
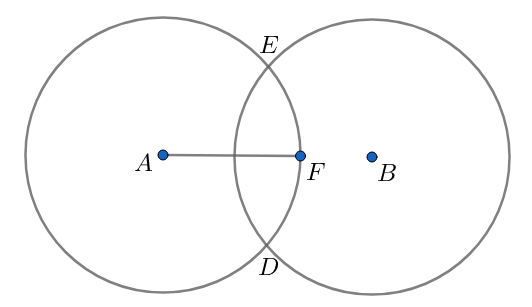
Two overlapping circles with equal radius form a shaded region as shown in the figure. Express the area of the region and the complete perimeter (combined arc length) in terms of r and the distance between centre D? Let $r=4$ , $D=6$ and calculate?

Answer
539.7k+ views
Hint: We first join A and E and express the angle between them in terms of r and D. After that, we find the length of the arc EFD in terms of this angle. We then find some fundamental areas like the area of sector AEFD, triangle AED and so on and then simplify these expressions to get the final equations. At last, we put the given values.
Complete step by step answer:
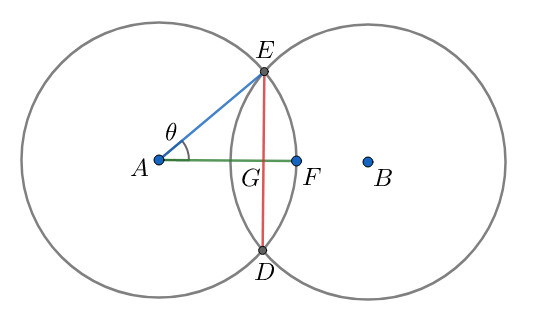
In the given figure, $AG=\dfrac{AB}{2}=\dfrac{D}{2}$ . Again, $AE=r$ . This means that,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \cos \theta =\dfrac{AG}{AE}=\dfrac{\dfrac{D}{2}}{r}=\dfrac{D}{2r}....\left( 1 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \theta ={{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{D}{2r} \right) \\
\end{align}$
The arc ED can be expressed in terms of the angle $\theta $ and the radius of the circle r. This can be done by,
$\begin{align}
& \overset\frown{EFD}=r\times 2\theta \\
& \Rightarrow \overset\frown{EFD}=2r{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{D}{2r} \right) \\
\end{align}$
Due to symmetricity of the figure, we can say that the other arc ED is same that that of the arc EFD. So, the total perimeter of the region becomes,
$\begin{align}
& P=2\times \overset\frown{EFD} \\
& \Rightarrow P=2\times 2r{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{D}{2r} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow P=4r{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{D}{2r} \right)....\left( 2 \right) \\
\end{align}$
The area of one of the circles is $area=\pi {{r}^{2}}$ . The area of the sector AEFD must be some fraction of the area of the circle and this fraction will be $\dfrac{2\theta }{2\pi }=\dfrac{\theta }{\pi }$ . Thus, the area of the sector AEFD will be,
$\begin{align}
& area(AEFD)=\dfrac{\theta }{\pi }\times \pi {{r}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow area(AEFD)=\theta {{r}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow area(AEFD)={{r}^{2}}{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{D}{2r} \right) \\
\end{align}$
Area of the triangle AED will be,
$\begin{align}
& area\left( \Delta AED \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\times ED\times AG \\
& \Rightarrow area\left( \Delta AED \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \left( 2\times r\sin \theta \right)\times \dfrac{D}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow area\left( \Delta AED \right)=\dfrac{Dr\sin \theta }{2} \\
\end{align}$
From equation $\left( 1 \right)$ , we get $\sin \theta =\sqrt{1-{{\left( \dfrac{D}{2r} \right)}^{2}}}$ . Using this value in the above equation, we get,
$\Rightarrow area\left( \Delta AED \right)=\dfrac{Dr}{2}\sqrt{1-{{\left( \dfrac{D}{2r} \right)}^{2}}}$
Thus, the area of the segment EFDE will be,
\[\begin{align}
& area(EFDE)=area(AEFD)-area(\Delta AED) \\
& \Rightarrow area(EFDE)={{r}^{2}}{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{D}{2r} \right)-\dfrac{Dr}{2}\sqrt{1-{{\left( \dfrac{D}{2r} \right)}^{2}}} \\
\end{align}\]
Thus, the total area of the shaded region will be,
$\begin{align}
& A=2\times area(EFDE) \\
& \Rightarrow A=2\times \left( {{r}^{2}}{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{D}{2r} \right)-\dfrac{Dr}{2}\sqrt{1-{{\left( \dfrac{D}{2r} \right)}^{2}}} \right)....\left( 3 \right) \\
\end{align}$
If we put the values of $r=4$ , $D=6$ in the equations $\left( 2 \right),\left( 3 \right)$ , we get,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow P=4\left( 4 \right){{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{6}{2\times 4} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow P=11.56 \\
\end{align}$ and $\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow A=2\times \left( {{\left( 4 \right)}^{2}}{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{6}{2\left( 4 \right)} \right)-\dfrac{6\times 4}{2}\sqrt{1-{{\left( \dfrac{6}{2\times 4} \right)}^{2}}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow A=7.25 \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, we can conclude that the perimeter is $11.56$ and the area is \[7.25\] of the shaded region.
Note: This problem is pretty long and thus requiring tremendous patience. In such problems, we should at first figure out a way in which we can find out the required perimeter and area and then proceed accordingly. We must always take the value of the angles in radians otherwise; it will lead to wrong answers.
Complete step by step answer:
In the given figure, $AG=\dfrac{AB}{2}=\dfrac{D}{2}$ . Again, $AE=r$ . This means that,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \cos \theta =\dfrac{AG}{AE}=\dfrac{\dfrac{D}{2}}{r}=\dfrac{D}{2r}....\left( 1 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \theta ={{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{D}{2r} \right) \\
\end{align}$
The arc ED can be expressed in terms of the angle $\theta $ and the radius of the circle r. This can be done by,
$\begin{align}
& \overset\frown{EFD}=r\times 2\theta \\
& \Rightarrow \overset\frown{EFD}=2r{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{D}{2r} \right) \\
\end{align}$
Due to symmetricity of the figure, we can say that the other arc ED is same that that of the arc EFD. So, the total perimeter of the region becomes,
$\begin{align}
& P=2\times \overset\frown{EFD} \\
& \Rightarrow P=2\times 2r{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{D}{2r} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow P=4r{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{D}{2r} \right)....\left( 2 \right) \\
\end{align}$
The area of one of the circles is $area=\pi {{r}^{2}}$ . The area of the sector AEFD must be some fraction of the area of the circle and this fraction will be $\dfrac{2\theta }{2\pi }=\dfrac{\theta }{\pi }$ . Thus, the area of the sector AEFD will be,
$\begin{align}
& area(AEFD)=\dfrac{\theta }{\pi }\times \pi {{r}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow area(AEFD)=\theta {{r}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow area(AEFD)={{r}^{2}}{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{D}{2r} \right) \\
\end{align}$
Area of the triangle AED will be,
$\begin{align}
& area\left( \Delta AED \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\times ED\times AG \\
& \Rightarrow area\left( \Delta AED \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \left( 2\times r\sin \theta \right)\times \dfrac{D}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow area\left( \Delta AED \right)=\dfrac{Dr\sin \theta }{2} \\
\end{align}$
From equation $\left( 1 \right)$ , we get $\sin \theta =\sqrt{1-{{\left( \dfrac{D}{2r} \right)}^{2}}}$ . Using this value in the above equation, we get,
$\Rightarrow area\left( \Delta AED \right)=\dfrac{Dr}{2}\sqrt{1-{{\left( \dfrac{D}{2r} \right)}^{2}}}$
Thus, the area of the segment EFDE will be,
\[\begin{align}
& area(EFDE)=area(AEFD)-area(\Delta AED) \\
& \Rightarrow area(EFDE)={{r}^{2}}{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{D}{2r} \right)-\dfrac{Dr}{2}\sqrt{1-{{\left( \dfrac{D}{2r} \right)}^{2}}} \\
\end{align}\]
Thus, the total area of the shaded region will be,
$\begin{align}
& A=2\times area(EFDE) \\
& \Rightarrow A=2\times \left( {{r}^{2}}{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{D}{2r} \right)-\dfrac{Dr}{2}\sqrt{1-{{\left( \dfrac{D}{2r} \right)}^{2}}} \right)....\left( 3 \right) \\
\end{align}$
If we put the values of $r=4$ , $D=6$ in the equations $\left( 2 \right),\left( 3 \right)$ , we get,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow P=4\left( 4 \right){{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{6}{2\times 4} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow P=11.56 \\
\end{align}$ and $\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow A=2\times \left( {{\left( 4 \right)}^{2}}{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{6}{2\left( 4 \right)} \right)-\dfrac{6\times 4}{2}\sqrt{1-{{\left( \dfrac{6}{2\times 4} \right)}^{2}}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow A=7.25 \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, we can conclude that the perimeter is $11.56$ and the area is \[7.25\] of the shaded region.

Note: This problem is pretty long and thus requiring tremendous patience. In such problems, we should at first figure out a way in which we can find out the required perimeter and area and then proceed accordingly. We must always take the value of the angles in radians otherwise; it will lead to wrong answers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

The Equation xxx + 2 is Satisfied when x is Equal to Class 10 Maths

Which Country is Called "The Land of Festivals"?

What is Contraception List its four different methods class 10 biology CBSE




