
T.O. Diener discovered a
(a) Bacteriophage
(b) Free infectious RNA
(c) Free infectious DNA
(d) Infectious protein
Answer
582.6k+ views
Hint: T.O. Diener, a plant pathologist, discovered that the disease- causing microorganism in potatoes was a subviral agent that lacks one of the essential components to be a virus known as viroid.
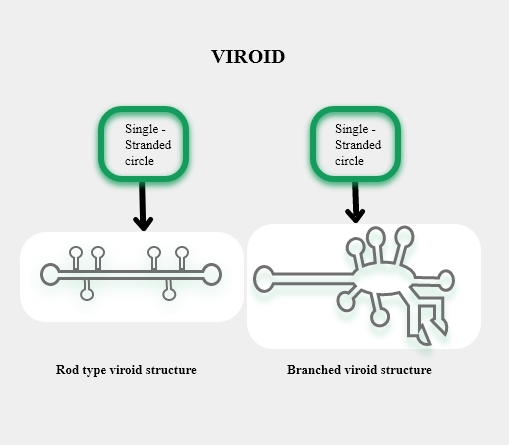
Complete Step by Step Answer: Theodor Otto Diener was a Swiss- American Plant pathologist who discovered small self- replicating particles which lacked protein coats and had infectious free RNA particles. He named these microorganisms as Viroid which meant L. virus- poison, eidos- diminutive. The molecular weight of viroids is very low, lower than the virus. These are the smallest causative agents known till now. Viroid replicates in the nucleus of the chloroplast through RNA replication mechanisms which are done in the presence of enzyme RNA polymerase II, which it takes from the host cell which uses it to synthesis mRNA from DNA. So, the correct answer is, “Free infectious RNA.”
Note: - Viroid is an obligate parasite and requires a host to survive.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




