
To observe refraction and lateral; deviation of a beam of light incident obliquely on a glass slab.
Answer
530.1k+ views
- Hint- Here we will proceed by bending the ray of incident towards normal since refraction takes place from rarer to denser medium. Then we will bend away the refracted ray from the normal since refraction takes place from dense to rarer medium to get the required answer.
Complete step-by-step solution -
What do we require- Glass slab, drawing board, white paper sheet, drawing pins, office pins, protractor.
Procedure-
Fix a white paper sheet by drawing pins on a drawing board.
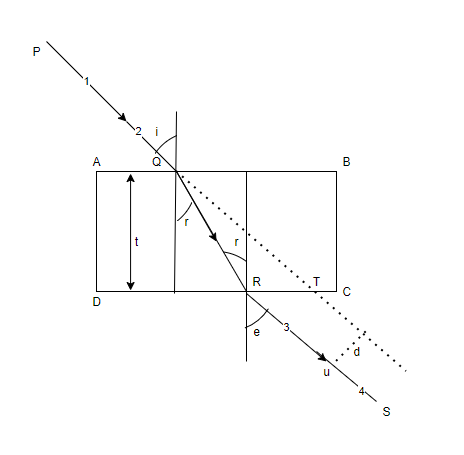
Take a glass slab and put it symmetrically in the middle of the paper as ABCD marked. Draw a normal at point Q on AB and draw a line PQ making an angle i with normal. PQ will represent incident rays.
Fix two points 1 and 2 on line PQ at distances 1cm. Also fix points 3 and 4 to cover the images of the first two pins all on a straight line. Draw straight line RS through points 3 and 4 to represent emergent ray.
Join QR to represent refracted rays. Draw normal at point R on face DC and measure angle e.
It comes to be equal to angle i. Produce PQ forward to cut DC at T. Draw TU perpendicular to RS. TU measures lateral displacement d.
Now take another set for different angles of incident and measure the lateral displacement.
Therefore, we conclude that-
Angle of incidence (i) = Angle of emergence (e)
The lateral displacement increases with the increase in the thickness of the slab.
The lateral displacement increases with the angle of incidence (i).
Note- While solving this question, we must concentrate that incident rays should be parallel to the emergent ray so that angle of incidence is equal to angle of emergence. Also one should make sure that glass slab is kept symmetrically to get the required result.
Complete step-by-step solution -

What do we require- Glass slab, drawing board, white paper sheet, drawing pins, office pins, protractor.
Procedure-
Fix a white paper sheet by drawing pins on a drawing board.
Take a glass slab and put it symmetrically in the middle of the paper as ABCD marked. Draw a normal at point Q on AB and draw a line PQ making an angle i with normal. PQ will represent incident rays.
Fix two points 1 and 2 on line PQ at distances 1cm. Also fix points 3 and 4 to cover the images of the first two pins all on a straight line. Draw straight line RS through points 3 and 4 to represent emergent ray.
Join QR to represent refracted rays. Draw normal at point R on face DC and measure angle e.
It comes to be equal to angle i. Produce PQ forward to cut DC at T. Draw TU perpendicular to RS. TU measures lateral displacement d.
Now take another set for different angles of incident and measure the lateral displacement.
Therefore, we conclude that-
Angle of incidence (i) = Angle of emergence (e)
The lateral displacement increases with the increase in the thickness of the slab.
The lateral displacement increases with the angle of incidence (i).
Note- While solving this question, we must concentrate that incident rays should be parallel to the emergent ray so that angle of incidence is equal to angle of emergence. Also one should make sure that glass slab is kept symmetrically to get the required result.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




