
Torsional strain in eclipsed conformations of a molecule is due to:
A. repulsion between the eclipsed carbons
B. repulsion between aligned electron pairs of the eclipsed bond
C. repulsions between aligned H
D. repulsions between C-H bond of eclipsed conformation
Answer
570k+ views
Hint: We know that the different spatial arrangements of atoms of groups of atoms which can be converted from one form to another by the rotation around the single bonds are known as conformations or the conformational isomers.
Complete step by step answer:
In the eclipsed conformation, the hydrogen atoms of both the carbon atoms present are facing each other which means that the carbon hydrogen bond pairs of the two carbon atoms are very close to each other. The rotation around the central bond leads to the increase in the potential energy of the molecule. The increase in the potential energy of the molecule is due to the repulsion between the electrons present in the bond. This increase in the potential energy of the molecule is known as torsional strain.
We can say that the torsional strain depends on the rotations around the central bond. For example let’s consider the staggered and eclipsed conformation of ethane.
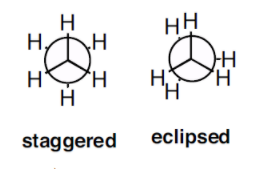
From the structure of ethane we can say that the torsional strain in the staggered conformation is less than the torsional strain in the eclipsed configuration. Thus the staggered conformation is more stable than the eclipsed configuration because of the torsional strain.
Hence the correct answer is option (b) i.e. torsional strain in eclipsed conformations of a molecule is due to repulsion between aligned electron pairs of the eclipsed bond.
Note: The rotation of carbon along the single bond is not free thus the potential energy of the molecule changes as the rotation occurs along the carbon-carbon single bond. The potential energy of the staggered configuration is minimum.
Complete step by step answer:
In the eclipsed conformation, the hydrogen atoms of both the carbon atoms present are facing each other which means that the carbon hydrogen bond pairs of the two carbon atoms are very close to each other. The rotation around the central bond leads to the increase in the potential energy of the molecule. The increase in the potential energy of the molecule is due to the repulsion between the electrons present in the bond. This increase in the potential energy of the molecule is known as torsional strain.
We can say that the torsional strain depends on the rotations around the central bond. For example let’s consider the staggered and eclipsed conformation of ethane.

From the structure of ethane we can say that the torsional strain in the staggered conformation is less than the torsional strain in the eclipsed configuration. Thus the staggered conformation is more stable than the eclipsed configuration because of the torsional strain.
Hence the correct answer is option (b) i.e. torsional strain in eclipsed conformations of a molecule is due to repulsion between aligned electron pairs of the eclipsed bond.
Note: The rotation of carbon along the single bond is not free thus the potential energy of the molecule changes as the rotation occurs along the carbon-carbon single bond. The potential energy of the staggered configuration is minimum.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




