
There is a pentagonal shaped park as shown in figure. For finding its area jyoti and kavita divided it into two different ways. Find the area of the park using both the ways.
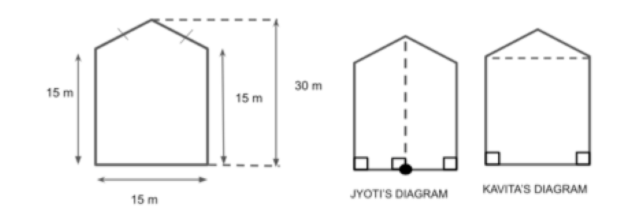

Answer
589.2k+ views
Hint: Here, we will first use the symmetry principle, the area of trapezium BCDF is equal to area of trapezium BAEF, \[{\text{Area of pentagon ABCDE}} = 2 \times {\text{Area of trapezium BCDF}}\], which we will find using the formula of a trapezium is \[\dfrac{1}{2} \times {\text{Sum of parallel sides}} \times {\text{Height}}\] from the diagram. Then we will find the area of pentagon ABCDE by adding the area of triangle ABC, where \[{\text{Area}} = \dfrac{1}{2} \times {\text{Base}} \times {\text{Height}}\] and area of square ACED, \[{\left( {{\text{side}}} \right)^2}\].
Complete step-by-step answer:
First, we will find the area of the jyoti’s diagram.
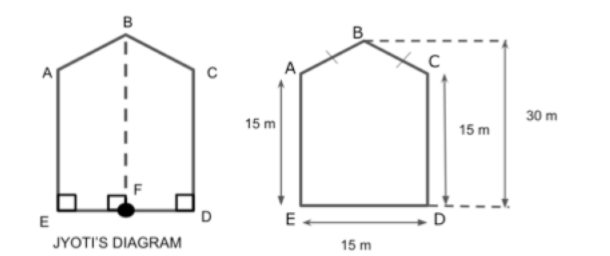
We know the area of pentagon ABCDE by adding the area of trapezium BCDF and area of trapezium BAEF.
Using the symmetry principle, the area of trapezium BCDF is equal to area of trapezium BAEF, we get
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{Area of pentagon ABCDE}} = 2 \times {\text{Area of trapezium BCDF}}\]
We know that in a trapezium BCDF, BF and CD are parallel sides, where DF is height.
Thus, we have from the given diagram.
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{BF}} = 30{\text{ m}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{CD}} = 15{\text{ m}}\]
\[
\Rightarrow {\text{DF}} = \dfrac{{{\text{DE}}}}{2} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{DF}} = \dfrac{{15}}{2}{\text{ m}} \\
\]
We will know use the formula of a trapezium is \[\dfrac{1}{2} \times {\text{Sum of parallel sides}} \times {\text{Height}}\] from the above values, we get
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{Area of trapezium BCDF}} = \dfrac{1}{2} \times \left( {{\text{BF}} + {\text{CD}}} \right) \times {\text{DF}}\]
Substituting the values of BF, CD and DF in the above values, we get
\[
\Rightarrow {\text{Area of trapezium BCDF}} = \dfrac{1}{2} \times \left( {30 + 15} \right) \times \dfrac{{15}}{2} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{Area of trapezium BCDF}} = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 45 \times \dfrac{{15}}{2} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{Area of trapezium BCDF}} = \dfrac{{45 \times 15}}{4} \\
\]
Multiplying the above equation by 2 to find the area of pentagon ABCDE, we get
\[
\Rightarrow {\text{Area of pentagon ABCDE}} = 2 \times \dfrac{{45 \times 15}}{4} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{Area of pentagon ABCDE}} = \dfrac{{675}}{2} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{Area of pentagon ABCDE}} = 337.5{\text{ }}{{\text{m}}^2} \\
\]
Thus, the area of pentagon ABCDE is \[337.5{\text{ }}{{\text{m}}^2}\].
Now, we will find the area of the Kavita’s diagram.
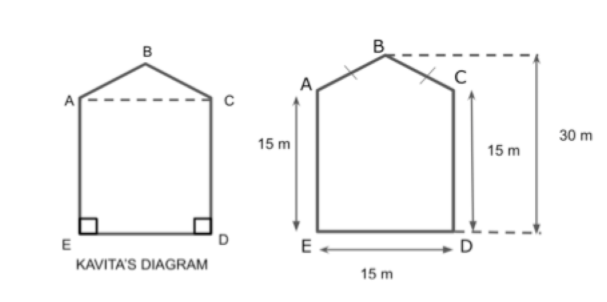
We know the area of pentagon ABCDE by adding the area of triangle ABC and area of square ACED.
Finding the area of triangle ABC using the formula of area of triangle \[{\text{Area}} = \dfrac{1}{2} \times {\text{Base}} \times {\text{Height}}\].
We know that the base of the triangle AC is 15 m.
Finding the height of the triangle from the above figure by subtracting the line CD from BD, we get
\[
\Rightarrow 30 - 15 \\
\Rightarrow 15{\text{ m}} \\
\]
We will know use the formula of a triangle is \[\dfrac{1}{2} \times {\text{Base}} \times {\text{Height}}\] from the above values, we get
\[
\Rightarrow {\text{Area}} = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 15 \times 15 \\
\Rightarrow {\text{Area}} = \dfrac{{225}}{2} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{Area}} = 112.5{\text{ }}{{\text{m}}^2} \\
\]
Using the symmetry principle, ACDE is a square with side 15 m.
Using the formula of area of square ACDE is \[{\left( {{\text{side}}} \right)^2}\], we get
\[
\Rightarrow {\text{Area of square ACDE}} = {15^2} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{Area of square ACDE}} = 225{\text{ }}{{\text{m}}^2} \\
\]
Thus, now we will find the area of pentagon ABCDE by adding the area of triangle ABC with area of square, we get
\[
\Rightarrow {\text{Area of pentagon ABCDE}} = 112.5 + 225 \\
\Rightarrow {\text{Area of pentagon ABCDE}} = 337.5{\text{ }}{{\text{m}}^2} \\
\]
Thus, the area of pentagon ABCDE is \[337.5{\text{ }}{{\text{m}}^2}\].
Note: While solving these types of questions, students should know the formulas of area of trapezium and area of pentagon. We need to use the symmetry principle to decrease calculations. The only key part to solve this problem is to remember the basic formulae of areas of the shapes to ease the solution. Do not forget to write the units properly. Avoid calculation mistakes.
Complete step-by-step answer:
First, we will find the area of the jyoti’s diagram.

We know the area of pentagon ABCDE by adding the area of trapezium BCDF and area of trapezium BAEF.
Using the symmetry principle, the area of trapezium BCDF is equal to area of trapezium BAEF, we get
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{Area of pentagon ABCDE}} = 2 \times {\text{Area of trapezium BCDF}}\]
We know that in a trapezium BCDF, BF and CD are parallel sides, where DF is height.
Thus, we have from the given diagram.
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{BF}} = 30{\text{ m}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{CD}} = 15{\text{ m}}\]
\[
\Rightarrow {\text{DF}} = \dfrac{{{\text{DE}}}}{2} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{DF}} = \dfrac{{15}}{2}{\text{ m}} \\
\]
We will know use the formula of a trapezium is \[\dfrac{1}{2} \times {\text{Sum of parallel sides}} \times {\text{Height}}\] from the above values, we get
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{Area of trapezium BCDF}} = \dfrac{1}{2} \times \left( {{\text{BF}} + {\text{CD}}} \right) \times {\text{DF}}\]
Substituting the values of BF, CD and DF in the above values, we get
\[
\Rightarrow {\text{Area of trapezium BCDF}} = \dfrac{1}{2} \times \left( {30 + 15} \right) \times \dfrac{{15}}{2} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{Area of trapezium BCDF}} = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 45 \times \dfrac{{15}}{2} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{Area of trapezium BCDF}} = \dfrac{{45 \times 15}}{4} \\
\]
Multiplying the above equation by 2 to find the area of pentagon ABCDE, we get
\[
\Rightarrow {\text{Area of pentagon ABCDE}} = 2 \times \dfrac{{45 \times 15}}{4} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{Area of pentagon ABCDE}} = \dfrac{{675}}{2} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{Area of pentagon ABCDE}} = 337.5{\text{ }}{{\text{m}}^2} \\
\]
Thus, the area of pentagon ABCDE is \[337.5{\text{ }}{{\text{m}}^2}\].
Now, we will find the area of the Kavita’s diagram.

We know the area of pentagon ABCDE by adding the area of triangle ABC and area of square ACED.
Finding the area of triangle ABC using the formula of area of triangle \[{\text{Area}} = \dfrac{1}{2} \times {\text{Base}} \times {\text{Height}}\].
We know that the base of the triangle AC is 15 m.
Finding the height of the triangle from the above figure by subtracting the line CD from BD, we get
\[
\Rightarrow 30 - 15 \\
\Rightarrow 15{\text{ m}} \\
\]
We will know use the formula of a triangle is \[\dfrac{1}{2} \times {\text{Base}} \times {\text{Height}}\] from the above values, we get
\[
\Rightarrow {\text{Area}} = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 15 \times 15 \\
\Rightarrow {\text{Area}} = \dfrac{{225}}{2} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{Area}} = 112.5{\text{ }}{{\text{m}}^2} \\
\]
Using the symmetry principle, ACDE is a square with side 15 m.
Using the formula of area of square ACDE is \[{\left( {{\text{side}}} \right)^2}\], we get
\[
\Rightarrow {\text{Area of square ACDE}} = {15^2} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{Area of square ACDE}} = 225{\text{ }}{{\text{m}}^2} \\
\]
Thus, now we will find the area of pentagon ABCDE by adding the area of triangle ABC with area of square, we get
\[
\Rightarrow {\text{Area of pentagon ABCDE}} = 112.5 + 225 \\
\Rightarrow {\text{Area of pentagon ABCDE}} = 337.5{\text{ }}{{\text{m}}^2} \\
\]
Thus, the area of pentagon ABCDE is \[337.5{\text{ }}{{\text{m}}^2}\].
Note: While solving these types of questions, students should know the formulas of area of trapezium and area of pentagon. We need to use the symmetry principle to decrease calculations. The only key part to solve this problem is to remember the basic formulae of areas of the shapes to ease the solution. Do not forget to write the units properly. Avoid calculation mistakes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




