
To use a transistor as an amplifier:
A. The emitter base junction is forward biased and the base collector junction is reverse biased.
B. No bias voltage is required.
C. Both junctions are forward biased
D. Both junctions are reverse biased.
Answer
537k+ views
Hint: In the common emitter configuration, the transistor is used as an amplifier. An amplifier circuit that uses a transistor is known as a transistor amplifier. The work of the amplifier is to amplify or strengthen the weak signal into a strong signal to make it travel at a longer distance.
Complete answer:
Transistors are composed of 3 parts, they are, the base, the collector and the emitter. The emitter emits the carriers into the base. The current carriers pass on to the collector through the base. The collector collects the carriers emitted by the emitter.
The transistor should be properly biased to use it as an amplifier. The DC bias voltage should be applied to the emitter base junction. This connection makes the transistor remain in the forward biased condition.
The circuit symbol diagram representing the transistor is given as follows.
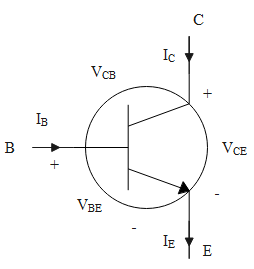
The diagram represents the emitter, base and collector currents and the base-emitter and the collector base voltages.
The performance of the transistor as an amplifier: The input resistance will be low as the input circuit, that is, the emitter base junction is forward biased. The output resistance will be high as the output circuit, that is, the base collector junction is reverse biased.
\[\therefore \]To use a transistor as an amplifier: the emitter base junction is forward biased and the base collector junction is reverse biased, thus, option (A) is correct.
Note:
In a transistor, the emitter base junction is always forward biased, whereas, the base collector junction is always reverse biased. The applications of the transistor amplifier circuits involve optical fibre, radio and audio communication.
Complete answer:
Transistors are composed of 3 parts, they are, the base, the collector and the emitter. The emitter emits the carriers into the base. The current carriers pass on to the collector through the base. The collector collects the carriers emitted by the emitter.
The transistor should be properly biased to use it as an amplifier. The DC bias voltage should be applied to the emitter base junction. This connection makes the transistor remain in the forward biased condition.
The circuit symbol diagram representing the transistor is given as follows.

The diagram represents the emitter, base and collector currents and the base-emitter and the collector base voltages.
The performance of the transistor as an amplifier: The input resistance will be low as the input circuit, that is, the emitter base junction is forward biased. The output resistance will be high as the output circuit, that is, the base collector junction is reverse biased.
\[\therefore \]To use a transistor as an amplifier: the emitter base junction is forward biased and the base collector junction is reverse biased, thus, option (A) is correct.
Note:
In a transistor, the emitter base junction is always forward biased, whereas, the base collector junction is always reverse biased. The applications of the transistor amplifier circuits involve optical fibre, radio and audio communication.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




