
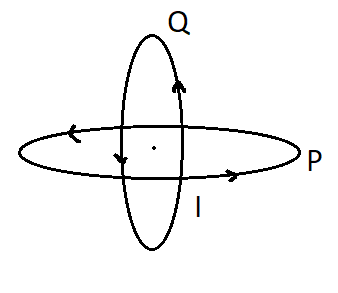
Two identical circular wires P and Q each of radius R and carrying current \[I\] are kept in perpendicular planes such that they have a common center as shown in the figure. Find the magnitude and direction of the net magnetic field at the common center of the two coils.

Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: The two wires are circular and perpendicular to each other. Due to symmetry it is easier to find the net Magnetic field due to each wire. Consider the wire to be loops and calculate the net magnetic field by using the formula \[{{B}_{net}}=\sqrt{{{B}_{1}}^{2}+{{B}_{2}}^{2}}\] . Also since the two wires are symmetrical hence the magnetic fields due to each wire will be equal.
Complete step by step solution: We are given that the two wires P and Q are circular. The wires are in the form of a loop through which current \[I\] is flowing and the radius of each loop is \[r\] units. Now the magnetic field at the central point will be resultant of the magnetic fields due to individual loops. The magnetic field due to circular wire at the center is given as:
\[B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}I}{2r}\]
Where \[B\] is the magnetic field at a distance \[r\]
\[{{\mu }_{0}}\] is a constant
\[r\] is the distance from the loop
As per the given question we have symmetrical set up hence the resultant magnetic field will be given as:
\[{{B}_{net}}=\sqrt{{{B}_{1}}^{2}+{{B}_{2}}^{2}}\]
Where \[{{B}_{net}}\] is the net magnetic field at a distance \[r\]
And \[{{B}_{1}}\] , \[{{B}_{2}}\] are the magnetic fields due loop P and Q respectively.
But \[{{B}_{1}}={{B}_{2}}\] due symmetry,
\[\Rightarrow {{B}_{net}}=\sqrt{{{B}_{1}}^{2}+{{B}_{1}}^{2}}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{B}_{net}}=\sqrt{2}{{B}_{1}}\]
And we know that,
\[B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}I}{2r}\]
Therefore,
\[\Rightarrow {{B}_{net}}=\sqrt{2}\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}I}{2r}\]
\[\therefore {{B}_{net}}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}I}{\sqrt{2}r}\]
Will be the net magnetic field at the center of two coils. The direction of the magnetic field can be identified using the right hand thumb rule, which is at an angle of \[{{45}^{\circ }}\] with the horizontal directed upwards.
Note: Due symmetry it was easy to calculate the net magnetic field. Same approach can be followed for circular wire having different radii. Also it must be noted that the direction is vertically upwards at an angle of \[{{45}^{\circ }}\] with the horizontal. The direction can also change if the direction of the current is reversed for any loop.
Complete step by step solution: We are given that the two wires P and Q are circular. The wires are in the form of a loop through which current \[I\] is flowing and the radius of each loop is \[r\] units. Now the magnetic field at the central point will be resultant of the magnetic fields due to individual loops. The magnetic field due to circular wire at the center is given as:
\[B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}I}{2r}\]
Where \[B\] is the magnetic field at a distance \[r\]
\[{{\mu }_{0}}\] is a constant
\[r\] is the distance from the loop
As per the given question we have symmetrical set up hence the resultant magnetic field will be given as:
\[{{B}_{net}}=\sqrt{{{B}_{1}}^{2}+{{B}_{2}}^{2}}\]
Where \[{{B}_{net}}\] is the net magnetic field at a distance \[r\]
And \[{{B}_{1}}\] , \[{{B}_{2}}\] are the magnetic fields due loop P and Q respectively.
But \[{{B}_{1}}={{B}_{2}}\] due symmetry,
\[\Rightarrow {{B}_{net}}=\sqrt{{{B}_{1}}^{2}+{{B}_{1}}^{2}}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{B}_{net}}=\sqrt{2}{{B}_{1}}\]
And we know that,
\[B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}I}{2r}\]
Therefore,
\[\Rightarrow {{B}_{net}}=\sqrt{2}\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}I}{2r}\]
\[\therefore {{B}_{net}}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}I}{\sqrt{2}r}\]
Will be the net magnetic field at the center of two coils. The direction of the magnetic field can be identified using the right hand thumb rule, which is at an angle of \[{{45}^{\circ }}\] with the horizontal directed upwards.
Note: Due symmetry it was easy to calculate the net magnetic field. Same approach can be followed for circular wire having different radii. Also it must be noted that the direction is vertically upwards at an angle of \[{{45}^{\circ }}\] with the horizontal. The direction can also change if the direction of the current is reversed for any loop.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




