
Toluene on reaction with N-bromosuccinimide gives:
A. p-bromomethyl benzene
B. o-bromomethyl benzene
C. Phenyl bromomethane
D. m-bromomethyl benzene
Answer
508.2k+ views
Hint: N-bromosuccinimide which is commonly represented as NBS, is a chemical reagent used in organic reactions for radical substitution, electrophilic addition and electrophilic substitution reaction. It is a convenient source for bromine radical i.e., $B{{r}^{\bullet }}$.
Complete answer:
N-bromosuccinimide is a white crystalline solid and is structurally represented as follows:
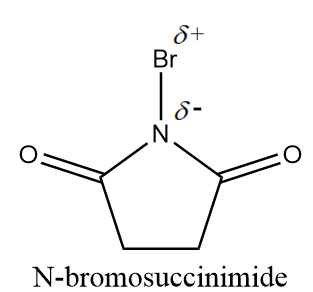
Due to presence of a partial positive charge on bromine, NBS acts as a good electrophile and has a tendency to give two major reactions i.e., allylic or benzylic bromination (most common) and bromohydrin formation.
On reaction of toluene with NBS, allylic bromination takes place as per following reaction mechanism:
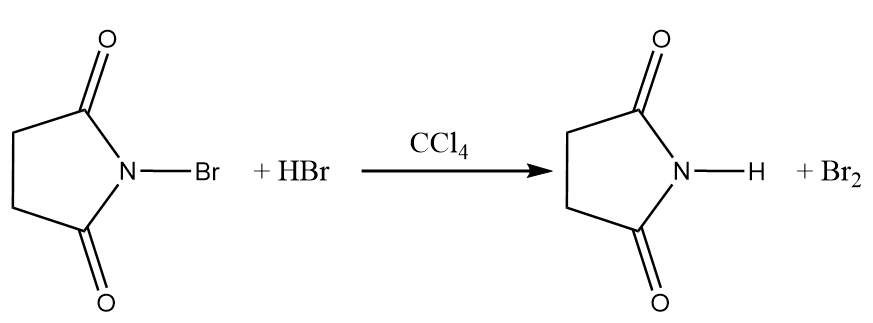
Step-1: NBS reacts with trace amounts of hydrogen bromide in order to form low concentration of bromine when suspended in carbon tetrachloride. The reaction takes place as follows:
Step-2: Bromine molecule in the presence of light breaks into its respective radicals and reaction takes place as follows:
$B{r_2}\xrightarrow{{h\upsilon }}2B{r^ \bullet }$
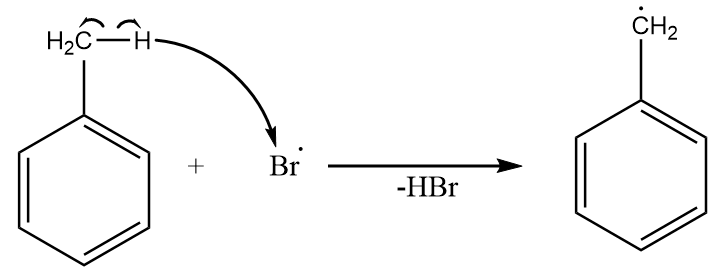
Step-3: One of the bromine radicals removes the allylic hydrogen from the molecule and a radical intermediate is formed which is resonance stabilized along with the removal of hydrogen bromide. The reaction takes place as follows:
Step-4: The radical intermediate formed in the previous step reacts with the other bromine radical to give the final product. The reaction proceeds as follows:
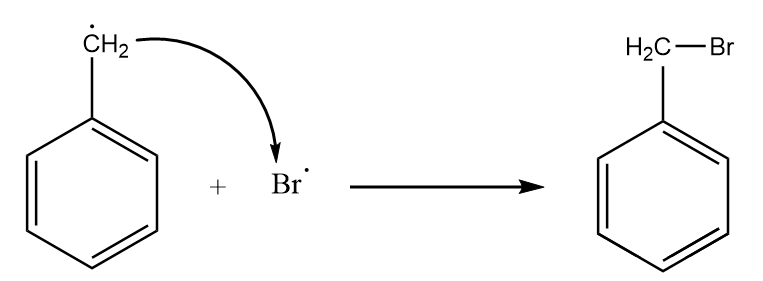
Hence, on reaction of toluene with N-bromosuccinimide, the formation of phenyl bromomethane takes place.
Thus, option (C) is the correct answer.
Note:
It is important to note that carbon tetrachloride should be maintained anhydrous throughout the reaction process because the presence of water may hydrolyse the desired product. To maintain anhydrous and acid-free conditions, barium carbonate is often added in the reaction.
Complete answer:
N-bromosuccinimide is a white crystalline solid and is structurally represented as follows:

Due to presence of a partial positive charge on bromine, NBS acts as a good electrophile and has a tendency to give two major reactions i.e., allylic or benzylic bromination (most common) and bromohydrin formation.
On reaction of toluene with NBS, allylic bromination takes place as per following reaction mechanism:
Step-1: NBS reacts with trace amounts of hydrogen bromide in order to form low concentration of bromine when suspended in carbon tetrachloride. The reaction takes place as follows:

Step-2: Bromine molecule in the presence of light breaks into its respective radicals and reaction takes place as follows:
$B{r_2}\xrightarrow{{h\upsilon }}2B{r^ \bullet }$
Step-3: One of the bromine radicals removes the allylic hydrogen from the molecule and a radical intermediate is formed which is resonance stabilized along with the removal of hydrogen bromide. The reaction takes place as follows:

Step-4: The radical intermediate formed in the previous step reacts with the other bromine radical to give the final product. The reaction proceeds as follows:

Hence, on reaction of toluene with N-bromosuccinimide, the formation of phenyl bromomethane takes place.
Thus, option (C) is the correct answer.
Note:
It is important to note that carbon tetrachloride should be maintained anhydrous throughout the reaction process because the presence of water may hydrolyse the desired product. To maintain anhydrous and acid-free conditions, barium carbonate is often added in the reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




