
The velocity of efflux of a liquid through an orifice in the bottom of the tank does not depend upon:
A. Size of orifice.
B. Height of liquid
C. Acceleration due to gravity
D. Density of liquid
Answer
591.6k+ views
Hint: The velocity of efflux is explained by two theorems. Torricelli’s theorem and Bernoulli’s theorem. Torricelli's theorem tells that speed of efflux v of a fluid through a well-defined orifice at the bottom of a tank filled to a depth h is exactly as same as that of velocity of a body which is acquired when falling freely from a height h.
Formula used:
${{p}_{0}}+\dfrac{1}{2}{{\rho }_{b}}{{v}^{2}}={{p}_{0}}+{{\rho }_{l}}gh$
Complete answer:
First of all we should know about the velocity of efflux .It is explained by two theorems. Torricelli’s theorem and Bernoulli’s theorem. Torricelli's theorem tells that speed of efflux v of a fluid through a well-defined orifice at the bottom of a tank filled to a depth h is exactly the same as that of velocity of a body which is acquired when falling freely from a height h. According to Bernoulli’s theorem, it is given that,
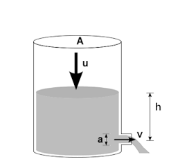
In which ${{\rho }_{b}}$ is the density of liquid at the bottom, v is the velocity of efflux, ${{p}_{0}}$ is the pressure, ${{\rho }_{l}}$ is the density of liquid, g is the acceleration due to gravity and h is the height of the liquid column. The density of the fluid is actually varying with height h. In certain times velocity of efflux depends on the density of the liquid also. And the velocity of efflux independent of the size of orifice.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
Bernoulli's equation is having great importance in solving this question. The formula used is
${{p}_{0}}+\dfrac{1}{2}{{\rho }_{b}}{{v}^{2}}={{p}_{0}}+{{\rho }_{l}}gh$
This has to be remembered well. The easiest form of Bernoulli's equation states that the sum of mechanical energy, potential energy and kinetic energy, along a streamline, is constant.
Formula used:
${{p}_{0}}+\dfrac{1}{2}{{\rho }_{b}}{{v}^{2}}={{p}_{0}}+{{\rho }_{l}}gh$
Complete answer:
First of all we should know about the velocity of efflux .It is explained by two theorems. Torricelli’s theorem and Bernoulli’s theorem. Torricelli's theorem tells that speed of efflux v of a fluid through a well-defined orifice at the bottom of a tank filled to a depth h is exactly the same as that of velocity of a body which is acquired when falling freely from a height h. According to Bernoulli’s theorem, it is given that,

In which ${{\rho }_{b}}$ is the density of liquid at the bottom, v is the velocity of efflux, ${{p}_{0}}$ is the pressure, ${{\rho }_{l}}$ is the density of liquid, g is the acceleration due to gravity and h is the height of the liquid column. The density of the fluid is actually varying with height h. In certain times velocity of efflux depends on the density of the liquid also. And the velocity of efflux independent of the size of orifice.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
Bernoulli's equation is having great importance in solving this question. The formula used is
${{p}_{0}}+\dfrac{1}{2}{{\rho }_{b}}{{v}^{2}}={{p}_{0}}+{{\rho }_{l}}gh$
This has to be remembered well. The easiest form of Bernoulli's equation states that the sum of mechanical energy, potential energy and kinetic energy, along a streamline, is constant.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




