
Two different dice are tossed together. Find the probability of getting a doublet.
Answer
621.6k+ views
Hint: A dice has the shape of a cube having one number from 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 printed on each of the faces of the cube. Getting a doublet means both the numbers on the dice are the same. A dice can have one of the six outcomes from 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have been given that two dice have been tossed. Since the number of outcomes on a single dice is 6, therefore the total number of outcomes when two dices are tossed will be \[6\times 6=36\]. This is called sample space or the total number of events that may occur. The different outcomes are shown in the table below:
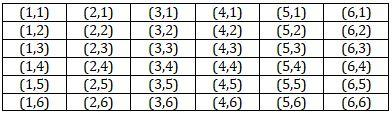
Observing the table carefully, we come to the conclusion that there are six doublets (1,1), (2,2), (3,3), (4,4), (5,5) and (6,6). These are the favourable outcomes. Hence, the number of favourable outcomes is 6.
Therefore we have sample space, denoted by \[n\left( s \right)=36\]. And number of favourable outcomes, denoted by \[n\left( e \right)=6\].
We know that the probability of an event, denoted by \[\text{P}\left( e \right)\] is given by:
$\text{P}(e)=\dfrac{n(e)}{n(s)}........................................(1)$
Here, we have \[n\left( s \right)=36\] and $n(e)=6$.
Substituting these values in equation \[\left( 1 \right)\], we get;
$\text{P}(e)=\dfrac{6}{36}=\dfrac{1}{6}.$
Note: One should properly know the concept of probability and its formula to solve questions. We should understand the meaning of terms like doublet, triplet and likewise. If there would have been three dice, then the total number of outcomes would have been $n(s)=6\times 6\times 6=216$. For $n$ number of dices, the total number of outcomes will be $n(s)={{6}^{n}}$.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have been given that two dice have been tossed. Since the number of outcomes on a single dice is 6, therefore the total number of outcomes when two dices are tossed will be \[6\times 6=36\]. This is called sample space or the total number of events that may occur. The different outcomes are shown in the table below:

Observing the table carefully, we come to the conclusion that there are six doublets (1,1), (2,2), (3,3), (4,4), (5,5) and (6,6). These are the favourable outcomes. Hence, the number of favourable outcomes is 6.
Therefore we have sample space, denoted by \[n\left( s \right)=36\]. And number of favourable outcomes, denoted by \[n\left( e \right)=6\].
We know that the probability of an event, denoted by \[\text{P}\left( e \right)\] is given by:
$\text{P}(e)=\dfrac{n(e)}{n(s)}........................................(1)$
Here, we have \[n\left( s \right)=36\] and $n(e)=6$.
Substituting these values in equation \[\left( 1 \right)\], we get;
$\text{P}(e)=\dfrac{6}{36}=\dfrac{1}{6}.$
Note: One should properly know the concept of probability and its formula to solve questions. We should understand the meaning of terms like doublet, triplet and likewise. If there would have been three dice, then the total number of outcomes would have been $n(s)=6\times 6\times 6=216$. For $n$ number of dices, the total number of outcomes will be $n(s)={{6}^{n}}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




