
Two different compounds have the formula \[{\text{Xe}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\]. How do you write the Lewis structures for these two compounds, and describe how measurement of dipole moments might be used to distinguish between them?
Answer
521.1k+ views
Hint:A Lewis Structure is a simplified representation of a molecule's valence shell electrons. It's used to demonstrate how electrons in a molecule are organised around individual atoms. Dipole moments are caused by variations in electronegativity and may occur between two ions in an ionic bond or between atoms in a covalent bond.
Complete answer:
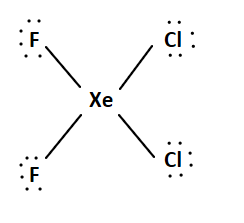
There are $32$ valence electrons in the trial structure.
\[{\text{1 Xe + 2 F + 2 Cl = 8 + 14 + 14 = 36 valence electrons}}\]
We add two-line pairs to the central atom since we have four extra electrons.
The Lewis structure is:
This system is an ${\text{A}}{{\text{X}}_4}{{\text{E}}_2}$system. It has an octahedral electron geometry. The F and Cl atoms will occupy the equatorial positions, while the bulky lone pairs will occupy the top and bottom axial positions. The molecule has a square planar geometry. We can arrange the atoms in two different ways.
The ${\text{F - Xe - F }}$and ${\text{Cl - Xe - Cl}}$ bond angles are 180 degrees in the trans isomer. The ${\text{Xe - Cl}}$ bond dipoles cancel the ${\text{Xe - F}}$ bond dipoles, and the ${\text{Xe - F}}$ bond dipoles cancel the ${\text{Xe - Cl}}$ bond dipoles. The trans isomer is nonpolar since there is no net dipole.
The \[{\text{Xe - F}}\] and ${\text{Xe - Cl}}$bond dipoles do not cancel in the cis-isomer. The molecule is polar in the cis isomer, which has a net dipole moment.
Note:
Cis isomers are molecules that have the same atom connectivity. They have side groups that are identical on the same side of a double bond. Molecules with identical side groups on opposite sides of a double bond are called trans isomers.
Complete answer:

There are $32$ valence electrons in the trial structure.
\[{\text{1 Xe + 2 F + 2 Cl = 8 + 14 + 14 = 36 valence electrons}}\]
We add two-line pairs to the central atom since we have four extra electrons.
The Lewis structure is:
This system is an ${\text{A}}{{\text{X}}_4}{{\text{E}}_2}$system. It has an octahedral electron geometry. The F and Cl atoms will occupy the equatorial positions, while the bulky lone pairs will occupy the top and bottom axial positions. The molecule has a square planar geometry. We can arrange the atoms in two different ways.
The ${\text{F - Xe - F }}$and ${\text{Cl - Xe - Cl}}$ bond angles are 180 degrees in the trans isomer. The ${\text{Xe - Cl}}$ bond dipoles cancel the ${\text{Xe - F}}$ bond dipoles, and the ${\text{Xe - F}}$ bond dipoles cancel the ${\text{Xe - Cl}}$ bond dipoles. The trans isomer is nonpolar since there is no net dipole.
The \[{\text{Xe - F}}\] and ${\text{Xe - Cl}}$bond dipoles do not cancel in the cis-isomer. The molecule is polar in the cis isomer, which has a net dipole moment.
Note:
Cis isomers are molecules that have the same atom connectivity. They have side groups that are identical on the same side of a double bond. Molecules with identical side groups on opposite sides of a double bond are called trans isomers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




