
Three charges -2q, q and q are placed as shown in the given configuration. Calculate the resultant dipole moment of the system.
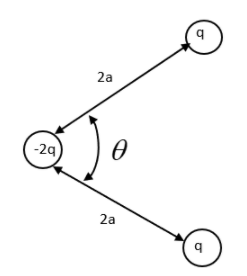

Answer
582.9k+ views
Hint: The distance between both the positive charges to the negative charge is equal. This can result in a stable equilibrium therefore. We will find the equivalent system and from it we can calculate the dipole moment of the system.
Complete answer:
Let us consider the given system. Obviously, we know that a pair of equal and opposite charges is called an electric dipole. The strength of such a pair or the electric dipole is called the electric dipole moment.
Dipole moment, \[\left| \mathbf{p} \right|=2a\left| q \right|\]
We need to reconsider the given system in order to find the dipole moment. From a quick observation we can understand the system is in equilibrium. The negative charge is held at position by the positive charges. We need to prove this theoretically.
Consider the first positive charge and the negative charge,
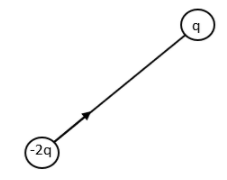
The arrow shows the resultant dipole moment. Now let us consider the other positive charged particle.
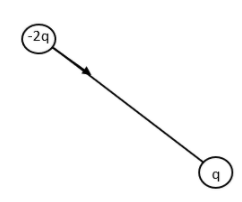
Now let us combine the two resultant figures.
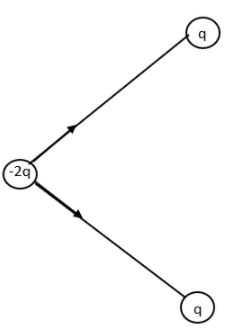
The arrows represent the Electric dipole moment due to charges q, q and -2q.
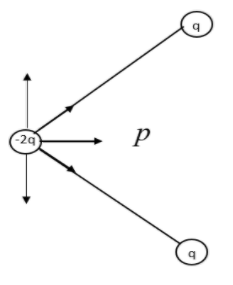
We have resolved the direction of dipole moment in the direction of the dark arrow. All the others stand cancelled.
As we know the direction of electric dipole is from negative to positive. The direction drawn from the information is valid with it. We also know that dipole moment is contributed equally by the two positive charges. So, let us consider, \[-2q=-q+-q\]
So, the dipole moment for each pair is given by,
\[{{p}_{1}}=2a.q\] and \[{{p}_{2}}=2a.q\]
The angle between the two dipoles is \[\theta \]. So, we can do the vector addition to find the total dipole moment between them.
The magnitude of the dipole moment is given by -
\[\begin{align}
& \therefore p=\sqrt{{{p}_{1}}^{2}+p_{2}^{2}+2{{p}_{1}}{{p}_{2}}\cos \theta } \\
& \Rightarrow p=\sqrt{{{(2aq)}^{2}}+{{(2aq)}^{2}}+2.2aq.2aq\cos \theta } \\
& \Rightarrow p=\sqrt{8{{a}^{2}}{{q}^{2}}(1+\cos \theta )} \\
& \Rightarrow p=2aq\sqrt{2(1+\cos \theta )} \\
\end{align}\]
The direction is as shown in the figure.
The electric dipole moment is widely calculated for chemical bonds.
Note:
The electric dipole moment is directed from negative to positive charge which is opposite to the conventional direction of current flow and electric field. It is measured in units called Debye (D). The concept of hydrogen bond comes from the higher value of dipole moment than the other covalent bonds.
The electric dipole moment is widely calculated for chemical bonds.
Complete answer:
Let us consider the given system. Obviously, we know that a pair of equal and opposite charges is called an electric dipole. The strength of such a pair or the electric dipole is called the electric dipole moment.
Dipole moment, \[\left| \mathbf{p} \right|=2a\left| q \right|\]
We need to reconsider the given system in order to find the dipole moment. From a quick observation we can understand the system is in equilibrium. The negative charge is held at position by the positive charges. We need to prove this theoretically.
Consider the first positive charge and the negative charge,

The arrow shows the resultant dipole moment. Now let us consider the other positive charged particle.

Now let us combine the two resultant figures.

The arrows represent the Electric dipole moment due to charges q, q and -2q.

We have resolved the direction of dipole moment in the direction of the dark arrow. All the others stand cancelled.
As we know the direction of electric dipole is from negative to positive. The direction drawn from the information is valid with it. We also know that dipole moment is contributed equally by the two positive charges. So, let us consider, \[-2q=-q+-q\]
So, the dipole moment for each pair is given by,
\[{{p}_{1}}=2a.q\] and \[{{p}_{2}}=2a.q\]
The angle between the two dipoles is \[\theta \]. So, we can do the vector addition to find the total dipole moment between them.
The magnitude of the dipole moment is given by -
\[\begin{align}
& \therefore p=\sqrt{{{p}_{1}}^{2}+p_{2}^{2}+2{{p}_{1}}{{p}_{2}}\cos \theta } \\
& \Rightarrow p=\sqrt{{{(2aq)}^{2}}+{{(2aq)}^{2}}+2.2aq.2aq\cos \theta } \\
& \Rightarrow p=\sqrt{8{{a}^{2}}{{q}^{2}}(1+\cos \theta )} \\
& \Rightarrow p=2aq\sqrt{2(1+\cos \theta )} \\
\end{align}\]
The direction is as shown in the figure.
The electric dipole moment is widely calculated for chemical bonds.
Note:
The electric dipole moment is directed from negative to positive charge which is opposite to the conventional direction of current flow and electric field. It is measured in units called Debye (D). The concept of hydrogen bond comes from the higher value of dipole moment than the other covalent bonds.
The electric dipole moment is widely calculated for chemical bonds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a labelled diagram of the human heart and label class 11 biology CBSE

What is 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p class 11 chemistry CBSE




