
The two strands of DNA molecules are antiparallel. What do you understand by antiparallel?
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: DNA molecules have two strands and these two strands usually run side by side but in the opposite direction. For example, when we arrange a palindrome next to each other it looks antiparallel. Example: Madam and madaM.
Complete step by step answer:
The two DNA strands run parallel to each other but in opposite directions. One strand's 5' end faces the other strand's 3' end. The path in one chain is 5 'to 3', whereas it is 3' to 5' in the opposite one.
A DNA molecule's antiparallel strands mean that at the beginning of two DNA strands, the phosphate groups are in opposite positions (pole). DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) consists of two chains of polynucleotides (nucleotide polymers), forming what looks like a ladder.
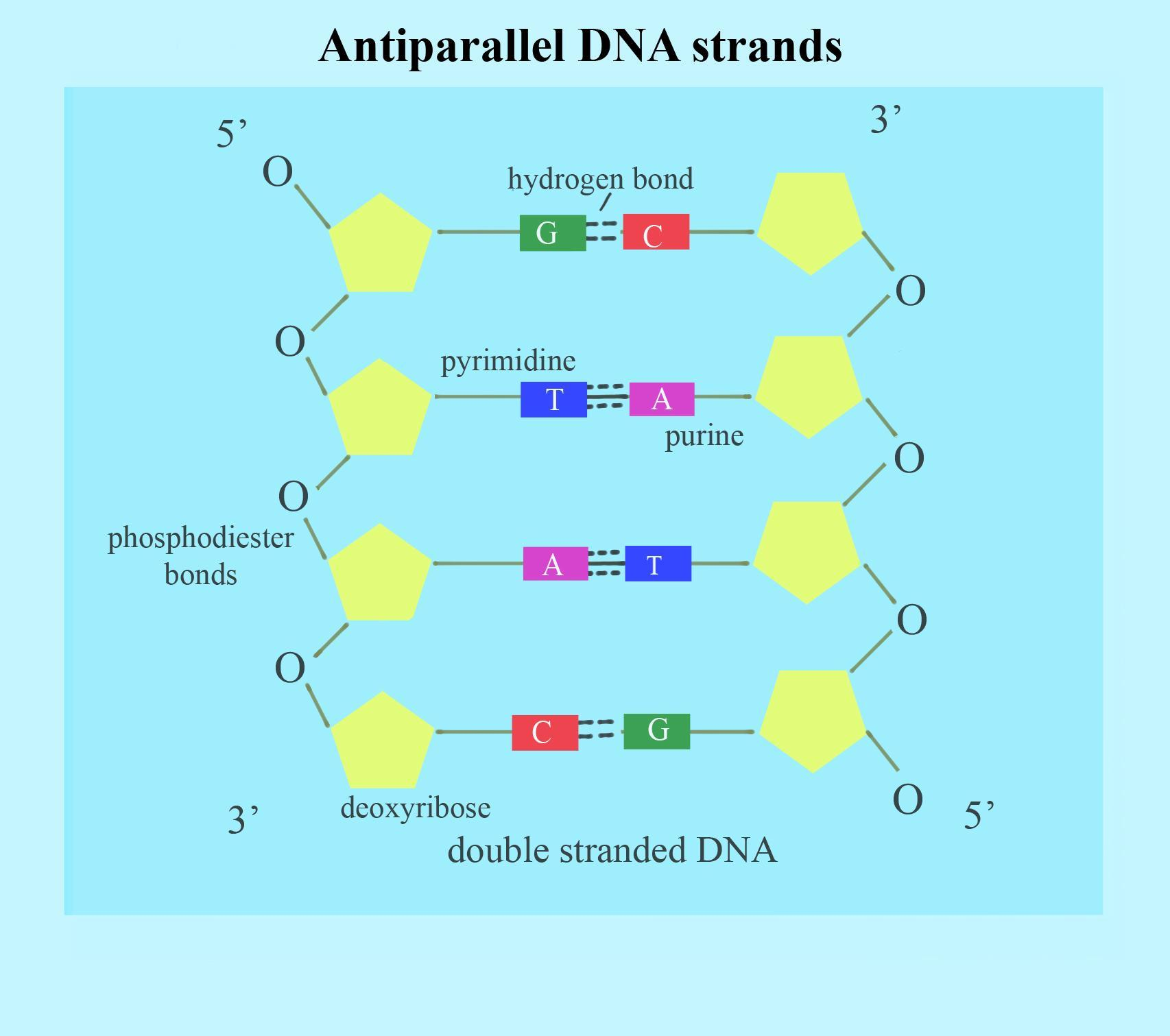
With nitrogenous bases projecting inwards, the two polynucleotide strands run 'antiparallel' to each other. The word 'antiparallel' suggests that, parallel to each other, the strands travel in opposite directions. In a complete DNA structure, the antiparallel strands curl, creating a double helix. It has a linkage of 3' to 5' and 5' to 3'. The 5' and 3' signify "five prime" and "three prime," which show the sugar backbone of the DNA's carbon numbers. A phosphate group is bound to the 5' carbon and the 3' carbon is a hydroxyl (OH) group. This asymmetry gives a "path" to a DNA strand.
Note: The antiparallel orientation enables one another to be complemented by the base pairs. Antiparallel DNA is also more stable than parallel DNA in terms of structure. DNA's antiparallel orientation has major consequences for DNA replication, as one strand allows steady replication at the replication fork, known as the leading strand, while the other becomes the lagging strand.
Complete step by step answer:
The two DNA strands run parallel to each other but in opposite directions. One strand's 5' end faces the other strand's 3' end. The path in one chain is 5 'to 3', whereas it is 3' to 5' in the opposite one.
A DNA molecule's antiparallel strands mean that at the beginning of two DNA strands, the phosphate groups are in opposite positions (pole). DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) consists of two chains of polynucleotides (nucleotide polymers), forming what looks like a ladder.

With nitrogenous bases projecting inwards, the two polynucleotide strands run 'antiparallel' to each other. The word 'antiparallel' suggests that, parallel to each other, the strands travel in opposite directions. In a complete DNA structure, the antiparallel strands curl, creating a double helix. It has a linkage of 3' to 5' and 5' to 3'. The 5' and 3' signify "five prime" and "three prime," which show the sugar backbone of the DNA's carbon numbers. A phosphate group is bound to the 5' carbon and the 3' carbon is a hydroxyl (OH) group. This asymmetry gives a "path" to a DNA strand.
Note: The antiparallel orientation enables one another to be complemented by the base pairs. Antiparallel DNA is also more stable than parallel DNA in terms of structure. DNA's antiparallel orientation has major consequences for DNA replication, as one strand allows steady replication at the replication fork, known as the leading strand, while the other becomes the lagging strand.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




