
To get n-type of semiconductor, germanium should be doped with:
A) Gallium
B) Arsenic
C) Aluminium
D) Boron
Answer
528.6k+ views
Hint: In an n-type semiconductor, the group 15 elements are added as the dopant or as an impurity to the silicon or germanium. The four electrons form a bond with the adjacent silicon and the extra electron is responsible for the conduction of electricity.
Complete answer:
> Semiconductor elements like silicon $\text{Si}$ and Germanium $\text{Ge}$ have the general electronic configuration as $\text{n}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{n}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}$ in the outer electron shell. The four electrons are used to form the bond with the neighbouring atom. These electrons are responsible for the conduction of such conductors called the intrinsic semiconductors.
> It is possible to increase the charge carriers by the introduction of an impurity called ‘dopant’ in the semiconductor. This process is called doping. Doping changes the intrinsic semiconductor to an extrinsic semiconductor.
> Pure silicon or germanium can be made more conducting by adding the dopant impurities. Dopants act as either an electron donor or acceptor. If a donor has more valence electrons then they donate the extra electron for the conduction of electricity.
> Silicon and Germanium are group 14 elements. The group 15 elements have the last shell configuration $\text{n}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{n}{{\text{p}}^{3}}$. They are pentavalent.
> An extremely small number of atoms of the silicon or germanium is replaced by the arsenic atom. The four-electron out of the five electrons forms a bond with the silicon in its framework. Only four electrons are engaged in bond formation. The fifth electron is not bonded. On the application of electricity, the free electron acts as a charge. The electricity experienced by this doped semiconductor is greater than that of the intrinsic semiconductor.
> Since the extra electron is responsible for the conduction is called the n-type of the semiconductor. The term n-type comes from the negative charge in the silicon framework. In n-type semiconductors, the electrons are the carriers of electricity. Common types of dopants are phosphorus or arsenic.
> In n-type semiconductors, the extra band named as the donor band is added in the between the conduction and valence band. This makes it easy for the excitation of an electron from the donor band to the conduction band.
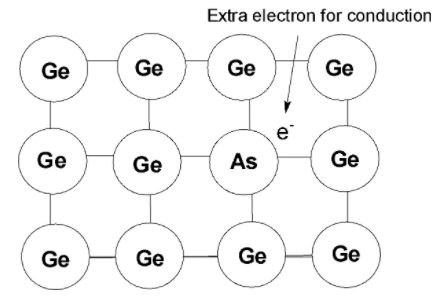
Thus the arsenic is doped to form n-type semiconductor.
Hence, (B) is the correct option.
Note: Do not get confused with the n and p-type of the semiconductor. The n stands for the extra electron or negative carrier and the p is termed use for the hole or positive carrier. Extra electron, when doped with a higher group element and hole, is generated when doped with lower group elements.
Complete answer:
> Semiconductor elements like silicon $\text{Si}$ and Germanium $\text{Ge}$ have the general electronic configuration as $\text{n}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{n}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}$ in the outer electron shell. The four electrons are used to form the bond with the neighbouring atom. These electrons are responsible for the conduction of such conductors called the intrinsic semiconductors.
> It is possible to increase the charge carriers by the introduction of an impurity called ‘dopant’ in the semiconductor. This process is called doping. Doping changes the intrinsic semiconductor to an extrinsic semiconductor.
> Pure silicon or germanium can be made more conducting by adding the dopant impurities. Dopants act as either an electron donor or acceptor. If a donor has more valence electrons then they donate the extra electron for the conduction of electricity.
> Silicon and Germanium are group 14 elements. The group 15 elements have the last shell configuration $\text{n}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{n}{{\text{p}}^{3}}$. They are pentavalent.
> An extremely small number of atoms of the silicon or germanium is replaced by the arsenic atom. The four-electron out of the five electrons forms a bond with the silicon in its framework. Only four electrons are engaged in bond formation. The fifth electron is not bonded. On the application of electricity, the free electron acts as a charge. The electricity experienced by this doped semiconductor is greater than that of the intrinsic semiconductor.
> Since the extra electron is responsible for the conduction is called the n-type of the semiconductor. The term n-type comes from the negative charge in the silicon framework. In n-type semiconductors, the electrons are the carriers of electricity. Common types of dopants are phosphorus or arsenic.
> In n-type semiconductors, the extra band named as the donor band is added in the between the conduction and valence band. This makes it easy for the excitation of an electron from the donor band to the conduction band.

Thus the arsenic is doped to form n-type semiconductor.
Hence, (B) is the correct option.
Note: Do not get confused with the n and p-type of the semiconductor. The n stands for the extra electron or negative carrier and the p is termed use for the hole or positive carrier. Extra electron, when doped with a higher group element and hole, is generated when doped with lower group elements.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




