
Two objects of masses 100g and 200g are moving along the same line and direction with velocities $2m{s^{ - 1}}$ and $1m{s^{ - 1}}$ respectively. They collide and after the collision, the second object moves with a velocity of $1.67m{s^{ - 1}}$. Determine the velocity of the first object:
A) $0.66m{s^{ - 1}}$
B) $0.55m{s^{ - 1}}$
C) $1.66m{s^{ - 1}}$
D) $0.33m{s^{ - 1}}$
Answer
589.8k+ views
Hint: Collision is short-duration interaction between two bodies or more than two bodies simultaneously causing a change in motion of bodies. Collision is of three types:
(i) Perfectly elastic collision.
(ii) Inelastic collision.
(iii) Perfectly inelastic collision.
To solve this type of question we use the law of conservation of momentum.
Complete step by step answer:
Given, ${m_1} = 100g,{m_2} = 200g,{u_1} = 2m/s,{u_2} = 1m/s,{v_2} = 1.67m/s$
We have to find the velocity of the first object $v_1$.
Flowing is the diagram showing the situation.
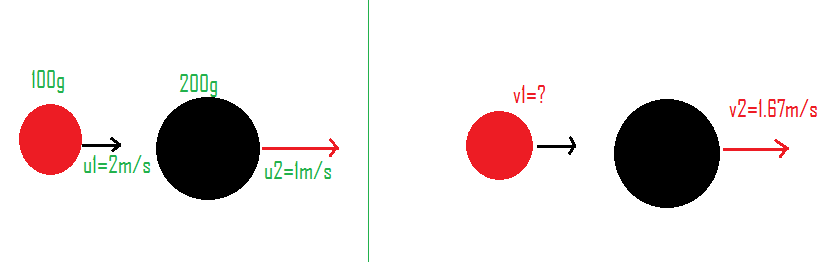
Now let us use the concept of conservation of linear momentum which states that the total initial momentum is equal to the total final momentum.
Initial momentum = Final momentum
Let us write the linear momentum of the system before the collision.
${P_{initial}} = {m_1}{u_1} + {m_2}{u_2}$
Let us now substitute the values.
$\Rightarrow {P_{initial}} = 0.1 \times 2 + 0.2 \times 1$
Let us simplify it.
$\Rightarrow {P_{initial}} = 0.4kgm/s$ ………...(1)
Let us write the linear momentum of the system after the collision.
$ {P_{final}} = {m_1}{v_1} + {m_2}{v_2}$
Let us now substitute the values.
$\Rightarrow {P_{final}} = 0.1{v_1} + 0.2 \times 1.67$
Let us simplify it.
$\Rightarrow {P_{final}} = 0.1{v_1} + 0.334$ …………..(2)
Now using linear momentum conservation, let us equate equation (1) and (2).
$\Rightarrow 0.4 = 0.1{v_1} + 0.334$
Let us simplify it.
$\Rightarrow 0.4 - 0.334 = 0.2{v_1} \Rightarrow {v_1} = \dfrac{{0.066}}{{0.2}}$
$\Rightarrow {v_1} = 0.33m/s$
$\therefore $ The velocity of the first object is 0.33m/sec. Hence, option (D) correct.
Note:
There are two types of collisions between two bodies as given below:
1) Head-on collisions (also known as one-dimensional collisions) – In this type of collision, the velocity of each body just before impact is along the line of impact after collision also.
2) Non-head-on collisions, (also known as two-dimensional collisions) – In this type of collision, the velocity of each body just before impact is not along the line of impact after the collision.
(i) Perfectly elastic collision.
(ii) Inelastic collision.
(iii) Perfectly inelastic collision.
To solve this type of question we use the law of conservation of momentum.
Complete step by step answer:
Given, ${m_1} = 100g,{m_2} = 200g,{u_1} = 2m/s,{u_2} = 1m/s,{v_2} = 1.67m/s$
We have to find the velocity of the first object $v_1$.
Flowing is the diagram showing the situation.

Now let us use the concept of conservation of linear momentum which states that the total initial momentum is equal to the total final momentum.
Initial momentum = Final momentum
Let us write the linear momentum of the system before the collision.
${P_{initial}} = {m_1}{u_1} + {m_2}{u_2}$
Let us now substitute the values.
$\Rightarrow {P_{initial}} = 0.1 \times 2 + 0.2 \times 1$
Let us simplify it.
$\Rightarrow {P_{initial}} = 0.4kgm/s$ ………...(1)
Let us write the linear momentum of the system after the collision.
$ {P_{final}} = {m_1}{v_1} + {m_2}{v_2}$
Let us now substitute the values.
$\Rightarrow {P_{final}} = 0.1{v_1} + 0.2 \times 1.67$
Let us simplify it.
$\Rightarrow {P_{final}} = 0.1{v_1} + 0.334$ …………..(2)
Now using linear momentum conservation, let us equate equation (1) and (2).
$\Rightarrow 0.4 = 0.1{v_1} + 0.334$
Let us simplify it.
$\Rightarrow 0.4 - 0.334 = 0.2{v_1} \Rightarrow {v_1} = \dfrac{{0.066}}{{0.2}}$
$\Rightarrow {v_1} = 0.33m/s$
$\therefore $ The velocity of the first object is 0.33m/sec. Hence, option (D) correct.
Note:
There are two types of collisions between two bodies as given below:
1) Head-on collisions (also known as one-dimensional collisions) – In this type of collision, the velocity of each body just before impact is along the line of impact after collision also.
2) Non-head-on collisions, (also known as two-dimensional collisions) – In this type of collision, the velocity of each body just before impact is not along the line of impact after the collision.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




