
The UV graph for a convex lens is a :
A. Straight line passing through the origin
B. Straight line having a y-intercept
C. Parabola
D. Hyperbola
Answer
564.6k+ views
Hint: As a first step, you could discuss the image formation of the convex lens for the object kept at different points on the principle axis of the lens. Thus you could make a plot showing the variation of the image distance with changing object distance. The plot thus formed will give you the answer.
Complete Step by step solution:
In the question, we are asked to find what shape the graph will have if we were to plot object distance U with the image distance V for a convex lens. In order to find the answer to this question, let us first discuss a bit about the image formation by a convex lens.
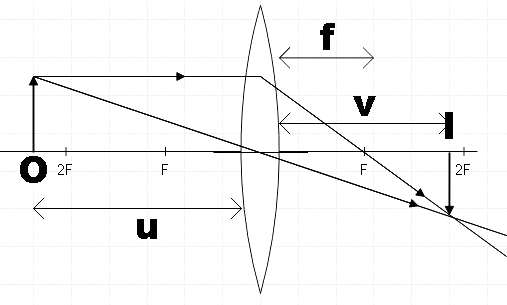
In the above figure we have formed an image of the object kept beyond 2F that is the centre of curvature. And the image found to be formed between F and 2F. By convention, the measurements are taken from the optic axis and the measurements taken to the left of optic axis is taken negative and measurements taken to the right of optic axis is taken positive. So clearly we see that the object distance u is negative and image distance and the focal length of the convex lens is positive.
We know that, when an object is placed at focal point, the image is formed at infinity and image of the object at infinity is formed at focal point. That is,
$u=-f\Rightarrow v=\infty $
$u=-\infty \Rightarrow v=f$
And for the object that is placed at the centre of curvature (-2F), the image will be formed at 2F with the same size but inverted.
Now, using all these points, if we were to plot a graph, we will get,
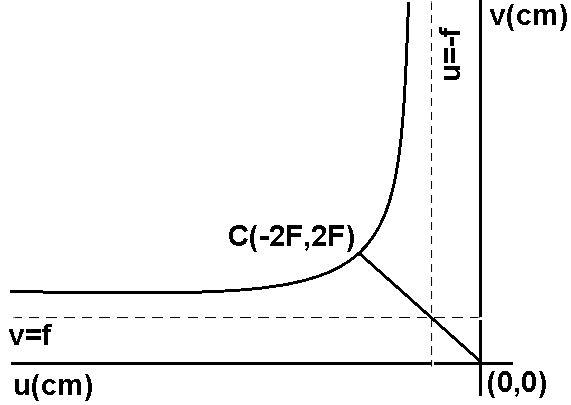
Thus, we have got the UV graph to be a hyperbola with asymptotes u=-f and v=f. We have discussed the reason for this above. Also, the point of intersection of the curve and the straight line shows the point where U and V have the same magnitudes but different signs.
Therefore, we found that the UV graph for a convex lens is a hyperbola.
Hence, option D is found to be the correct answer.
Note:
Convex lens is one among the spherical lenses formed by bonding two spherical transparent surfaces together. Convex lenses are called converging lenses as they converge the rays falling on it. In order to solve farsightedness or hypermetropia, convex lenses are used.
Complete Step by step solution:
In the question, we are asked to find what shape the graph will have if we were to plot object distance U with the image distance V for a convex lens. In order to find the answer to this question, let us first discuss a bit about the image formation by a convex lens.

In the above figure we have formed an image of the object kept beyond 2F that is the centre of curvature. And the image found to be formed between F and 2F. By convention, the measurements are taken from the optic axis and the measurements taken to the left of optic axis is taken negative and measurements taken to the right of optic axis is taken positive. So clearly we see that the object distance u is negative and image distance and the focal length of the convex lens is positive.
We know that, when an object is placed at focal point, the image is formed at infinity and image of the object at infinity is formed at focal point. That is,
$u=-f\Rightarrow v=\infty $
$u=-\infty \Rightarrow v=f$
And for the object that is placed at the centre of curvature (-2F), the image will be formed at 2F with the same size but inverted.
Now, using all these points, if we were to plot a graph, we will get,

Thus, we have got the UV graph to be a hyperbola with asymptotes u=-f and v=f. We have discussed the reason for this above. Also, the point of intersection of the curve and the straight line shows the point where U and V have the same magnitudes but different signs.
Therefore, we found that the UV graph for a convex lens is a hyperbola.
Hence, option D is found to be the correct answer.
Note:
Convex lens is one among the spherical lenses formed by bonding two spherical transparent surfaces together. Convex lenses are called converging lenses as they converge the rays falling on it. In order to solve farsightedness or hypermetropia, convex lenses are used.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




