
Two identical charged particles enter a uniform magnetic field with the same speed but at angles ${30^0}$ and ${60^0}$ with the field. Let a, b, and c be the ratio of their time periods, radii, and pitches of the helical paths then:
A. $abc = 1$
B. $abc > 1$
C. $abc < 1$
D. $a = bc$
Answer
489.3k+ views
Hint: As we know that a moving charge produces a magnetic field. Similarly, a moving charge experiences a thrust in a magnetic field which depends on the speed and angle at which the particle enters the magnetic field. Depending on this angle the particle takes different paths.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us first write the information given in the question.
The charged particles enter the uniform magnetic field with different angles and the same velocities.
${\theta _1} = 30,{\theta _2} = 60$ , and a, b, and c are the ratio of their time-period, radii, and pitches.
We have the following formula to calculate the time period of a charged particle in a magnetic field.
$T = \dfrac{{2\pi m}}{{qB}}$
Here, $m$ is the mass of the particle, $q$ is the charge of the particle, and $B$ is the magnetic field.
So, the ratio of the time periods of these two particles is given below.
$\dfrac{{{T_1}}}{{{T_2}}} = 1 = a$ (1)
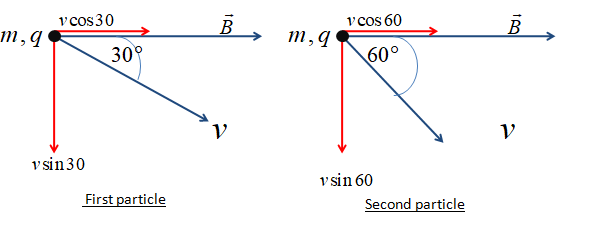
Now the formula to calculate the radius is given below.
$R = \dfrac{{mv\sin \theta }}{{qB}}$
Here, $m$ is the mass, $v$ is the speed, $q$ is a charge, $B$ is the magnetic field, and $\theta $ is the angle with which it enters the magnetic field.
Now, let us find the ratio of their radii.
$\dfrac{{{R_1}}}{{{R_2}}} = \dfrac{{\sin 30}}{{\sin 60}} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} = b$ (2)
The formula to calculate the pitch of the path is given by the following formula.
$l = tv\cos \theta $
Here, $t$is the time, $v$ is the velocity and $\theta $ is the angle with which the particle entered.
Now, let us find the ratio of their pitches.
$\dfrac{{{l_1}}}{{{l_2}}} = \dfrac{{\cos 30}}{{\cos 60}} = \sqrt 3 = c$ (3)
Now let us multiply equations (1), (2), and (3).
$abc = 1$
Hence, the correct option is (A) $abc = 1$.
Note:
When a particle enters at an angle less than a right angle, its path is helical. Similarly, when a particle enters perpendicular to the magnetic field its path is circular.
When a particle enters in the direction of a magnetic field it experiences no force. Similarly, when it enters just opposite the direction of a magnetic field, the force experienced is maximum but in both cases, the path will be a straight line.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us first write the information given in the question.
The charged particles enter the uniform magnetic field with different angles and the same velocities.
${\theta _1} = 30,{\theta _2} = 60$ , and a, b, and c are the ratio of their time-period, radii, and pitches.
We have the following formula to calculate the time period of a charged particle in a magnetic field.
$T = \dfrac{{2\pi m}}{{qB}}$
Here, $m$ is the mass of the particle, $q$ is the charge of the particle, and $B$ is the magnetic field.
So, the ratio of the time periods of these two particles is given below.
$\dfrac{{{T_1}}}{{{T_2}}} = 1 = a$ (1)

Now the formula to calculate the radius is given below.
$R = \dfrac{{mv\sin \theta }}{{qB}}$
Here, $m$ is the mass, $v$ is the speed, $q$ is a charge, $B$ is the magnetic field, and $\theta $ is the angle with which it enters the magnetic field.
Now, let us find the ratio of their radii.
$\dfrac{{{R_1}}}{{{R_2}}} = \dfrac{{\sin 30}}{{\sin 60}} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} = b$ (2)
The formula to calculate the pitch of the path is given by the following formula.
$l = tv\cos \theta $
Here, $t$is the time, $v$ is the velocity and $\theta $ is the angle with which the particle entered.
Now, let us find the ratio of their pitches.
$\dfrac{{{l_1}}}{{{l_2}}} = \dfrac{{\cos 30}}{{\cos 60}} = \sqrt 3 = c$ (3)
Now let us multiply equations (1), (2), and (3).
$abc = 1$
Hence, the correct option is (A) $abc = 1$.
Note:
When a particle enters at an angle less than a right angle, its path is helical. Similarly, when a particle enters perpendicular to the magnetic field its path is circular.
When a particle enters in the direction of a magnetic field it experiences no force. Similarly, when it enters just opposite the direction of a magnetic field, the force experienced is maximum but in both cases, the path will be a straight line.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




