
Triangle ABC and parallelogram ABEP are on the same base AC in between the same parallel AB and EF. Prove that area $\left( \vartriangle ABC \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}$ ar parallelogram (ABEP).
Answer
553.8k+ views
Hint: We are given that we have a $\left( \vartriangle ABC \right)$ and a parallelogram that lie on the same base we have to show that
$\left( \vartriangle ABC \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}$ar (||gm ABEP)
To do so we do construction we draw BH||AC that meet FE at H
Then we use that diagonal of parallelogram to divide it into two congruent triangles and we use that two parallelograms on the same base between the same parallel are equal in area. Using them we get our required solution.
Complete step by step answer:
We are given that $\left( \vartriangle ABC \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}$ar (||gm ABEP) are on the same base while AC is between the same parallel AB and EF
So, using these data we will first draw our figure to get better understanding of problem
Now as Ab is common to $\vartriangle ABC$and parallelogram ABEF, so, common base in AB. So, we have,
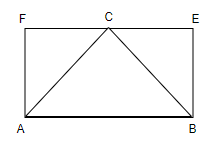
Now to solve this problem and get our required solution,
Through B we draw BH||AC to meet FE provided at H
Such that ABHC is a parallelogram.
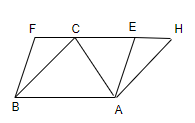
As we know that diagonal of parallelogram divide it into two congruent,
So, as CB is diagonal at ||ABHC
So, $\vartriangle ABC\cong \vartriangle BHC$
A congruent triangle has some area.
So, $ar\left( \vartriangle ABC \right)=ar\left( \vartriangle BHC \right)..........(i)$
Now as
$ar\left( ||gmABHC \right)=ar\left( \vartriangle ABC \right)+ar\left( BHC \right)$
Why (i), we get
$ar\left( ||gmABHC \right)=ar\left( \vartriangle ABC \right)+ar\left( BHC \right)$
So, we get
$ar\left( \vartriangle ABC \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( ar\left( ||gm\,ABHC \right) \right).......(ii)$
Now
We know that two parallelograms on same base and between same parallel are equal in equal we have that
||gm ABHC and ||gm ABEP are on the same base AB and between the same parallel AB and EF.
So,
$ar\left( ||gmABHC \right)=ae\left( ||gmABEF \right)........(iii)$
Now, using (iii) and (ii)
$ar\left( \vartriangle ABC \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( ||gmABEF \right)$
Hence proved
Note:
Parallelogram divide into two parts by the diagonal as we can see that through diagonal we have $\vartriangle ABC\,\operatorname{and}\vartriangle ACD$ in ||gm ABCD.
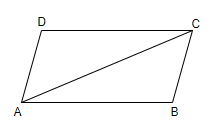
In $\vartriangle ABC\,\operatorname{and}\vartriangle ACD$, AB=CD (opposite sides are equal in parallelogram)
BC=AD (opposite sides are equal common)
AC=AC
So, using SSS rule, we have these two are congruent.
$\left( \vartriangle ABC \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}$ar (||gm ABEP)
To do so we do construction we draw BH||AC that meet FE at H
Then we use that diagonal of parallelogram to divide it into two congruent triangles and we use that two parallelograms on the same base between the same parallel are equal in area. Using them we get our required solution.
Complete step by step answer:
We are given that $\left( \vartriangle ABC \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}$ar (||gm ABEP) are on the same base while AC is between the same parallel AB and EF
So, using these data we will first draw our figure to get better understanding of problem
Now as Ab is common to $\vartriangle ABC$and parallelogram ABEF, so, common base in AB. So, we have,

Now to solve this problem and get our required solution,
Through B we draw BH||AC to meet FE provided at H
Such that ABHC is a parallelogram.

As we know that diagonal of parallelogram divide it into two congruent,
So, as CB is diagonal at ||ABHC
So, $\vartriangle ABC\cong \vartriangle BHC$
A congruent triangle has some area.
So, $ar\left( \vartriangle ABC \right)=ar\left( \vartriangle BHC \right)..........(i)$
Now as
$ar\left( ||gmABHC \right)=ar\left( \vartriangle ABC \right)+ar\left( BHC \right)$
Why (i), we get
$ar\left( ||gmABHC \right)=ar\left( \vartriangle ABC \right)+ar\left( BHC \right)$
So, we get
$ar\left( \vartriangle ABC \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( ar\left( ||gm\,ABHC \right) \right).......(ii)$
Now
We know that two parallelograms on same base and between same parallel are equal in equal we have that
||gm ABHC and ||gm ABEP are on the same base AB and between the same parallel AB and EF.
So,
$ar\left( ||gmABHC \right)=ae\left( ||gmABEF \right)........(iii)$
Now, using (iii) and (ii)
$ar\left( \vartriangle ABC \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( ||gmABEF \right)$
Hence proved
Note:
Parallelogram divide into two parts by the diagonal as we can see that through diagonal we have $\vartriangle ABC\,\operatorname{and}\vartriangle ACD$ in ||gm ABCD.

In $\vartriangle ABC\,\operatorname{and}\vartriangle ACD$, AB=CD (opposite sides are equal in parallelogram)
BC=AD (opposite sides are equal common)
AC=AC
So, using SSS rule, we have these two are congruent.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

The draft of the Preamble of the Indian Constitution class 10 social science CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who gave "Inqilab Zindabad" slogan?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?




