
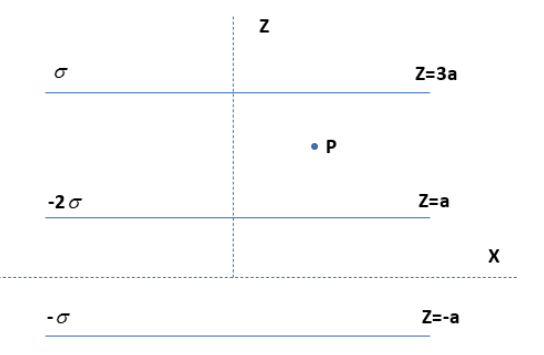
Three infinitely long charge sheets are placed as shown in the figure. The electric field at point P is going to be
A. \[\dfrac{2\sigma }{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\hat{k}\]
B. \[-\dfrac{2\sigma }{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\hat{k}\]
C. \[\dfrac{4\sigma }{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\hat{k}\]
D. \[-\dfrac{4\sigma }{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\hat{k}\]

Answer
527.7k+ views
Hint: We can calculate the electric field at the point P by using the formula of the electric field of an infinite sheet of charges. This formula is generated from Gauss' law. Since the charges are different, we have to consider the direction of the electric field produced by each sheet. Parallel plate capacitors are also working with this principle.
Formula used:
\[E=\dfrac{\sigma }{2{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\], where \[\sigma \] is the charge density and \[{{\varepsilon }_{0}}\] is the permittivity of free space.
Complete step by step answer:
In this question, three infinitely long sheets are placed as shown in the figure. As we know, the electric field due to the charged sheet is E.
\[E=\dfrac{\sigma }{2{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\], where \[\sigma \] is the charge density and \[{{\varepsilon }_{0}}\] is the permittivity of free space.
Each sheet has a different charge density. The electric field due to the sheet is depending upon the charge. If it is negative then the electric field goes towards the sheet. If it is positive, the electric field goes outward. Each sheet will make an impact on other sheets also. It is shown in different colours in the figure given below.
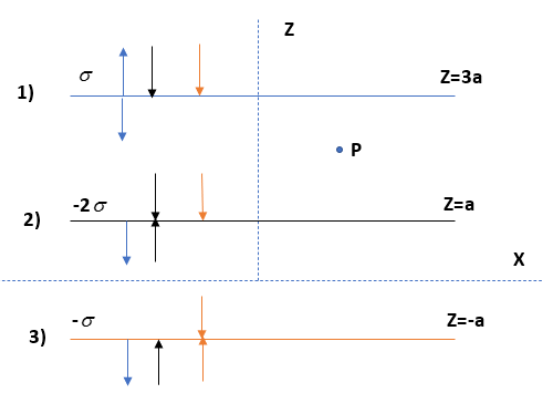
The electric field of sheet 1 at the point P can be written as,
\[{{E}_{1}}=\dfrac{\sigma }{2{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}(-\hat{k})\], since it is acting on the point P along the negative y-axis direction.
The electric field of sheet 2 at the point P can be written as,
\[{{E}_{2}}=\dfrac{2\sigma }{2{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}(-\hat{k})\]
Here the electric field acts towards the sheet 2 Since the charge density is negative. Thus the electric field due to sheet 2, is acting downwards.
The electric field of sheet 3 at the point P can be written as,
\[{{E}_{3}}=\dfrac{\sigma }{2{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}(-\hat{k})\]
Here also the charge density is negative. Thus the electric field of sheet 3 acting downwards.
Therefore the net electric field acting on the point P will be,
\[E={{E}_{1}}+{{E}_{2}}+{{E}_{3}}\]
\[E=\dfrac{\sigma }{2{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}(-\hat{k})+\dfrac{2\sigma }{2{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}(-\hat{k})+\dfrac{\sigma }{2{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}(-\hat{k})\]
\[E=\dfrac{4\sigma }{2{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}(-\hat{k})\]
\[E=\dfrac{2\sigma }{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}(-\hat{k})\]
This is the total electric field acting on the point P and which is acting along the negative y-axis direction.
So the correct answer is option B.
Note: In the question, the charge densities are shown in negative signs. In the calculations, we don’t have to consider that. We consider the magnitude of the charge densities. Since the sign of charge density is arising because of the charges. It won’t make any difference in the charge densities. We took the sign in the electric field since the electric field direction depended upon the polarity of charges.
Formula used:
\[E=\dfrac{\sigma }{2{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\], where \[\sigma \] is the charge density and \[{{\varepsilon }_{0}}\] is the permittivity of free space.
Complete step by step answer:
In this question, three infinitely long sheets are placed as shown in the figure. As we know, the electric field due to the charged sheet is E.
\[E=\dfrac{\sigma }{2{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\], where \[\sigma \] is the charge density and \[{{\varepsilon }_{0}}\] is the permittivity of free space.
Each sheet has a different charge density. The electric field due to the sheet is depending upon the charge. If it is negative then the electric field goes towards the sheet. If it is positive, the electric field goes outward. Each sheet will make an impact on other sheets also. It is shown in different colours in the figure given below.

The electric field of sheet 1 at the point P can be written as,
\[{{E}_{1}}=\dfrac{\sigma }{2{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}(-\hat{k})\], since it is acting on the point P along the negative y-axis direction.
The electric field of sheet 2 at the point P can be written as,
\[{{E}_{2}}=\dfrac{2\sigma }{2{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}(-\hat{k})\]
Here the electric field acts towards the sheet 2 Since the charge density is negative. Thus the electric field due to sheet 2, is acting downwards.
The electric field of sheet 3 at the point P can be written as,
\[{{E}_{3}}=\dfrac{\sigma }{2{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}(-\hat{k})\]
Here also the charge density is negative. Thus the electric field of sheet 3 acting downwards.
Therefore the net electric field acting on the point P will be,
\[E={{E}_{1}}+{{E}_{2}}+{{E}_{3}}\]
\[E=\dfrac{\sigma }{2{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}(-\hat{k})+\dfrac{2\sigma }{2{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}(-\hat{k})+\dfrac{\sigma }{2{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}(-\hat{k})\]
\[E=\dfrac{4\sigma }{2{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}(-\hat{k})\]
\[E=\dfrac{2\sigma }{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}(-\hat{k})\]
This is the total electric field acting on the point P and which is acting along the negative y-axis direction.
So the correct answer is option B.
Note: In the question, the charge densities are shown in negative signs. In the calculations, we don’t have to consider that. We consider the magnitude of the charge densities. Since the sign of charge density is arising because of the charges. It won’t make any difference in the charge densities. We took the sign in the electric field since the electric field direction depended upon the polarity of charges.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




