
Two mirrors A and B are placed at right angles to each other as shown in the figure. A ray of light incident on mirror A at an angle ${{25}^{\circ }}$ falls on mirror B after reflection. The angle of reflection for the ray reflected from mirror B would be
a) ${{25}^{\circ }}$
b) ${{50}^{\circ }}$
c) ${{65}^{\circ }}$
d) ${{115}^{\circ }}$

Answer
533.7k+ views
Hint: In the above question we observe that the two mirrors are inclined to each other at an angle of ${{90}^{\circ }}$ . The ray of light gets reflected from the mirror A and then it will definitely hit mirror B as the ray of light after reflection from A is not parallel to mirror B. Hence using the laws of reflection, tracing the path of the ray of light will enable us to determine the angle of reflection for the ray reflected from mirror B
Complete answer:
In case of a plane mirror the ray of light after reflection follows the laws of reflection. The first law of reflection states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection such that they lie in the same plane. Now using this information let us try to trace the ray further after reflection.
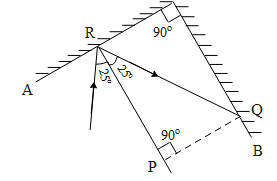
From the above diagram We can see that the ray of light after reflection from point R propagates further and meets the mirror B at point Q. From the above diagram we can also observe that points P, Q and R form a right angled triangle. Since the total sum of the triangle is 180 degrees, we can imply that $\angle Q={{65}^{\circ }}$ . Further $\angle Q$ is the angle at which the ray is incident on the mirror B with respect to the normal of the mirror i.e. PQ. Since $\angle Q={{65}^{\circ }}$ is the angle of incidence of the ray on mirror B, first law of reflection the angle of reflection is also equal to ${{65}^{\circ }}$ .
Therefore the correct answer of the above question is option c.
Note:
The problem can also be solved by obtaining the angle at which the ray is incident on mirror B with respect to the mirror. However the answer obtained will be the same. It is also to be noted that in case of a plane mirror, the object distances are always the same.
Complete answer:
In case of a plane mirror the ray of light after reflection follows the laws of reflection. The first law of reflection states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection such that they lie in the same plane. Now using this information let us try to trace the ray further after reflection.

From the above diagram We can see that the ray of light after reflection from point R propagates further and meets the mirror B at point Q. From the above diagram we can also observe that points P, Q and R form a right angled triangle. Since the total sum of the triangle is 180 degrees, we can imply that $\angle Q={{65}^{\circ }}$ . Further $\angle Q$ is the angle at which the ray is incident on the mirror B with respect to the normal of the mirror i.e. PQ. Since $\angle Q={{65}^{\circ }}$ is the angle of incidence of the ray on mirror B, first law of reflection the angle of reflection is also equal to ${{65}^{\circ }}$ .
Therefore the correct answer of the above question is option c.
Note:
The problem can also be solved by obtaining the angle at which the ray is incident on mirror B with respect to the mirror. However the answer obtained will be the same. It is also to be noted that in case of a plane mirror, the object distances are always the same.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




