
Three forces of magnitude \[30,60\] and $P$ acting at a point are in equilibrium. If the angle between the first two is \[{60^0}\], the value of $P$ is
A.\[30\sqrt 7 \]
B.\[30\sqrt 3 \]
C.\[20\sqrt 6 \]
D.\[25\sqrt 2 \]
Answer
498.6k+ views
Hint: The forces are acting at a point of equilibrium. So the third force will be equal to the resultant force of the other two. That is the third force will be equal in magnitude but opposite in direction. For equilibrium the sum of all the three forces must be zero.
Complete answer:
When a body is acted upon by two or more forces then the total of all the forces which cause the resulting effect is the resultant force or net force. A suitable combination of several forces can also result in zero causing no net effect. For equilibrium the sum of all the three forces must be zero.
\[R.F = \sqrt[2]{{{F_1}^2 + {F_2}^2 + 2{F_1}{F_2}\cos \theta }}\]
Here, \[R.F\]is the resulting force
\[{F_1}\]And\[{F_2}\] are the known two forces
\[\theta \] is the angle between the two forces.
Given Forces \[{F_1}\]And \[{F_2}\]are \[30,60\]respectively. Also \[\theta \]=\[{60^0}\]
Substituting all the known values in the formula we get,
\[R.F = \sqrt[2]{{{{30}^2} + {{60}^2} + 2(30)(60)\cos {{60}^0}}}\]
\[R.F = \sqrt[2]{{900 + 3600 + 2(30)(60) \times \dfrac{1}{2}}}\]
\[R.F = \sqrt[2]{{900 + 3600 + 1800}}\]
\[R.F = \sqrt[2]{{6300}}\]
\[R.F = 30\sqrt 7 \]
As we already said the equilibrium sum of all three forces will be zero.
\[R.F + P\]\[ = 0\]
Here P is the third force
\[30\sqrt 7 + P = 0\]
\[P = - 30\sqrt 7 \]
Here the negative sign indicates that the force is acting in the opposite direction. And hence the magnitude of the third force is \[30\sqrt 7 \]
So the correct answer is option A= \[30\sqrt 7 \]
Note:
This problem can also be solved by Lami’s theorem.
Lami’s theorem states that when three forces related to the vector magnitude acting at the point of, equilibrium, each force of the system is always proportional to the sine of the angle which lies between the two other forces.
By the diagram given below let us consider three forces given above A, B, and P acting on a point making angles \[\alpha ,\beta ,\gamma \] with each other
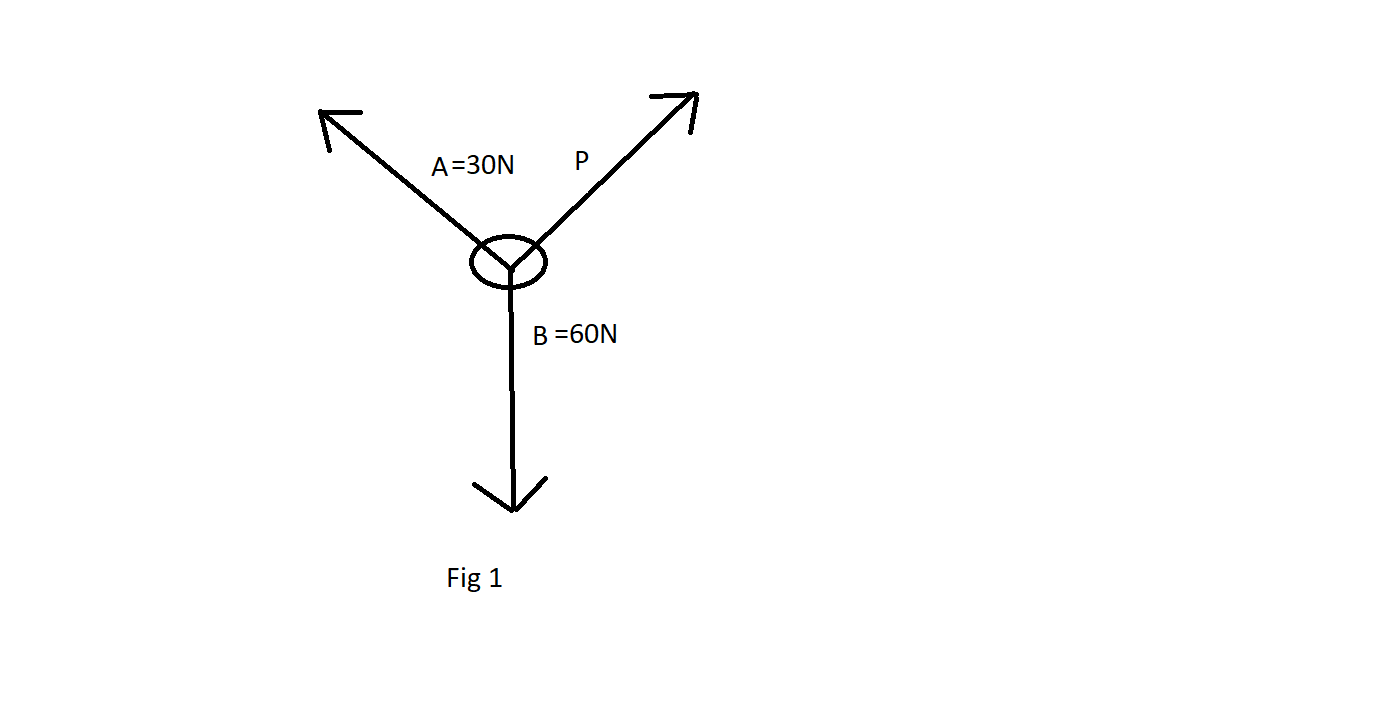
The angle A and B is \[\gamma \]. The angle between A and C is \[\beta \] and the angle between B and C is \[\alpha \].
We know that \[\gamma \]=\[{60^0}\] from the question. Since the total angle is \[{360^0}\] the angles opposite to \[P,30Nand60N\] will be \[{60^0},\theta ,(300 - \theta )\]. So according to Lami’s theorem, we will have,
\[\dfrac{P}{{\sin {{60}^0}}} = \dfrac{{30}}{{\sin (300 - \theta )}} = \dfrac{{60}}{\theta }\]
Solving for \[P\]and \[\theta \]
\[\dfrac{{30}}{{\sin (300 - \theta )}} = \dfrac{{60}}{\theta }\]
\[2\sin (300 - \theta ) = \sin \theta \]
\[2sin\theta = - \sqrt 3 cos\theta \]
\[\tan \theta = \dfrac{{ - \sqrt 3 }}{2}\]
\[\sin \theta = \sqrt {\dfrac{3}{7}} \]
\[\dfrac{P}{{\sin {{60}^o}}} = \dfrac{{60}}{{\sin \theta }}\]
\[P = 30\sqrt 7 N\]
Complete answer:
When a body is acted upon by two or more forces then the total of all the forces which cause the resulting effect is the resultant force or net force. A suitable combination of several forces can also result in zero causing no net effect. For equilibrium the sum of all the three forces must be zero.
\[R.F = \sqrt[2]{{{F_1}^2 + {F_2}^2 + 2{F_1}{F_2}\cos \theta }}\]
Here, \[R.F\]is the resulting force
\[{F_1}\]And\[{F_2}\] are the known two forces
\[\theta \] is the angle between the two forces.
Given Forces \[{F_1}\]And \[{F_2}\]are \[30,60\]respectively. Also \[\theta \]=\[{60^0}\]
Substituting all the known values in the formula we get,
\[R.F = \sqrt[2]{{{{30}^2} + {{60}^2} + 2(30)(60)\cos {{60}^0}}}\]
\[R.F = \sqrt[2]{{900 + 3600 + 2(30)(60) \times \dfrac{1}{2}}}\]
\[R.F = \sqrt[2]{{900 + 3600 + 1800}}\]
\[R.F = \sqrt[2]{{6300}}\]
\[R.F = 30\sqrt 7 \]
As we already said the equilibrium sum of all three forces will be zero.
\[R.F + P\]\[ = 0\]
Here P is the third force
\[30\sqrt 7 + P = 0\]
\[P = - 30\sqrt 7 \]
Here the negative sign indicates that the force is acting in the opposite direction. And hence the magnitude of the third force is \[30\sqrt 7 \]
So the correct answer is option A= \[30\sqrt 7 \]
Note:
This problem can also be solved by Lami’s theorem.
Lami’s theorem states that when three forces related to the vector magnitude acting at the point of, equilibrium, each force of the system is always proportional to the sine of the angle which lies between the two other forces.
By the diagram given below let us consider three forces given above A, B, and P acting on a point making angles \[\alpha ,\beta ,\gamma \] with each other

The angle A and B is \[\gamma \]. The angle between A and C is \[\beta \] and the angle between B and C is \[\alpha \].
We know that \[\gamma \]=\[{60^0}\] from the question. Since the total angle is \[{360^0}\] the angles opposite to \[P,30Nand60N\] will be \[{60^0},\theta ,(300 - \theta )\]. So according to Lami’s theorem, we will have,
\[\dfrac{P}{{\sin {{60}^0}}} = \dfrac{{30}}{{\sin (300 - \theta )}} = \dfrac{{60}}{\theta }\]
Solving for \[P\]and \[\theta \]
\[\dfrac{{30}}{{\sin (300 - \theta )}} = \dfrac{{60}}{\theta }\]
\[2\sin (300 - \theta ) = \sin \theta \]
\[2sin\theta = - \sqrt 3 cos\theta \]
\[\tan \theta = \dfrac{{ - \sqrt 3 }}{2}\]
\[\sin \theta = \sqrt {\dfrac{3}{7}} \]
\[\dfrac{P}{{\sin {{60}^o}}} = \dfrac{{60}}{{\sin \theta }}\]
\[P = 30\sqrt 7 N\]
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




