
To convert a galvanometer into an ammeter, we connect
A. Low resistance in series
B. Low resistance in parallel
C. High resistance in series
D. High resistance in parallel
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: The deflection of the galvanometer is proportional to the current flowing through it. Therefore, it must allow a maximum flow of current through it. To do so, its effective resistance should be very low.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that a galvanometer is used to detect very small current passing through it if any. The coil in the galvanometer is suspended between the strong shoe magnets and when the current passes through the coil, it shows deflection. We know that the deflection of the galvanometer is proportional to the current flowing through it.
We know that the ammeter measures a current flowing through it whether it is a small current or large. To convert the galvanometer into an ammeter, the galvanometer should measure large current passing through it. To do so, a low resistance is connected across the galvanometer known as shunt resistance as shown in the figure below.
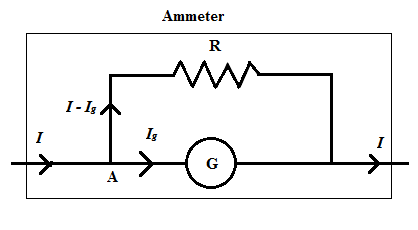
When the current I pass through the above circuit, it divides at the junction A. We know that the voltage remains constant in parallel arrangement, therefore,
\[{V_g} = {V_S}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {I_g}{R_g} = \left( {I - {I_g}} \right)S\]
\[ \Rightarrow {I_g} = \dfrac{S}{{S + {R_g}}}I\]
Therefore, we can say that the current flowing through the galvanometer is proportional to the current flowing through the circuit. We know that the deflection of the galvanometer is proportional to the current flowing through it, we can say the deflection of the galvanometer is also proportional to the current passing through the circuit.
If we connect the high shunt resistor S across the galvanometer, the current through the galvanometer will always be less than the current in the circuit as from the above expression. Therefore, the value of the shunt resistor should be low.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
To measure the current, the ammeter must allow all the incoming current to pass through it. Therefore, the resistance of the ammeter is very low. Thus, the other way to answer this question is the need of connecting the resistance across it. We know that in parallel combination, the resistance decreases. So, the low resistance is connected across the galvanometer to reduce the effective resistance.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that a galvanometer is used to detect very small current passing through it if any. The coil in the galvanometer is suspended between the strong shoe magnets and when the current passes through the coil, it shows deflection. We know that the deflection of the galvanometer is proportional to the current flowing through it.
We know that the ammeter measures a current flowing through it whether it is a small current or large. To convert the galvanometer into an ammeter, the galvanometer should measure large current passing through it. To do so, a low resistance is connected across the galvanometer known as shunt resistance as shown in the figure below.

When the current I pass through the above circuit, it divides at the junction A. We know that the voltage remains constant in parallel arrangement, therefore,
\[{V_g} = {V_S}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {I_g}{R_g} = \left( {I - {I_g}} \right)S\]
\[ \Rightarrow {I_g} = \dfrac{S}{{S + {R_g}}}I\]
Therefore, we can say that the current flowing through the galvanometer is proportional to the current flowing through the circuit. We know that the deflection of the galvanometer is proportional to the current flowing through it, we can say the deflection of the galvanometer is also proportional to the current passing through the circuit.
If we connect the high shunt resistor S across the galvanometer, the current through the galvanometer will always be less than the current in the circuit as from the above expression. Therefore, the value of the shunt resistor should be low.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
To measure the current, the ammeter must allow all the incoming current to pass through it. Therefore, the resistance of the ammeter is very low. Thus, the other way to answer this question is the need of connecting the resistance across it. We know that in parallel combination, the resistance decreases. So, the low resistance is connected across the galvanometer to reduce the effective resistance.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




