
The variation of gravitational intensity (${E_G}$) due to earth with distance r from the centre of the earth is shown by the curve.
A.
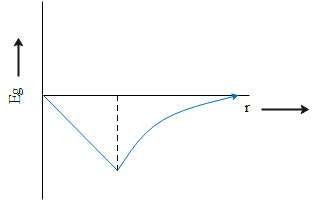
B.
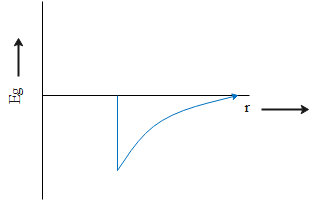
C.
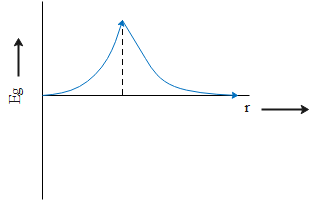
D.
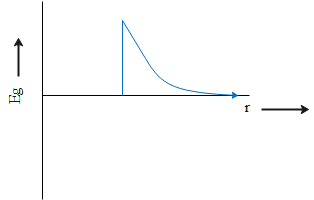



Answer
558.6k+ views
Hint: The gravitational intensity is equivalent to acceleration due to gravity. The variation of gravitational intensity can be studied by studying the equations relating it with the distance from the surface of earth. The value of acceleration due to gravity is maximum on the surface of earth.
Complete step by step solution:
The gravitational intensity of the earth can be defined as the gravitational force exerted by earth per unit mass of the object. Dimensionally, the force per unit mass is equal to the acceleration so we can say that we are talking about the acceleration due to gravity when we refer to the gravitational intensity of earth.
The variation of acceleration due to gravity with distance from the surface of earth is given as:
$g' = g\left( {1 - \dfrac{h}{R}} \right)$
Here g is the value of acceleration due to gravity on the surface of earth while g’ is the acceleration due to gravity at a distance h from the surface of earth. R represents the radius of earth.
The value of gravitational intensity is maximum at the surface of earth where h = 0.
As we go towards the centre of earth, the distance from surface of earth increases and at the centre of earth value of h is equal to the radius of earth and we get the value of acceleration due to gravity at the centre of earth to be
$g' = g\left( {1 - \dfrac{R}{R}} \right) = 0$
Similarly, as we go higher above the surface of earth, the value of acceleration due to gravity decreases with increase in height above the surface of earth.
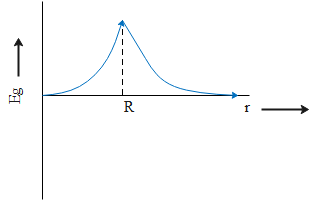
Therefore, based on this discussion, the correct trend in gravitational intensity is option C.
Note:
1. The value of acceleration due to gravity is equal to $9.8m/{s^2}$ only near the surface of earth or at small distances from the surface of earth. With increase in distance from the surface of earth, the value of acceleration due to gravity goes on decreasing.
2. The value of acceleration due to gravity is never negative which means it never causes deceleration due to which first two options can be considered wrong immediately.
Complete step by step solution:
The gravitational intensity of the earth can be defined as the gravitational force exerted by earth per unit mass of the object. Dimensionally, the force per unit mass is equal to the acceleration so we can say that we are talking about the acceleration due to gravity when we refer to the gravitational intensity of earth.
The variation of acceleration due to gravity with distance from the surface of earth is given as:
$g' = g\left( {1 - \dfrac{h}{R}} \right)$
Here g is the value of acceleration due to gravity on the surface of earth while g’ is the acceleration due to gravity at a distance h from the surface of earth. R represents the radius of earth.
The value of gravitational intensity is maximum at the surface of earth where h = 0.
As we go towards the centre of earth, the distance from surface of earth increases and at the centre of earth value of h is equal to the radius of earth and we get the value of acceleration due to gravity at the centre of earth to be
$g' = g\left( {1 - \dfrac{R}{R}} \right) = 0$
Similarly, as we go higher above the surface of earth, the value of acceleration due to gravity decreases with increase in height above the surface of earth.

Therefore, based on this discussion, the correct trend in gravitational intensity is option C.
Note:
1. The value of acceleration due to gravity is equal to $9.8m/{s^2}$ only near the surface of earth or at small distances from the surface of earth. With increase in distance from the surface of earth, the value of acceleration due to gravity goes on decreasing.
2. The value of acceleration due to gravity is never negative which means it never causes deceleration due to which first two options can be considered wrong immediately.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




