecule that reads the information encoded in the mRNA and transfers the appropriate amino acid to a growing polypeptide chain during protein synthesis. The tRNA consists of a single strand of RNA folded into a three dimensional structure.
The hydrogen-bonding pattern of tRNA forms a cloverleaf structure with four arms
1. The acceptor arm or amino acid arm that carries a specific amino acid residue at the 3’ end of the tRNA
2. The TΨC arm which contains ribothymidine (T), pseudouridine (Ψ) and cytidine (C) which has an unusual carbon–carbon bond between the base and ribose
3. The anticodon arm which contains the anticodon. Anticodon is a nucleotide triplet that interacts with a particular codon in mRNA through hydrogen bonding of complementary bases.
4. The D arm, which contains dihydrouridine (D), a nucleotide which is not usually present in RNAs.

Fig: Clover leaf model of tRNA
- Only a specific tRNA molecule contains the suitable anticodon for a particular codon in the mRNA, and each tRNA molecule can be activated with only one specific amino acid. Therefore, each codon specifies only one amino acid.
- In every cell, there is at least one species of tRNA corresponding to each of the 20 amino acids required for protein synthesis.
- For a particular amino acid, the codon of the mRNA and the anticodon of tRNA molecules are complementary to each other and the alignment of the two RNAs is antiparallel, i.e., the tRNA anticodon (in 3’-5’ direction) base-pairs with mRNA codon (in 5’-3’ direction) specifically via base-pairing rules.
- According to Chargaff’s base-pairing rules and antiparallel alignment of anticodon and codon, we can say that the tRNA anticodon 3’-UAC-5’ will pair with the mRNA codon 5’-AUG-3’. This codon AUG is the initiation codon and it codes for formyl-Methionine.
Thus, the correct answer is C i.e., 5’-AUG-3’.
Note: Clover leaf model of tRNA was given by Robert Holley. According to this model, apart from the four arms discussed above there is an extra arm which is very short and known as variable arm. The function of this arm is to recognize the specific enzyme required for the activation of the tRNA.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




