
Two similarly and equally charged identical metal spheres A and B repel each other with a force of $2\times {{10}^{-5}}$N. A third identical uncharged sphere C is touched with A and then placed at the midpoint between A and B. Find the net electric force on C:
(A) $4\times {{10}^{-5}}$N away from sphere B
(B) $4\times {{10}^{-5}}$N toward sphere B
(C) $2\times {{10}^{-5}}$N away from sphere B
(D) $2\times {{10}^{-5}}$N toward sphere B
Answer
553.2k+ views
Hint: When two identical metal spheres, one charged and other uncharged are touched then the charge of the charged sphere is equally distributed among the two spheres and the net force on a sphere is the sum of the forces acting on it with sign.
Complete answer:
Let us consider two spheres A and B at a distance r apart, both similarly and equally charged as shown in the figure below.
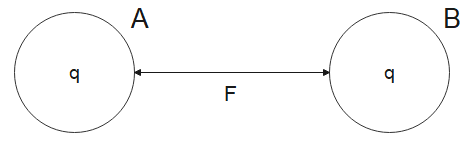
Let the charge on each sphere be q and they repel each other with a force F given by,
$F=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\in }_{0}}}\dfrac{q\times q}{{{r}^{2}}}=\dfrac{k{{q}^{2}}}{{{r}^{2}}}=2\times {{10}^{-5}}$N ….(i)
Where, $k=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\in }_{0}}}$
Now, according to the question, a third identical uncharged sphere C is first touched with sphere A and then placed at the midpoint between A and B, as shown in the figure below,
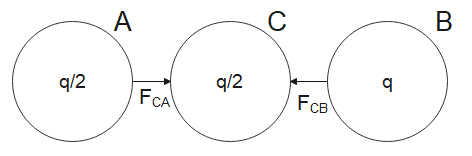
The charge on sphere A is equally distributed between sphere A and sphere C. Therefore,
Charge on sphere A = Charge on sphere C $=\dfrac{q}{2}$
Now we calculate the force on sphere C due to sphere A is,
${{F}_{CA}}=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\in }_{0}}}\dfrac{\dfrac{q}{2}\times \dfrac{q}{2}}{\dfrac{{{r}^{2}}}{4}}=\dfrac{k{{q}^{2}}}{{{r}^{2}}}$ ….(ii)
Then calculating the force on sphere C due to sphere B is,
${{F}_{CB}}=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\in }_{0}}}\dfrac{\dfrac{q}{2}\times q}{\dfrac{{{r}^{2}}}{4}}=\dfrac{2k{{q}^{2}}}{{{r}^{2}}}$ ….(iii)
Now, to calculate the net force acting on sphere C, we subtract equation (ii) and equation (iii), we get,
${{F}_{C}}={{F}_{CB}}-{{F}_{CA}}=\dfrac{2k{{q}^{2}}}{{{r}^{2}}}-\dfrac{k{{q}^{2}}}{{{r}^{2}}}=\dfrac{k{{q}^{2}}}{{{r}^{2}}}$ ….(iv)
Comparing equation (i) and equation (iv), we get the net force on sphere C as,
$\dfrac{k{{q}^{2}}}{{{r}^{2}}}=2\times {{10}^{-5}}$N
As we can see that force on sphere C due to sphere B is greater than force on sphere C due to sphere A, i.e. ${{F}_{CB}}\rangle {{F}_{CA}}$, therefore the net force on sphere C is away from sphere B.
Thus, the correct answer is option C.
Note:
The formula for calculating Coulomb's force between two charges separated by a distance apart should be remembered. The phenomenon of charges being uniformly distributed between two conducting bodies when brought in contact with each other is called conduction.
Complete answer:
Let us consider two spheres A and B at a distance r apart, both similarly and equally charged as shown in the figure below.

Let the charge on each sphere be q and they repel each other with a force F given by,
$F=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\in }_{0}}}\dfrac{q\times q}{{{r}^{2}}}=\dfrac{k{{q}^{2}}}{{{r}^{2}}}=2\times {{10}^{-5}}$N ….(i)
Where, $k=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\in }_{0}}}$
Now, according to the question, a third identical uncharged sphere C is first touched with sphere A and then placed at the midpoint between A and B, as shown in the figure below,

The charge on sphere A is equally distributed between sphere A and sphere C. Therefore,
Charge on sphere A = Charge on sphere C $=\dfrac{q}{2}$
Now we calculate the force on sphere C due to sphere A is,
${{F}_{CA}}=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\in }_{0}}}\dfrac{\dfrac{q}{2}\times \dfrac{q}{2}}{\dfrac{{{r}^{2}}}{4}}=\dfrac{k{{q}^{2}}}{{{r}^{2}}}$ ….(ii)
Then calculating the force on sphere C due to sphere B is,
${{F}_{CB}}=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\in }_{0}}}\dfrac{\dfrac{q}{2}\times q}{\dfrac{{{r}^{2}}}{4}}=\dfrac{2k{{q}^{2}}}{{{r}^{2}}}$ ….(iii)
Now, to calculate the net force acting on sphere C, we subtract equation (ii) and equation (iii), we get,
${{F}_{C}}={{F}_{CB}}-{{F}_{CA}}=\dfrac{2k{{q}^{2}}}{{{r}^{2}}}-\dfrac{k{{q}^{2}}}{{{r}^{2}}}=\dfrac{k{{q}^{2}}}{{{r}^{2}}}$ ….(iv)
Comparing equation (i) and equation (iv), we get the net force on sphere C as,
$\dfrac{k{{q}^{2}}}{{{r}^{2}}}=2\times {{10}^{-5}}$N
As we can see that force on sphere C due to sphere B is greater than force on sphere C due to sphere A, i.e. ${{F}_{CB}}\rangle {{F}_{CA}}$, therefore the net force on sphere C is away from sphere B.
Thus, the correct answer is option C.
Note:
The formula for calculating Coulomb's force between two charges separated by a distance apart should be remembered. The phenomenon of charges being uniformly distributed between two conducting bodies when brought in contact with each other is called conduction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




