
The working cycle in case of a four stroke engine is completed in the following number of revolutions of the crankshaft.
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
Answer
558k+ views
Hint: A four-stroke engine is an internally combustible engine that uses four separate cylinder (piston) strokes (intake-stroke, compression-stroke, power-stroke, and exhaust-stroke ) to finish one working cycle. The piston make two complete passes in the cylinder to finish one working cycle
Complete step-by-step solution:
A four-stroke engine also known as a four-cycle engine is an internal combustion (IC) engine. In this type of engine the piston completes four separate strokes while turning the crankshaft. A stroke means that the full travel of the piston along the cylinder, in either direction.
A working cycle requires two revolutions \[\left( 720{}^\circ \right)\]of the crank-shaft. The four-stroke cycle engine is the most well-known kind of small motor. A four-stroke cycle motor finishes four-Strokes in one working cycle including intake-stroke, compression-stroke, ignition-stroke, power-stroke, and exhaust-stroke.
So in a four-stroke engine the working cycle comprises the \[720{}^\circ \]revolution of crank-shaft. One complete revolution is \[360{}^\circ \], so \[720{}^\circ \]is two complete revolutions of crank-shafts.
So the correct option is B.
Additional Information:
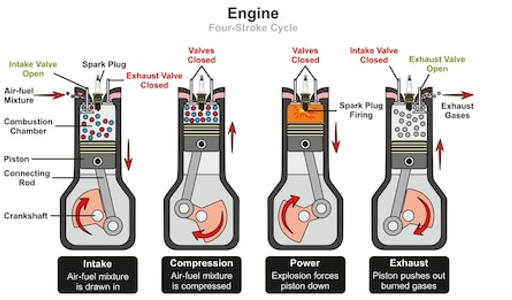
A four-stroke cycle motor finishes four Strokes in one working cycle. These are,
(i)Intake-stroke: It is also known as induction or suction stroke. In this process the stroke of the piston starts at the top dead centre(T.D.C) and terminates at bottom dead centre(B.D.C). In intake-stroke the intake valve must be opened when the piston pulls an air-fuel mixture into the cylinder by producing vacuum pressure into the cylinder through its downward motion. As the piston moves down the air is being sucked in by the downward motion against the piston.
(ii) compression-stroke: It starts at the end of intake stroke. In this process the piston compresses the air-fuel mixture in preparation for ignition during the power stroke. Both the intake valve and exhaust valve are closed during the compression-stroke stage.
(iv)power-stroke: this process is the start of the second revolution of the four stroke engine cycle. At the beginning of this stroke the crankshaft has completed a full 360 degree revolution. While the piston is at T.D.C. (the end of the compression stroke) the compressed air-fuel mixture is ignited by a spark plug (in a gasoline engine) forcefully returning the piston to B.D.C. This stroke produces mechanical work from the engine to turn the crankshaft.
(iv)Exhaust-stroke: Also known as output-stroke. During this process the piston once again returns from B.D.C. to T.D.C. while the exhaust valve is open. Exhaust-stroke action expels the spent air-fuel mixture through the exhaust valve.
Note: Four-stroke engines have several benefits over two stroke engines. They have better fuel efficiency, durability, gives more power and hence more torque and more cleaner emissions. But these are more expensive and complicated to make and they need valves for intake and exhaust of gases.
Complete step-by-step solution:
A four-stroke engine also known as a four-cycle engine is an internal combustion (IC) engine. In this type of engine the piston completes four separate strokes while turning the crankshaft. A stroke means that the full travel of the piston along the cylinder, in either direction.
A working cycle requires two revolutions \[\left( 720{}^\circ \right)\]of the crank-shaft. The four-stroke cycle engine is the most well-known kind of small motor. A four-stroke cycle motor finishes four-Strokes in one working cycle including intake-stroke, compression-stroke, ignition-stroke, power-stroke, and exhaust-stroke.
So in a four-stroke engine the working cycle comprises the \[720{}^\circ \]revolution of crank-shaft. One complete revolution is \[360{}^\circ \], so \[720{}^\circ \]is two complete revolutions of crank-shafts.
So the correct option is B.
Additional Information:

A four-stroke cycle motor finishes four Strokes in one working cycle. These are,
(i)Intake-stroke: It is also known as induction or suction stroke. In this process the stroke of the piston starts at the top dead centre(T.D.C) and terminates at bottom dead centre(B.D.C). In intake-stroke the intake valve must be opened when the piston pulls an air-fuel mixture into the cylinder by producing vacuum pressure into the cylinder through its downward motion. As the piston moves down the air is being sucked in by the downward motion against the piston.
(ii) compression-stroke: It starts at the end of intake stroke. In this process the piston compresses the air-fuel mixture in preparation for ignition during the power stroke. Both the intake valve and exhaust valve are closed during the compression-stroke stage.
(iv)power-stroke: this process is the start of the second revolution of the four stroke engine cycle. At the beginning of this stroke the crankshaft has completed a full 360 degree revolution. While the piston is at T.D.C. (the end of the compression stroke) the compressed air-fuel mixture is ignited by a spark plug (in a gasoline engine) forcefully returning the piston to B.D.C. This stroke produces mechanical work from the engine to turn the crankshaft.
(iv)Exhaust-stroke: Also known as output-stroke. During this process the piston once again returns from B.D.C. to T.D.C. while the exhaust valve is open. Exhaust-stroke action expels the spent air-fuel mixture through the exhaust valve.
Note: Four-stroke engines have several benefits over two stroke engines. They have better fuel efficiency, durability, gives more power and hence more torque and more cleaner emissions. But these are more expensive and complicated to make and they need valves for intake and exhaust of gases.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




